Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Indium For Sale Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for indium for sale
Navigating the intricate landscape of sourcing indium for sale poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for high-purity indium, crucial in industries ranging from electronics to renewable energy, often collides with fluctuating prices and supply chain complexities. Understanding the diverse forms of indium—such as ingots, shots, and powders—alongside their specific applications is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers, detailing the various types of indium available, its applications across different sectors, and critical factors for supplier vetting. By providing insights into cost structures and market trends, this guide empowers buyers to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring they secure the best quality products at competitive prices.
In an increasingly interconnected world, informed decision-making is essential for businesses looking to leverage indium’s unique properties. Whether you are sourcing for manufacturing processes in Vietnam or exploring new market opportunities in Brazil, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the indium market, ultimately enhancing your procurement strategy and driving business success.
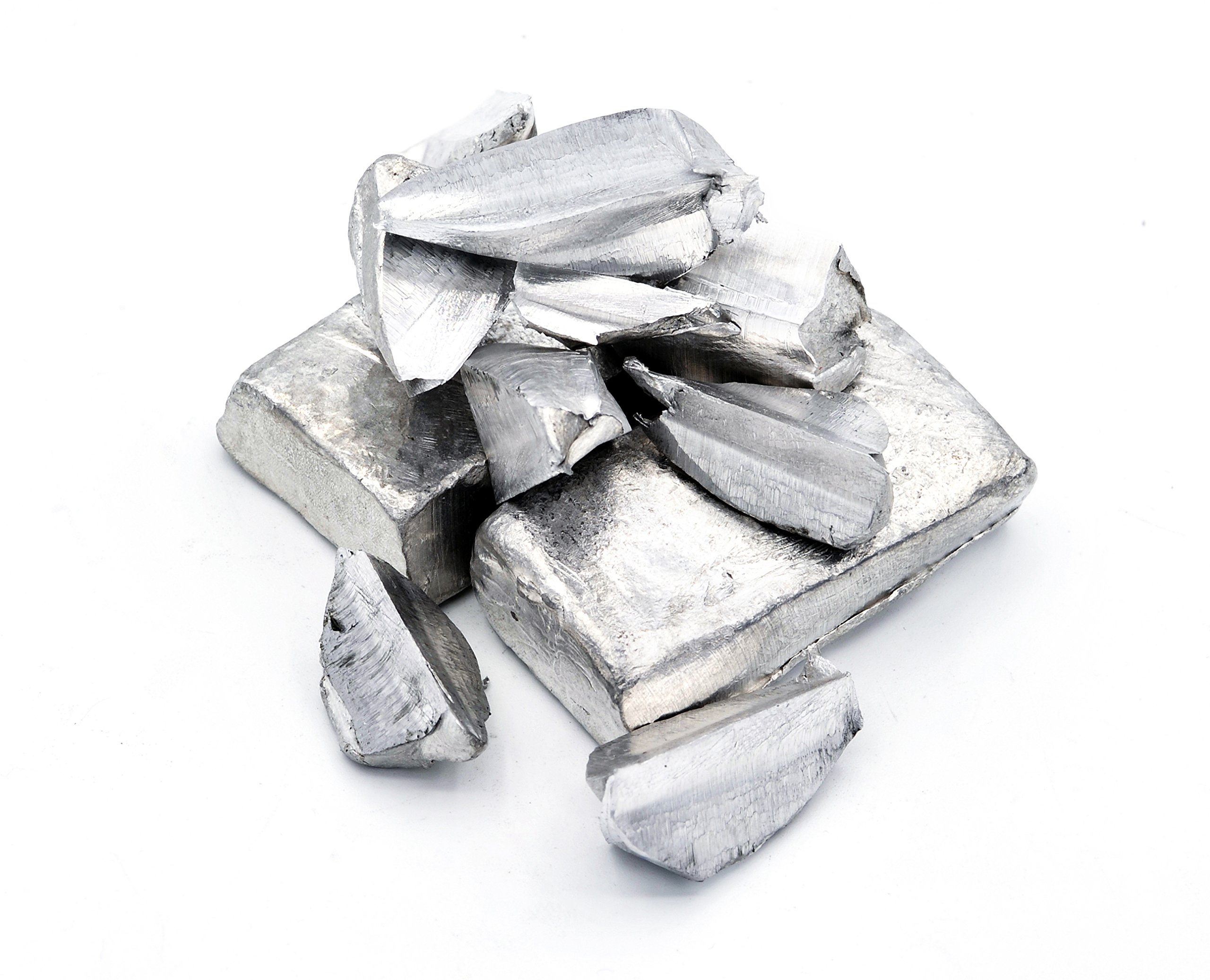
Understanding indium for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indium Ingot | Solid form available in various purities (99.9% to 99.999%) | Electronics, semiconductor manufacturing | Pros: High purity, versatile shapes. Cons: Higher cost for premium grades. |
| Indium Shot | Small, uniform pieces, often used in soldering | Soldering, thermal interface materials | Pros: Easy to handle, good for precision applications. Cons: Limited to specific uses. |
| Indium Powder | Fine particles, high surface area, available in various grades | Coatings, electronics, and research applications | Pros: Versatile, can be tailored for specific applications. Cons: Handling requires caution due to fine particles. |
| Indium Wire | Thin strands, often used in specialized soldering | Electronics assembly, thermal management | Pros: Flexible, suitable for intricate applications. Cons: May require specialized equipment for application. |
| Indium Foil | Thin sheets, easy to manipulate, available in various thicknesses | Electrical contacts, sealing applications | Pros: Lightweight, excellent conductivity. Cons: Fragile, care needed during handling. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Indium Ingots for B2B Buyers?
