Scrap Railroad Rail For Sale: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for scrap railroad rail for sale
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, sourcing scrap railroad rail for sale presents unique challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These challenges include fluctuating prices, inconsistent quality, and the need for reliable suppliers. This guide is designed to empower international buyers by providing comprehensive insights into the different types of scrap railroad rail available, their applications, and critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
From understanding the specifications of used rail, such as weight and material standards, to exploring their potential applications in construction, manufacturing, and transportation, this guide covers all essential aspects. It also delves into the intricacies of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy partners who offer quality products at competitive prices. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations, including shipping logistics and potential tariffs, which can significantly impact overall expenses.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and practical strategies, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that drive operational efficiency and enhance project outcomes. Whether you are in Brazil looking for reliable rail options for a new construction project or in Vietnam seeking to source materials for industrial applications, this guide will serve as your essential resource for navigating the global market for scrap railroad rail.
Understanding scrap railroad rail for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relay Rail | Typically reused rail from previous applications, available in various weights (e.g., 90 lb, 115 lb) | Light transport lines, temporary tracks, construction sites | Pros: Cost-effective, sustainable; Cons: May require refurbishment. |
| Used Steel Rail | Worn rails, often refurbished, characterized by neat appearance and minimal defects | Industrial transport, crane tracks, light locomotive lines | Pros: Extends rail life, stable performance; Cons: Limited availability of specific sizes. |
| Heavy Rail | High-strength rails, often used in heavy-haul applications, available in sizes like R50 and R65 | Mainline railroads, heavy freight transport | Pros: High durability, suitable for heavy loads; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Crane Rail | Specially designed for crane operations, typically lighter and with unique specifications | Heavy lifting operations, industrial sites | Pros: Tailored for specific applications; Cons: Less versatile than standard rail types. |
| Scrap Rail | Non-functional rail sections, often sold as scrap metal, available in various conditions | Recycling, metal recovery, construction material | Pros: Low cost, recyclable material; Cons: Quality and usability can vary significantly. |
What Are the Characteristics of Relay Rail and Its B2B Suitability?
Relay rail is primarily used rail that has been removed from service but is still in good condition for reuse. It is available in various weights, such as 90 lb and 115 lb, making it versatile for different applications. B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions for light transport lines or temporary tracks often opt for relay rail. Key purchasing considerations include the rail’s condition, the supplier’s reputation, and shipping logistics, especially since lengths over 15 feet typically require flatbed transport.
How Does Used Steel Rail Compare for Industrial Applications?
Used steel rail refers to previously utilized tracks that have been refurbished to ensure a neat appearance and structural integrity. Commonly found in weights like 43 kg and 50 kg, these rails are ideal for light transport lines and crane tracks. B2B buyers should consider the material’s maintenance history and potential refurbishment needs. Although used steel rail offers a sustainable option, the availability of specific sizes may pose a challenge, necessitating thorough supplier vetting.
What Are the Benefits of Heavy Rail for Freight Transport?
Heavy rail is designed for high-strength applications, making it suitable for mainline railroads and heavy freight transport. Common sizes like R50 and R65 provide the durability needed for demanding environments. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the long-term performance benefits, as heavy rail can significantly enhance line stability and reduce maintenance costs. However, the higher upfront price may deter some buyers, making it essential to evaluate the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Unique Features of Crane Rail in Industrial Settings?
Crane rail is specifically engineered for heavy lifting operations, characterized by its lighter weight and specialized design. These rails are commonly used in industrial environments where cranes are prevalent, providing a tailored solution for such applications. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their lifting operations when selecting crane rail, as improper specifications can lead to operational inefficiencies. While crane rail offers targeted benefits, its limited versatility compared to standard rail types may restrict its use in broader applications.
How Can Scrap Rail Serve as a Cost-effective Material for Various Industries?
Scrap rail consists of non-functional rail sections that can be sold as scrap metal. This option is often pursued by B2B buyers involved in recycling or construction, as it offers a low-cost material solution. However, the quality and usability of scrap rail can vary significantly, so buyers must conduct careful assessments before purchase. While the potential for cost savings is attractive, ensuring that the material meets specific project requirements is crucial for successful implementation.
Key Industrial Applications of scrap railroad rail for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of scrap railroad rail for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Temporary access roads and tracks for heavy machinery | Cost-effective solution for creating durable infrastructure | Quantity, rail condition, and compliance with local regulations |
| Mining | Tracks for transporting materials within mines | Enhances operational efficiency and safety in material handling | Rail strength, dimensions, and ability to withstand heavy loads |
| Agriculture | Tracks for loading and unloading equipment in rural areas | Improves logistics and reduces downtime during harvest seasons | Availability of various lengths and weights suited for agricultural needs |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Crane rails for warehouses and distribution centers | Facilitates efficient movement of goods and materials | Specific weight requirements and customization options |
| Energy and Utilities | Support structures for wind turbine installations | Provides robust support for heavy machinery in remote locations | Material specifications and environmental considerations |
How is Scrap Railroad Rail Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, scrap railroad rail is often repurposed to create temporary access roads and tracks for heavy machinery. This application is particularly beneficial for projects in remote areas where traditional road infrastructure may be lacking. The durability of used rail ensures that it can withstand the weight of heavy equipment, minimizing maintenance costs and downtime. International buyers should consider factors like the quantity needed, the condition of the rails, and compliance with local building regulations to ensure they meet project specifications.
What Role Does Scrap Railroad Rail Play in Mining Operations?
In mining operations, scrap railroad rail is utilized to construct tracks for transporting materials within the mine. This application is crucial for improving operational efficiency, as it allows for the safe and effective movement of heavy loads. The use of heavy-duty scrap rail can significantly enhance safety by providing stable pathways for equipment and personnel. Buyers in the mining sector should prioritize sourcing rails that meet specific strength and dimensional requirements to ensure they can handle the operational demands of their site.
How is Scrap Railroad Rail Beneficial for Agricultural Logistics?
Agricultural operations often require efficient logistics for loading and unloading equipment, especially during peak seasons. Scrap railroad rail can be employed to create makeshift tracks that facilitate this process, providing a sturdy and reliable surface for agricultural machinery. This not only improves the speed of operations but also reduces the risk of equipment damage. Buyers should look for various lengths and weights of scrap rail that align with their specific agricultural needs to optimize their logistical setup.
In What Ways Does Scrap Railroad Rail Support Logistics and Warehousing?
In logistics and warehousing, scrap railroad rail is commonly used as crane rails to support the movement of goods within distribution centers. This application allows for efficient loading and unloading of materials, significantly enhancing productivity. The robust nature of railroad rail ensures that it can support heavy loads, making it an ideal choice for warehouses that handle large volumes of inventory. Buyers should focus on specific weight requirements and customization options to ensure the rails fit their operational layouts.
How Can Scrap Railroad Rail Aid Energy and Utilities Projects?
In the energy sector, particularly for wind turbine installations, scrap railroad rail can serve as support structures. This is especially valuable in remote locations where robust and durable materials are essential for stability. The strength of scrap rail ensures that it can withstand harsh environmental conditions, providing a reliable foundation for heavy machinery. Buyers in this sector must consider material specifications and environmental regulations to ensure compliance and safety during installation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘scrap railroad rail for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Assessing the Quality of Scrap Railroad Rail
The Problem:
Many international B2B buyers often find it challenging to evaluate the quality of scrap railroad rail before purchase. This concern is particularly prevalent among buyers from regions with varying standards and practices for rail materials. Without the ability to inspect the rails physically, buyers may worry about hidden defects such as cracks, bends, or rust, which could compromise the integrity of their projects. This uncertainty can lead to financial loss, delays in project timelines, and ultimately, the risk of safety hazards.