Indium ingots are available in various purities, typically ranging from 99.9% to 99.999%. They are solid and can be cut or shaped as needed, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, particularly in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific purity required for their applications, as higher purities often correlate with higher costs but can significantly enhance performance in sensitive electronic components.
How Do Indium Shots Benefit Specialized Applications?
Indium shot consists of small, uniform pieces that are easy to handle and ideal for soldering applications. Their consistent size allows for precise melting and application, making them a preferred choice in thermal interface materials and soldering processes. Buyers should assess their specific soldering needs, as the size and purity of indium shot can directly influence the quality and reliability of the final product.
What Are the Advantages of Using Indium Powder in Various Industries?
Indium powder, characterized by its fine particles and high surface area, is versatile and can be tailored for specific applications, including coatings and electronics. This form is essential in research and development settings, where precise material properties are crucial. However, buyers must consider safe handling practices, as the fine particles can pose inhalation risks and require special equipment for application.
Why Choose Indium Wire for Electronics Assembly?
Indium wire is a flexible and thin strand of indium, making it suitable for intricate soldering tasks in electronics assembly. Its adaptability allows for use in thermal management systems, where precise application is necessary. Buyers should evaluate the specific gauge and purity required for their applications, as these factors can affect the performance and longevity of the connections made.
What Are the Key Considerations When Using Indium Foil?
Indium foil is available in various thicknesses and is lightweight, making it an excellent choice for electrical contacts and sealing applications. Its high conductivity is a significant advantage, but the foil can be fragile, necessitating careful handling during installation. Buyers should weigh the benefits of conductivity against the potential for damage during use, ensuring that their applications can accommodate the material’s delicate nature.
Key Industrial Applications of indium for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of indium for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) in Display Devices | High transparency and excellent electrical conductivity improve device performance. | Ensure high purity levels (99.99% or higher) for optimal performance. |
| Renewable Energy | Photovoltaic Cells | Enhances efficiency in solar panels, leading to better energy conversion rates. | Source from suppliers with experience in renewable energy applications. |
| Aerospace & Defense | Soldering Materials | Provides superior thermal and electrical conductivity for critical components. | Verify compliance with international standards and certifications. |
| Telecommunications | RF and Microwave Applications | Improves signal integrity in high-frequency applications. | Consider the form (powder vs. ingot) based on specific application needs. |
| Medical Devices | Biomedical Applications | Used in sensors and imaging devices for improved accuracy and performance. | Assess the supplier’s ability to meet stringent medical-grade specifications. |
How is Indium Used in Electronics and What Are the Benefits?
In the electronics sector, indium is primarily utilized in the form of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO), which is crucial for modern display technologies such as LCDs and OLEDs. ITO’s high transparency coupled with its electrical conductivity makes it an ideal material for touchscreens, televisions, and smartphones. For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-purity indium is essential, as impurities can significantly degrade performance. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee 99.99% purity and provide reliable shipping options.
What Role Does Indium Play in Renewable Energy Solutions?
Indium is pivotal in the renewable energy sector, particularly in enhancing the efficiency of photovoltaic cells. When used in thin-film solar panels, indium helps to improve energy conversion rates, making solar technology more viable and cost-effective. For businesses in emerging markets, such as Vietnam and Brazil, sourcing indium for solar applications requires a focus on suppliers who understand the renewable energy landscape and can provide the necessary quantity and purity. This ensures that solar panels meet performance expectations in diverse environmental conditions.
Why is Indium Important in Aerospace and Defense Industries?