The Solution:
To mitigate these quality assessment challenges, buyers should demand detailed specifications and condition reports from suppliers. This includes requesting photographs of the rails, documentation of previous usage, and any maintenance records. When sourcing scrap railroad rail, utilize a checklist that outlines specific quality indicators, such as the absence of visible scars, consistent weight specifications, and compliance with recognized standards (e.g., ASTM or EN). Engaging a third-party inspection service can also provide an unbiased quality assessment, ensuring that the materials meet project requirements. By implementing these practices, buyers can confidently select high-quality scrap rails that align with their operational needs.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Shipping and Logistics for Scrap Rail
The Problem:
For B2B buyers, especially those based in remote regions or countries with limited infrastructure, arranging the shipping of scrap railroad rail can be a daunting task. The logistics involved—from coordinating flatbed shipments for long lengths to navigating customs regulations—can often lead to delays and increased costs. Furthermore, the complexity of managing multiple suppliers can result in inconsistent delivery schedules and potential project disruptions.
The Solution:
To streamline shipping and logistics processes, buyers should establish relationships with logistics providers that specialize in heavy materials like scrap railroad rail. These providers can offer tailored solutions, including optimized transport routes and compliance with local regulations. Additionally, buyers should consolidate orders from a single supplier when possible, reducing the number of shipments and simplifying customs processes. Utilizing technology, such as logistics management software, can also help track shipments in real time, allowing for proactive management of potential delays. By focusing on logistics partnerships and technology, buyers can enhance the efficiency of their supply chain.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Pricing and Market Variability of Scrap Railroad Rail
The Problem:
The scrap railroad rail market is known for its price fluctuations driven by various factors, including global demand, material availability, and regional economic conditions. B2B buyers often struggle to understand these pricing dynamics, leading to the risk of overpaying for materials or missing out on favorable market conditions. This uncertainty can impact budgeting, project planning, and overall cost management.
The Solution:
To gain a clearer understanding of pricing trends, buyers should engage in comprehensive market research. This includes monitoring industry reports, subscribing to newsletters from reputable rail suppliers, and participating in relevant trade shows or forums. Establishing a network with other buyers can also provide insights into market movements and pricing strategies. Additionally, buyers should negotiate long-term contracts with suppliers that allow for price adjustments based on market indices, providing a buffer against volatility. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can better navigate the complexities of scrap railroad rail pricing and make informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for scrap railroad rail for sale
What Are the Key Materials Used in Scrap Railroad Rail for Sale?
When considering scrap railroad rail for sale, several materials are commonly utilized, each with unique properties and implications for performance and application. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Scrap Railroad Rail?
Steel is the most prevalent material used in railroad rails due to its excellent strength and durability. It typically exhibits high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for heavy loads and high-speed applications. Steel rails can withstand significant pressure and are often treated to enhance their corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
Pros: Steel is durable, cost-effective, and widely available, making it a preferred choice for many applications. Its recyclability also contributes to sustainability efforts.
Cons: Steel can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, particularly in humid or saline environments. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specific standards to ensure quality.
Impact on Application: Steel rails are compatible with various media, including heavy freight and passenger transport. Their performance is critical in maintaining safety and efficiency on rail networks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, which govern steel quality. In regions like Brazil and Vietnam, understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and recycling can significantly impact procurement strategies.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Scrap Railroad Rail?
Aluminum is less common but is increasingly being explored for specific applications, particularly in lighter rail systems. It is lightweight and exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments where weight reduction is essential.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and installation. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of the rail in specific applications.
Cons: Aluminum is generally less durable than steel and may not support the same heavy loads. Its higher cost can also be a drawback for large-scale projects.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for light rail systems and temporary tracks. Its properties make it suitable for urban transport solutions where weight and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific applications where aluminum is appropriate and ensure compliance with relevant standards. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect material performance, understanding the thermal properties of aluminum is essential.
What Role Does Composite Material Play in Scrap Railroad Rail?
Composite materials, often a blend of various substances, are emerging as a viable option for specific rail applications. These materials can be engineered to provide unique properties, such as enhanced corrosion resistance and reduced weight.
Pros: Composites can be tailored for specific performance requirements, including resistance to environmental factors and reduced maintenance needs.
Cons: The initial cost of composite materials can be higher than traditional metals, and their long-term durability in heavy-load applications is still being evaluated.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suited for environments that require high corrosion resistance, such as coastal areas or industrial sites. Their lightweight nature can also facilitate easier installation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the evolving standards for composite materials is essential, especially in regions where traditional materials dominate the market. Buyers should also consider the lifecycle costs associated with composites.
Summary Table of Key Materials for Scrap Railroad Rail
| Material | Typical Use Case for scrap railroad rail for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy freight and passenger transport | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Light rail systems and urban transport | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under heavy loads | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications in harsh environments | Tailored properties and low maintenance | Higher initial cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when sourcing scrap railroad rail. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can help optimize procurement strategies tailored to specific project needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for scrap railroad rail for sale
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Scrap Railroad Rail?
The manufacturing process for scrap railroad rail is a critical aspect of ensuring that the recycled material meets industry standards and is suitable for reuse in various applications. The process typically involves several key stages:
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves sourcing scrap metal, which may include used railroad rails from decommissioned tracks. This material undergoes a thorough inspection for quality, identifying any defects or inconsistencies that could affect the final product. The scrap is then sorted by type and grade, which is essential for maintaining uniformity in the end product.
-
Forming: Once the material is prepared, it is subjected to forming processes that reshape the scrap into usable rail sections. Techniques such as hot rolling may be employed, where the metal is heated and passed through rollers to achieve the desired dimensions. This stage ensures that the rails conform to specific standards, such as weight and profile, which are critical for performance and safety.
-
Assembly: Although scrap rails typically do not require extensive assembly, they may be bundled or packaged for shipment. This includes grouping rails by type and length, which facilitates easier handling and transport. Proper assembly ensures that the product remains intact during shipping and can be easily installed upon arrival at the buyer’s location.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying protective coatings or treatments to enhance the longevity of the rails. This may include rust inhibitors or surface treatments to prevent degradation during transport. The finishing process is essential, particularly for international shipments, to ensure the product arrives in optimal condition.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in Scrap Railroad Rail Production?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the manufacturing process of scrap railroad rail, ensuring that the final product meets both international standards and customer specifications. The QC process typically includes:
-
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers adhere to standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for safety and compliance, are crucial for ensuring that the scrap rails meet European standards.
-
Quality Checkpoints: QC is integrated into various stages of production through several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to verify their quality before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring ensures that the processes remain within specified parameters.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a comprehensive evaluation of the finished product is conducted to confirm that it meets all technical specifications and quality standards.
-
Testing Methods: Common testing methods for scrap railroad rail include tensile strength tests, hardness tests, and non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle testing. These tests help identify any internal defects that could compromise the rail’s integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Quality Control in Scrap Railroad Rail Suppliers?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are some strategies to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insight into their QC processes. This includes reviewing documentation related to their quality management system and observing their production practices firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications from suppliers can help assess their compliance with international standards. These documents should outline their QC processes, testing results, and any relevant certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can perform inspections and testing on behalf of the buyer, ensuring that the supplier’s claims are validated by an unbiased entity.
-
Understanding Certification Nuances: Different regions may have varying certification requirements. For example, European buyers may require CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may look for compliance with specific local standards. Understanding these nuances is crucial for ensuring that the product meets local regulations and expectations.
What Are the Benefits of Adhering to Quality Control Standards in Scrap Railroad Rail Production?
Adhering to quality control standards not only enhances the reputation of manufacturers but also provides significant benefits for B2B buyers:
-
Increased Reliability: Ensuring that scrap railroad rails meet high-quality standards increases the reliability of the product, which is vital for safety in transportation infrastructure.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Quality assurance processes help minimize defects and reduce the likelihood of costly recalls or repairs, making it a cost-effective approach for both manufacturers and buyers.