In the aerospace and defense industries, indium serves as a key component in soldering materials used for critical electronic components. Its superior thermal and electrical conductivity ensures that devices function reliably under extreme conditions. International buyers in this sector must consider sourcing from suppliers who comply with stringent aerospace standards and can provide certifications. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of aerospace applications, especially when dealing with international regulations.
How is Indium Beneficial in Telecommunications?
Indium is increasingly employed in the telecommunications sector, particularly in RF and microwave applications. Its properties enhance signal integrity, which is vital for the performance of communication devices. B2B buyers should consider the specific form of indium they require—whether as powder or ingot—based on their application needs. Furthermore, ensuring that suppliers can meet the required specifications and provide consistent quality is essential for maintaining the performance of telecommunications equipment.
What is Indium’s Role in Medical Devices?
In the medical field, indium is utilized in various applications, including sensors and imaging devices. Its unique properties enable improved accuracy and performance in diagnostic equipment. For international B2B buyers, it is crucial to assess potential suppliers for their ability to meet stringent medical-grade specifications. This includes verifying the purity of indium and ensuring compliance with health regulations, which is particularly important for businesses operating in regions with strict medical device standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘indium for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Finding Reliable Suppliers for Indium
The Problem: One of the major challenges B2B buyers face when searching for indium is the difficulty in identifying reliable suppliers. With numerous online marketplaces and local vendors, buyers may encounter discrepancies in purity claims, inconsistent pricing, and varying lead times. This can lead to frustration and the risk of procuring low-quality materials, which can severely impact production processes and product quality. In regions such as Africa or South America, where access to international suppliers may be limited, this issue is compounded by a lack of local expertise in sourcing specialized materials like indium.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence before committing to a supplier. Begin by requesting detailed product specifications, including certificates of analysis (CoA) that validate purity levels. Utilize industry networks and forums to gather feedback and reviews from other businesses that have sourced indium from potential suppliers. Moreover, consider establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to create a competitive bidding environment, which not only enhances your negotiating power but also provides backup options in case of supply disruptions. Engaging with suppliers who offer transparent communication and a robust return policy can also mitigate risks associated with procurement.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Indium Purity and Quality
The Problem: Buyers often grapple with concerns regarding the purity and quality of indium, particularly when sourcing materials for high-tech applications such as electronics or solar panels. Variations in indium purity can lead to significant performance issues in end products, such as reduced conductivity in electronic components. This concern is particularly pressing in competitive markets where quality standards are stringent, and any deviation can result in costly recalls or reputational damage.
The Solution: To ensure the highest quality indium, buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation of their materials. Request purity certifications (e.g., 99.99% or higher) and inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes. Additionally, consider investing in third-party testing services to independently verify the purity of the indium before incorporating it into production. Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers who are willing to invest in quality assurance and can demonstrate consistent performance history is also key. Implementing a rigorous supplier evaluation process can help businesses secure high-quality indium for their specific applications.
Scenario 3: High Costs and Price Fluctuations for Indium
The Problem: Fluctuating prices and high costs associated with indium can significantly impact the budgeting and financial planning of B2B buyers. This is particularly true for industries reliant on indium for manufacturing electronics or specialized coatings, where price volatility can lead to unexpected increases in production costs. Buyers in regions with limited access to raw materials may face even steeper prices, complicating their ability to compete in global markets.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of price fluctuations, buyers should consider implementing strategic sourcing practices. This could involve negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers to lock in prices, thus providing greater cost predictability. Additionally, exploring alternative materials or substitutes for indium, where feasible, can help diversify sourcing options and reduce dependency on a single element. Regularly monitoring market trends and engaging with industry analysts can provide valuable insights into pricing patterns, allowing buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Lastly, leveraging bulk purchasing strategies can help reduce per-unit costs, making it financially viable to stock up during periods of lower prices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for indium for sale
What Are the Key Properties of Indium for B2B Buyers?
Indium is a versatile metal known for its unique properties, making it suitable for various applications in electronics, manufacturing, and specialized industries. The most common forms available for B2B buyers include indium ingots, shots, and powders.