-
Enhanced Marketability: Products that comply with international standards are often more appealing to buyers, allowing manufacturers to access broader markets and potentially command higher prices.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a reputation for quality can foster long-term relationships between suppliers and buyers, promoting repeat business and collaboration on future projects.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with scrap railroad rail production is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these areas, buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality materials that meet their operational needs and comply with relevant regulations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘scrap railroad rail for sale’
This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing scrap railroad rail. By following these steps, you can ensure a successful procurement process that meets your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start sourcing, clearly outline the technical specifications of the scrap railroad rail you need. Consider factors such as rail type (e.g., RE, RA, or other designations), weight, length, and material composition. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure the rails meet your project’s requirements.
- Weight and Type: Specify the weight (e.g., 43kg, 50kg) and type to avoid mismatches.
- Length Variability: Determine if you need standard lengths or can work with random lengths.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of scrap railroad rail. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry, positive customer reviews, and relevant certifications.
- Supplier Credentials: Verify if suppliers are compliant with local and international regulations.
- Industry Reputation: Seek recommendations or reviews from other businesses in your region or sector.
Step 3: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have a list of potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Ensure the quotes include pricing, minimum order quantities, delivery terms, and any additional costs like shipping or handling.
- Breakdown of Costs: Look for transparency in pricing to avoid hidden fees.
- Lead Times: Understand the expected delivery times to align with your project schedule.
Step 4: Evaluate Product Condition
Assess the condition of the scrap railroad rail being offered. Ensure that the rails are free from major defects such as bending, fractures, or excessive wear.
- Visual Inspection: If possible, arrange for a physical inspection of the rails before purchase.
- Supplier Guarantees: Inquire if the supplier provides any guarantees or warranties on the quality of the rails.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations regarding payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings later on and foster a better working relationship with the supplier.
- Payment Flexibility: Discuss options like letters of credit or installment payments for larger orders.
- Cancellation Policies: Understand the terms around order cancellations or changes to avoid penalties.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
After negotiations, ensure that all terms are documented in a formal contract. This document should outline all agreed-upon specifications, pricing, delivery dates, and any contingencies.
- Legal Review: Consider having a legal expert review the contract to protect your interests.
- Signature and Copies: Ensure both parties sign the contract and keep copies for reference.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, coordinate the logistics for transporting the scrap railroad rail. Ensure that you have the necessary arrangements in place for loading, transport, and unloading at your facility.
- Transportation Method: Decide whether flatbed shipping or other methods are necessary based on rail lengths.
- Receiving Protocols: Prepare your facility for receiving and inspecting the rails upon delivery.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process for scrap railroad rail and make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for scrap railroad rail for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Scrap Railroad Rail?
When sourcing scrap railroad rail, several critical cost components come into play. The primary material cost reflects the price of the scrap itself, which varies based on the rail type, condition, and market demand. Labor costs are incurred during the collection, processing, and transportation of the rail, which can significantly impact overall pricing. Manufacturing overhead includes expenses related to facility maintenance, equipment depreciation, and energy costs associated with processing the rail. Additionally, tooling costs may arise if specialized equipment is required for refurbishment or customization.
Quality control (QC) is vital in ensuring that the rails meet specified standards. This involves inspection processes that can add to labor and overhead costs. Lastly, logistics costs cover the transportation of the rails from the supplier to the buyer, including shipping fees, tariffs, and insurance, which are crucial for international transactions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Scrap Railroad Rail?
Several factors influence the pricing of scrap railroad rail, notably the volume of the order, specifications, and customization requests. Bulk purchases often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider the specifications required for their projects, as certain rail types or custom modifications may carry premium pricing.
Material quality and certifications are significant price influencers as well. Rails that meet international quality standards or come with certifications may attract higher prices but offer better reliability and longevity. Supplier factors, including reputation and reliability, also play a crucial role. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance processes.