-
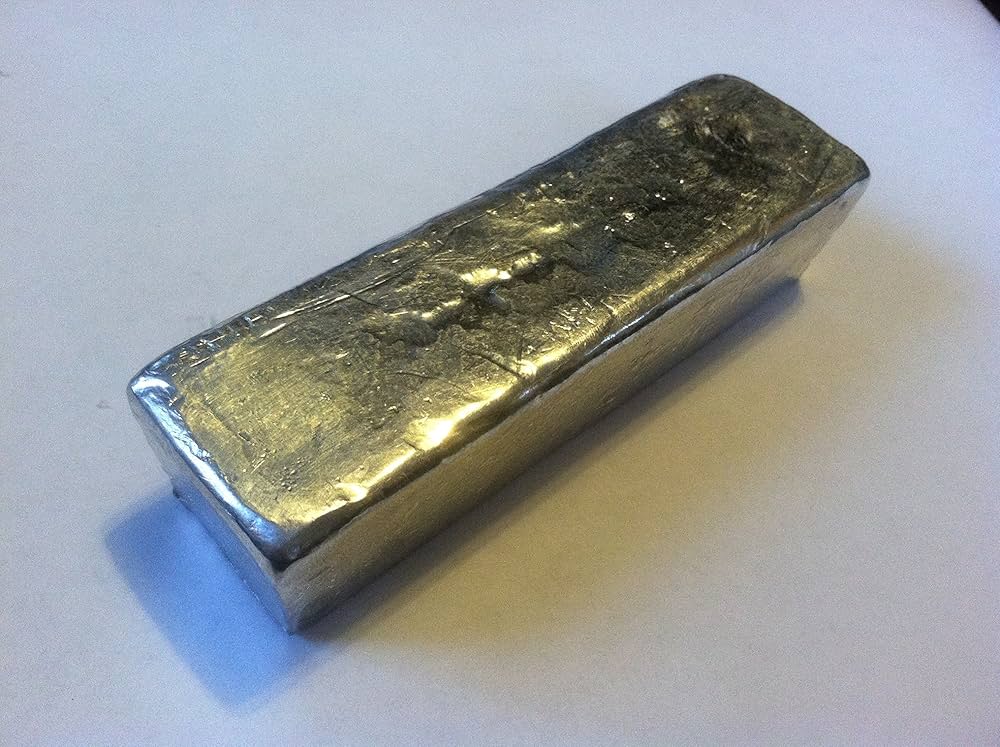
Indium Ingots
– Key Properties: Indium ingots typically have a purity level of 99.99% or higher, with a melting point of approximately 156.6°C (313.9°F). They exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and are stable at room temperature.
– Pros & Cons: The durability of indium ingots makes them ideal for applications requiring structural integrity. However, their higher cost compared to other metals can be a barrier for some buyers. Manufacturing complexity is relatively low, as they can be easily cast into desired shapes.
– Impact on Application: Indium ingots are primarily used in the production of indium tin oxide (ITO), which is crucial for touch screens and display technologies. Their compatibility with high-temperature processes makes them suitable for various electronic applications.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of import regulations and compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Understanding local market conditions can also influence purchasing decisions. -
Indium Shots
– Key Properties: Indium shots are small pieces of indium, often used in soldering applications. They maintain high purity levels and have a melting point similar to ingots.
– Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of indium shots is their ease of use in various applications, particularly in electronics for soldering. However, they may not be as durable as ingots, leading to potential limitations in high-stress environments. The cost is generally moderate, making them accessible for many businesses.
– Impact on Application: Indium shots are particularly effective in low-temperature soldering, providing excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Their size and form factor allow for precise application in intricate electronic components.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the indium shots meet specific local and international standards for soldering materials, as compliance can affect product reliability. -
Indium Powder
– Key Properties: Indium powder is available in various mesh sizes, with a purity of 99.99% or higher. It is highly malleable and can be easily processed into different forms.
– Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of indium powder is its versatility; it can be used in coatings, solders, and various electronic applications. However, its handling requires careful attention to avoid contamination, which can affect performance. The cost is generally higher due to the processing required to achieve fine particle sizes.
– Impact on Application: Indium powder is commonly used in the production of ITO coatings for displays and solar cells. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for diverse applications, including pharmaceuticals and chemical processing.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific requirements for powder handling and storage, as well as compliance with safety regulations in their region. Understanding the local market’s demand for indium powder can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Indium Materials for B2B Buyers
| Material | Typical Use Case for indium for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indium Ingots | Used in electronics and ITO production | High structural integrity | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Indium Shots | Soldering in electronic components | Easy to use and apply | Less durable than ingots | Medium |
| Indium Powder | Coatings and specialized applications | Versatile and adaptable | Requires careful handling | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials related to indium for sale, highlighting essential properties, advantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors can help businesses make informed decisions when sourcing indium products.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for indium for sale
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Indium?
The manufacturing process of indium involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-purity metal suitable for various applications. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation:
The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, primarily indium ores such as sphalerite and chalcopyrite. These ores are processed to extract indium through various methods, including flotation and leaching. The extracted indium is then refined to achieve the desired purity levels, often exceeding 99.99%. -
Forming:
Once the indium is refined, it can be formed into various shapes, such as ingots, shots, or powders. Techniques like casting and powder metallurgy are commonly used. For instance, molten indium can be poured into molds to create ingots, while mechanical processes can produce indium powder, which is essential for specific applications like soldering and electronics. -
Assembly:
In the assembly phase, the formed indium products may undergo further processes, such as alloying with other metals or combining with compounds like indium tin oxide (ITO). This step is crucial for applications in electronics, where indium is used in transparent conductive films for displays. -
Finishing:
The final stage involves surface treatments and packaging. This ensures that the indium products are free from contaminants and meet the specifications required by clients. Techniques such as vacuum sealing and inert gas environments may be employed to preserve the integrity of the indium during storage and transportation.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Indium Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the production of indium, particularly due to its applications in sensitive industries such as electronics and aerospace. Several international standards and industry-specific certifications govern the quality of indium products.
-
ISO 9001:
This is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures companies maintain effective processes for consistent quality. Manufacturers of indium should be ISO 9001 certified, demonstrating their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. -
CE Certification:
For products sold within the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers in Europe should look for this certification when sourcing indium. -
API Standards:
For indium products used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial. These standards ensure that the materials meet the rigorous demands of the industry.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Indium Production?
Quality assurance in indium manufacturing involves several checkpoints throughout the production process. These checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This stage involves inspecting the raw materials and components before production begins. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) to validate the purity and quality of the indium ores. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During manufacturing, continuous monitoring of the production process is essential. Sampling and testing at various stages help ensure that the products meet the specified standards. This may involve checking the purity levels of indium and the physical properties of the formed products. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
Before the final shipment, thorough testing is conducted to confirm that the indium products meet all customer specifications and international standards. This can include dimensional inspections, purity tests, and environmental assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to ensure they are sourcing indium from reputable suppliers. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC processes:
-
Supplier Audits:
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities and quality control processes firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality management systems and employee training. -
Quality Reports:
Requesting detailed quality reports and certificates of analysis for each batch of indium can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers should examine these documents to ensure they meet the required specifications. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an impartial assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These services typically include testing samples for purity and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing indium.
-
Regulatory Compliance:
Different countries have varying regulations concerning the importation of metals. Buyers must ensure that the indium they purchase complies with both local and international regulations to avoid legal issues. -
Cultural and Communication Barriers:
Language differences and cultural nuances can impact the clarity of quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear communication channels with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding of quality standards and specifications. -
Logistical Challenges:
The transportation of indium can be affected by geopolitical issues, tariffs, and shipping regulations. Buyers should consider these factors when planning their procurement strategies and ensure that suppliers have robust logistics solutions in place.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with indium is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can ensure they source high-quality indium that meets their specific needs. In today’s global market, a thorough approach to quality control is not just beneficial—it’s essential for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring operational success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘indium for sale’
This guide serves as a practical resource for international B2B buyers seeking to procure indium. Whether for manufacturing, research, or other applications, following these steps will help ensure a smooth and effective sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search, clearly outline your requirements for indium. Consider factors such as purity levels (e.g., 99.99%, 99.999%), form (shot, ingot, or powder), and quantity. This clarity will streamline your procurement process and help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers. Look for established companies with a solid reputation in the industry. Check their websites for product listings, certifications, and customer testimonials. Platforms like LinkedIn can also provide insights into their professional standing.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verification of supplier certifications is crucial in ensuring product quality and compliance. Request documentation such as ISO certifications and material safety data sheets (MSDS). This step is essential to confirm that the indium meets industry standards and regulations, particularly for buyers in regulated markets.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before placing a large order, request samples of the indium you intend to purchase. Testing samples will allow you to verify purity and assess the material’s suitability for your specific application. Ensure that the samples are representative of the bulk material to avoid discrepancies.
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures
Pricing for indium can vary significantly based on purity, form, and market conditions. Request quotes from multiple suppliers and compare them. Be sure to clarify what is included in the price, such as shipping costs and potential bulk discounts. This understanding will help you make an informed purchasing decision.
Step 6: Assess Shipping and Delivery Options
Evaluate the shipping capabilities of your chosen suppliers. Consider factors such as lead times, shipping methods, and costs. For international buyers, it’s important to understand customs regulations and any potential delays that could affect your supply chain.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms. Discuss payment methods, delivery timelines, and any warranties or return policies. Clear communication at this stage will prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing indium, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for indium for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Indium Pricing for B2B Buyers?