Incoterms can further complicate pricing structures, especially for international buyers. Understanding which costs are borne by the seller versus the buyer is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Strategies Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for Scrap Railroad Rail?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to substantial cost savings when sourcing scrap railroad rail. Buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand current pricing trends and establish a benchmark for negotiations. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing, particularly for repeat purchases.
Consider negotiating based on total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs. TCO includes maintenance, potential refurbishment, and the longevity of the rail, which can justify a higher initial price if the product proves more durable. Additionally, leveraging competitive quotes from multiple suppliers can enhance bargaining power.
International buyers should be aware of pricing nuances related to their specific regions. For instance, shipping costs and tariffs can vary significantly between countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these factors can provide leverage in negotiations.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Scrap Railroad Rail?
International buyers must navigate various complexities when sourcing scrap railroad rail. Currency fluctuations can impact pricing, so it’s advisable to lock in rates where possible. Understanding local regulations regarding scrap material imports is crucial, as compliance can prevent costly delays.
Buyers should also factor in logistics and shipping timelines, as longer transit times can affect project schedules. Collaborating with logistics experts familiar with rail transport can streamline this process.
Lastly, always request a detailed quote that breaks down all costs involved, including logistics and any potential duties or taxes. This transparency will aid in understanding the true cost of the rail and avoid surprises down the line.
Disclaimer on Indicative Pricing
Pricing for scrap railroad rail is subject to market fluctuations and can vary based on multiple factors. The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers for accuracy. Always conduct due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing scrap railroad rail for sale With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Scrap Railroad Rail for Sale
When considering options for track material in industrial applications, it’s vital to evaluate various alternatives to scrap railroad rail. Each option comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that can significantly impact project outcomes. This section provides a comparative analysis of scrap railroad rail against two viable alternatives: New Steel Rail and Composite Rail Systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Scrap Railroad Rail For Sale | New Steel Rail | Composite Rail Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for light to medium loads; refurbished for stability | High performance; suitable for heavy loads | Excellent resistance to corrosion and wear |
| Cost | Generally lower cost; dependent on condition and quantity | Higher initial cost; value in longevity | Moderate to high; initial investment offset by durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires inspection and potential refurbishment | Straightforward installation; minimal prep required | Requires specialized installation techniques |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance if refurbished properly | Regular maintenance needed; durable but can wear | Minimal maintenance; resistant to environmental factors |
| Best Use Case | Temporary or light rail applications in industrial settings | Mainline and heavy-duty applications | Environments with high corrosion, such as coastal areas |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of New Steel Rail?
New steel rail is a robust solution for heavy-duty applications. It is manufactured to meet stringent quality standards, ensuring high performance under significant loads. However, the cost is significantly higher than scrap options, which may not be feasible for all projects. While new rails require less initial maintenance, they still need periodic inspections and upkeep to maintain their longevity.
How Do Composite Rail Systems Compare?
Composite rail systems present an innovative alternative, combining materials like fiberglass and resin to create a lightweight, corrosion-resistant product. This option excels in environments prone to moisture and corrosive elements, making it ideal for coastal or industrial settings. However, the installation process can be complex, requiring specialized skills, which could lead to higher labor costs. Despite the upfront investment, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance make composite systems an appealing choice for some buyers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate rail solution hinges on understanding specific project requirements and constraints. For buyers seeking cost-effective, temporary solutions, scrap railroad rail can be an excellent choice, particularly when refurbished. In contrast, projects requiring high durability and load-bearing capacity may benefit more from investing in new steel rail. Lastly, for environments with high exposure to corrosive conditions, composite rail systems provide a modern, low-maintenance alternative. Ultimately, assessing performance needs, budget constraints, and environmental factors will guide B2B buyers toward the most suitable rail solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for scrap railroad rail for sale
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Scrap Railroad Rail?
When purchasing scrap railroad rail, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring the material meets project specifications and regulatory requirements. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade indicates the quality and strength of the rail. Common grades include 45Mn and 50Mn, which are used for their durability and resistance to wear. Selecting the right material grade is essential for applications such as light transport lines or industrial tracks, where load-bearing capacity is critical.
2. Rail Weight
Rail weight is typically expressed in pounds per yard (lb/yd) or kilograms per meter (kg/m). Common weights for scrap railroad rails range from 43 kg (approximately 95 lb) to 50 kg (approximately 110 lb) and beyond. The weight affects the rail’s strength and stability, making it a key consideration for buyers focused on specific load requirements.
3. Dimensions and Tolerances
The height, width, and thickness of the rail, along with the tolerances allowed in manufacturing, dictate how the rail will fit with other components. For example, a typical 43 kg rail may have dimensions such as a height of 140 mm, width of 114 mm, and web thickness of 14.5 mm. Proper dimensional specifications ensure compatibility with existing track systems and reduce the risk of installation issues.
4. Condition and Appearance
The physical condition of the scrap rail is a significant factor. It should exhibit no bending, fractures, or excessive wear. A neat appearance often indicates that the rail has been well-maintained and can be reused effectively. This is important for B2B buyers who require reliability and safety in their rail applications.
5. Standard Compliance
Scrap rails should conform to industry standards, such as GB 2585-2007 for Chinese rail specifications. Compliance ensures that the material meets safety and performance criteria necessary for specific applications. Buyers should verify that the scrap rail adheres to applicable standards to mitigate risks.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Scrap Railroad Rail Market?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the scrap railroad rail market. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of scrap rail, OEM specifications can dictate the quality and dimensions of the rail required for specific applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For scrap railroad rails, MOQs can vary significantly based on supplier policies and rail type. Understanding MOQs helps buyers plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit price offers from suppliers. This is a critical step in the purchasing process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple vendors before making a decision.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping, delivery, and insurance. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaging in cross-border transactions to avoid misunderstandings.
5. Relay Rail
Relay rail refers to used rails that have been refurbished and are suitable for reuse in lower-density applications. Understanding this term is important for buyers looking for cost-effective solutions without compromising quality.
By being well-versed in these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing scrap railroad rails, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the scrap railroad rail for sale Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Scrap Railroad Rail Sector?
The scrap railroad rail market is witnessing significant shifts driven by global economic factors, technological advancements, and evolving buyer preferences. Increased urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, are driving demand for cost-effective materials. As countries enhance their transportation networks, the reuse of scrap rail becomes a practical solution, facilitating both cost savings and sustainability goals. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is enabling international buyers to connect more efficiently with suppliers, streamlining the purchasing process.
Key trends shaping the market include the growing preference for relay rails, which are recycled from decommissioned rail lines. These rails are appealing due to their lower environmental impact and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, advancements in logistics technology, including real-time tracking and automated inventory management, are enhancing the efficiency of supply chains in the scrap rail sector. International buyers are also becoming increasingly aware of the importance of quality standards, with a focus on sourcing rails that meet specific specifications for durability and strength.
Emerging markets, particularly in regions like Vietnam and the Middle East, are becoming critical players in the scrap rail market. These regions are investing heavily in rail infrastructure, creating a robust demand for both new and used rail materials. International suppliers must adapt to these dynamics by ensuring they can meet diverse regulatory requirements and offer competitive pricing structures that appeal to these markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Scrap Railroad Rail Market?
Sustainability is a key consideration for buyers in the scrap railroad rail market. The environmental impact of sourcing materials is under scrutiny, with a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economies. The scrap rail industry inherently supports sustainability by recycling materials that would otherwise contribute to landfill waste.
Ethical sourcing practices are becoming increasingly vital, with buyers seeking suppliers who prioritize environmentally responsible methods in their operations. This includes adhering to regulations regarding the disposal of hazardous materials, such as creosote-treated ties. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming critical for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, buyers are looking for transparency in their supply chains. This means suppliers must provide clear documentation regarding the sourcing of their materials and the processes involved in recycling and refurbishing scrap rail. As B2B buyers become more discerning, those suppliers who can showcase their sustainable practices and ethical sourcing will likely gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What Is the Historical Context of the Scrap Railroad Rail Market?