When sourcing indium, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The price of indium is largely influenced by global market rates, which can fluctuate due to mining yields and geopolitical factors. Buyers should monitor market trends and consider long-term contracts to hedge against price volatility.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region of production. Suppliers from different areas may have different wage structures, which can impact the overall cost of indium. For instance, suppliers in regions with higher labor costs may charge more for their products.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the facilities and utilities needed for production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs low, which is beneficial for buyers seeking competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Customization of indium products, such as specific shapes or sizes, often requires specialized tooling. This can increase initial costs but may lead to better fit and function for the end application.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high purity levels (e.g., 99.9% or higher) requires rigorous QC measures, which can add to costs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certification to guarantee the quality of the indium.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the shipping distance and chosen Incoterms. International buyers should factor in customs duties, insurance, and potential delays in transit.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on their market position and operational efficiencies. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide insights into pricing and negotiation strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Indium Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the price of indium, and being aware of these can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often dictate pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional processing or specialized equipment. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The purity level of indium directly impacts its price. Higher purity levels (e.g., 99.999% vs. 99.9%) command premium prices. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide relevant certifications for quality assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) or FOB (Free on Board) can significantly affect the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Indium Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing indium.
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms with suppliers. Discuss pricing based on volume and explore options for longer-term contracts to lock in favorable rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the total cost, including shipping, tariffs, and potential delays. A lower upfront price may not always lead to savings if logistics costs are high.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and how they may impact pricing. Consider establishing payment terms that protect against currency risks.
-
Supplier Relationship Management: Build strong relationships with suppliers to foster trust and reliability. A good relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and flexibility in negotiations.
-
Market Intelligence: Stay informed about market trends and emerging suppliers. This knowledge can empower you to make strategic decisions and switch suppliers if necessary.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for indium can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific product requirements. The prices referenced in various sources should be treated as indicative and subject to change. Always consult suppliers directly for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing indium for sale With Other Solutions
In the market for specialized materials, businesses often face a dilemma when selecting the right solution for their needs. Indium, a soft and malleable metal prized for its excellent conductivity and versatility, is available for sale in various purities and forms. However, other alternatives may offer competitive advantages depending on the specific application, budget, and operational requirements. This section will explore some viable alternatives to indium, providing B2B buyers with a comprehensive analysis to make informed purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Indium For Sale | Alternative 1: Tin | Alternative 2: Gallium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High electrical conductivity; ideal for electronics | Good conductivity; widely used in soldering | Excellent conductivity; used in electronics and optics |
| Cost | $483 – $789 per kg (99.99% pure) | $10 – $30 per kg | $100 – $300 per kg |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and storage | Easy to handle; standard practices in many industries | Requires careful handling due to toxicity |
| Maintenance | Minimal; stable under normal conditions | Low; widely available and easy to store | Moderate; must be stored properly to avoid contamination |
| Best Use Case | Display technologies, photovoltaics, and electronics | Solder for electronics, coatings | Semiconductors, LEDs, and thermoelectric devices |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Tin as an Alternative to Indium?
Tin is a well-established alternative, particularly in electronics for soldering applications. It is less expensive than indium and has a long history of use in various industries. The primary advantage of tin lies in its cost-effectiveness and widespread availability, making it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce expenses. However, tin does not match the electrical performance of indium and may not be suitable for high-performance applications. Additionally, tin can be more prone to oxidation, which can affect its long-term reliability in certain environments.
How Does Gallium Compare to Indium in Terms of Application and Use Cases?
Gallium is another metal that presents a compelling alternative to indium, particularly in the electronics and optics sectors. It boasts excellent electrical conductivity and is often used in the production of semiconductors and LEDs. One significant advantage of gallium is its ability to remain liquid at a slightly elevated temperature, which can be beneficial in specific applications. However, gallium is more expensive than tin and may require careful handling due to its toxicity in certain forms. Its market is also less stable than indium, which can lead to fluctuations in availability and price.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose Between Indium and Its Alternatives?
When deciding between indium and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific application for which the metal is intended. Indium excels in high-performance applications but comes at a higher cost. Tin offers a cost-effective solution for standard applications, while gallium provides unique advantages for specific technologies but may require more careful handling. Assessing the long-term needs of the business and the potential for future scalability will also guide the decision-making process. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on a balanced evaluation of these factors to meet the specific demands of the industry.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for indium for sale
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Indium for Sale?
Indium is a versatile metal with several critical properties that make it valuable in various industrial applications. Understanding these specifications is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Purity Levels (Material Grade)
Indium is available in various purity levels, typically expressed as 3N (99.9%), 4N (99.99%), and 5N (99.999%). The higher the purity, the better the performance in applications like electronics and coatings. Buyers should consider the required purity for their specific applications, as it directly affects product performance and cost. -
Melting Point
The melting point of indium is approximately 156.6°C (313.9°F). This property is crucial for industries that use indium in soldering and bonding applications, as it determines the conditions under which the metal can be processed. Knowing the melting point helps manufacturers select appropriate materials for their processes. -
Form Factor
Indium is available in various forms, including ingots, shots, and powders. Each form has distinct applications—ingots are often used for bulk applications, while powders are utilized in coatings and thin films. Understanding these options allows buyers to choose the best form for their specific use case. -
Density
The density of indium is approximately 7.31 g/cm³. This property is significant for applications where weight and space are critical, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. Buyers should consider how density impacts the overall design and functionality of their products. -
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Indium possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for use in electronics, especially in indium tin oxide (ITO) applications for touch screens and solar cells. Understanding conductivity ratings helps buyers assess how well indium will perform in their specific applications. -
Toxicity and Safety Data
Indium is generally considered safe to handle, but like any metal, it requires proper safety precautions during processing. Buyers should review Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for handling, storage, and disposal information to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Indium Market?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms related to indium sales:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of indium, OEMs may require high-purity indium for manufacturing electronic devices. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to gauge whether a supplier meets their purchasing needs, especially for smaller companies or specific projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of indium. It is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is crucial for managing costs and logistics in the global indium market. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes for a supplier to fulfill an order after it has been placed. Understanding lead times is critical for inventory management and production planning, particularly in industries that rely on just-in-time manufacturing. -
SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
An SDS provides detailed information about the properties of a substance, including hazards, handling, and storage recommendations. Buyers should review the SDS for indium to ensure safe handling and compliance with regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the indium market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the indium for sale Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Indium for Sale?
The indium market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by its indispensable role in electronics, particularly in the production of indium tin oxide (ITO), which is essential for touchscreens, LCDs, and solar panels. As global demand for advanced electronic devices rises, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking reliable sources of high-purity indium. Additionally, the transition towards renewable energy solutions has bolstered the demand for indium in photovoltaic applications, making it a critical material in the green technology sector.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as digital sourcing platforms and enhanced supply chain transparency, are reshaping how buyers approach indium procurement. These platforms facilitate direct connections between suppliers and manufacturers, enabling buyers to access competitive pricing and improve their sourcing efficiency. Moreover, advancements in logistics technology are streamlining the transportation of indium, reducing lead times and costs associated with international shipping, which is particularly beneficial for buyers in geographically distant markets.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Trends Shaping the Indium Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the indium market. Environmental impacts associated with mining and refining processes have led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as minimizing waste and utilizing renewable energy in production.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly seeking certifications that attest to the sustainable sourcing of materials, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or certifications indicating adherence to fair labor practices. Additionally, the trend towards ‘green’ materials is gaining traction, with companies looking to source indium that meets stringent environmental criteria, thus enhancing their brand reputation and compliance with regulations.
How Has the Indium Market Evolved Over Time?
Historically, indium was first discovered in 1863 and gained prominence in various industrial applications over the decades. Initially, it was used in alloys and sold at relatively low volumes. However, the advent of modern electronics in the late 20th century propelled indium into the spotlight, particularly for its unique properties as a transparent conductor.
As technology evolved, so did the applications of indium, transitioning from niche uses to becoming a staple in high-tech industries. Today, indium is not just a material of choice for electronics but also a key component in innovative technologies such as flexible electronics and advanced energy solutions. This evolution has positioned indium as a critical commodity in the global marketplace, prompting B2B buyers to navigate its dynamics with a keen focus on sourcing reliability and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of indium for sale
-
How do I verify the quality of indium before purchase?
To ensure you are sourcing high-quality indium, request Certificates of Analysis (CoA) from suppliers. These documents provide details about the purity and composition of the metal. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the supplier’s production processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider conducting independent lab testing if you’re purchasing in large quantities or for critical applications. This due diligence can help you avoid subpar products that could impact your operations. -
What is the best form of indium for electronic applications?
For electronic applications, indium in the form of indium tin oxide (ITO) is highly preferred due to its excellent electrical conductivity and transparency. This combination makes it ideal for use in display devices, touch screens, and solar cells. Suppliers typically offer indium as powder or shot, which can be processed into ITO. Ensure you specify your application needs to the supplier to get the most suitable form and purity level. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for indium?
Minimum order quantities for indium can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 1 kg to 100 kg or more. When sourcing indium, it’s essential to clarify the MOQ with potential suppliers, especially if you are looking to make bulk purchases. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or long-term contracts, so be sure to negotiate based on your specific requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when buying indium internationally?
Payment terms for international indium purchases can differ by supplier and region. Common practices include payment in advance, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to discuss and agree on terms that protect both parties, including currency, payment methods, and any necessary documentation. Additionally, consider the impact of tariffs and taxes based on your country’s regulations when budgeting for your purchase. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of indium shipments?
To ensure timely delivery of indium, confirm the supplier’s lead times and shipping methods before placing an order. Effective communication regarding your deadlines is crucial. You may also want to establish a logistics plan, including tracking shipments and understanding customs requirements in your region. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can facilitate smoother transactions and expedite problem resolution if delays occur. -
What factors should I consider when vetting indium suppliers?
When vetting indium suppliers, consider their reputation, production capabilities, and certifications. Research their history in the industry, and seek out reviews from other B2B buyers. It’s also wise to inquire about their sourcing practices for raw materials, as well as their adherence to environmental and safety standards. A reliable supplier will provide transparency and be willing to share details about their quality assurance processes. -
What are the common uses of indium in various industries?
Indium is primarily used in the electronics industry, especially in the production of ITO for displays and touch screens. It is also utilized in soldering applications, as indium-based solders have a low melting point and good wetting properties. Additionally, indium is employed in the manufacturing of semiconductors and photovoltaic cells. Understanding these applications can help you identify the right indium product for your specific business needs. -
How do I handle customs and import regulations when sourcing indium?
Handling customs and import regulations involves understanding the specific requirements for indium in your country. Research import duties, tariffs, and any necessary permits or licenses. It’s advisable to work with a customs broker who can navigate the complexities of international trade and ensure compliance with local laws. Additionally, ensure your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates, to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Indium For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Luciteria – Indium Metal 99.995%
Domain: luciteria.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Indium metal 99.995%, CAS 7440-74-6, available in quantities of 1 gram (labeled bottle), 10 grams, 100 grams, and 1 kilogram, starting from $3.00.
2. Solder – Pure Indium Shot
Domain: buy.solder.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”99.9% Pure Indium Shot”,”purity”:”3N”,”weight”:”1kg”,”price”:”$509.00″},{“name”:”99.99% Pure Indium Shot”,”purity”:”4N”,”weight”:”1kg”,”price”:”$520.00″},{“name”:”99.999% Pure Indium Shot”,”purity”:”5N”,”weight”:”1kg”,”price”:”$546.00″},{“name”:”99.9% Indium Ingot Bar”,”purity”:”3N”,”weight”:”1kg”,”price”:”$483.00″},{“name”:”99.9% Indium Ingot Bar”,”purity”:”3N”,”weight”:”500…
3. RotoMetals – Indium Metal
Domain: rotometals.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Indium Metal available in powder and ingot form. Melting Point: 313.9°F. Available quantities: 1 ounce to 100 kilos. Key products include: 10 grams Indium Shot (99.99% Pure) for $27.99, 1 KG Indium Shot (99.99% Pure) for $789.00, 1 oz Indium (99.99% Pure) for $49.99, 8 oz Indium Ingot (99.99% Pure) for $229.00, 4 oz Indium Ingot (99.99% Pure) for $129.00, and 1 KG Indium Ingot (99.99% Pure) for $6…
4. Fisher Scientific – Indium Ingot, 99.999%
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Indium ingot, 99.999% (metals basis)”, “Catalog Number”: “AA1472009”, “Quantity”: “10 g”, “CAS Number”: “7440-74-6”, “Molecular Formula”: “In”, “Molecular Weight (g/mol)”: “114.82”, “MDL Number”: “MFCD00134048”, “InChI Key”: “APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N”, “Synonyms”: [“indium”, “elemental”, “unii-045a6v3vfx”, “powder”, “shot”, “powder,-100 mesh”, “indio”, “shot”, “tear drop”, “4m…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for indium for sale
In the evolving landscape of indium sourcing, strategic procurement emerges as a critical element for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As indium’s applications in electronics, particularly in indium tin oxide for display technologies, continue to expand, so does the importance of securing high-purity indium. Buyers should focus on reputable suppliers that offer various forms of indium—such as shot, ingots, and powder—ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for their applications.
The competitive pricing observed across different markets highlights the need for diligent sourcing strategies. Buyers are encouraged to leverage market intelligence to negotiate better terms and explore bulk purchasing options that can yield significant cost savings. Additionally, understanding the supply chain dynamics and maintaining relationships with suppliers can enhance reliability and responsiveness to market fluctuations.
Looking ahead, the demand for indium is expected to rise, driven by advancements in technology and sustainability initiatives. International B2B buyers should act now to establish strong partnerships, ensuring a stable supply of this valuable resource. Engage with suppliers today to secure your indium needs and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.