The scrap railroad rail market has evolved significantly over the decades, reflecting broader changes in transportation and infrastructure development. Initially, railroad rails were designed for long-term use; however, as rail technology advanced and rail lines were upgraded, older rails became available for recycling.
This evolution began gaining traction in the mid-20th century when the economic benefits of reusing materials became apparent. The introduction of environmental regulations in the 1970s further propelled the recycling movement, as industries sought ways to minimize waste and comply with new standards. The globalization of trade in the late 20th century allowed scrap rail to be sourced and sold across borders, creating a more interconnected market.
Today, the scrap railroad rail sector is characterized by a blend of traditional practices and modern technological innovations, providing a robust framework for international B2B buyers seeking sustainable and cost-effective solutions. As the demand for infrastructure continues to rise, the market for scrap railroad rail is poised for further growth and transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of scrap railroad rail for sale
-
1. How can I ensure the quality of scrap railroad rail before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of scrap railroad rail, request detailed specifications from the supplier, including rail type, dimensions, and material composition. Conduct a thorough inspection or ask for recent quality assurance reports, particularly focusing on any signs of damage such as bending, fractures, or excessive wear. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to assess the inventory firsthand. Additionally, consider requesting samples or photographs to verify the condition before committing to a larger order. -
2. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier for scrap railroad rail?
When selecting a supplier, evaluate their reputation, experience in the industry, and customer reviews. Check if they comply with international standards and regulations concerning rail quality and environmental practices. It is also beneficial to assess their logistics capabilities, including shipping options and timelines, as well as their flexibility in meeting order quantities. Establishing clear communication channels and understanding their payment terms and conditions can also foster a reliable business relationship. -
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for scrap railroad rail purchases?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers based on inventory levels and shipping logistics. Typically, MOQs for scrap railroad rail range from a few tons to several hundred tons. It’s essential to clarify the MOQ with potential suppliers during your initial discussions. Additionally, some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so it’s worth negotiating terms that suit your purchasing needs. -
4. What payment terms should I expect when buying scrap railroad rail internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of scrap railroad rail often include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or open account terms, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Standard practices may require a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings and to facilitate smooth transactions. -
5. How can I customize my order of scrap railroad rail to meet specific project needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for scrap railroad rail, allowing you to specify dimensions, weight classes, and material types based on your project requirements. When discussing your needs with potential suppliers, clearly communicate the intended application and any specific standards or regulations you must adhere to. Suppliers may also provide recommendations on suitable rail types for particular uses, ensuring that your order aligns with your operational goals. -
6. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing scrap railroad rail?
Logistics for importing scrap railroad rail involve several considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier provides a detailed shipping plan, including freight costs and estimated delivery dates. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations of your country, including tariffs and documentation requirements. Collaborating with a freight forwarder or logistics provider experienced in heavy materials can help streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
7. How can I verify the authenticity of a supplier’s claims regarding their scrap railroad rail?
To verify a supplier’s authenticity, conduct thorough due diligence, including checking their business licenses, industry certifications, and references from previous clients. Utilize online platforms to read reviews and feedback about their services. If possible, request third-party audits or certifications that confirm their compliance with industry standards. Engaging in direct communication and asking detailed questions about their sourcing and quality assurance practices can further establish their credibility. -
8. What are the environmental considerations when purchasing scrap railroad rail?
When purchasing scrap railroad rail, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of the sourcing and processing practices of the supplier. Ensure that the supplier adheres to sustainable practices, such as proper recycling methods and compliance with local environmental regulations. Additionally, inquire about their policies on hazardous materials, particularly if the rail has been treated with chemicals. Opting for suppliers who prioritize sustainability can not only enhance your corporate responsibility but also align with regulatory requirements in many regions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Scrap Railroad Rail For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
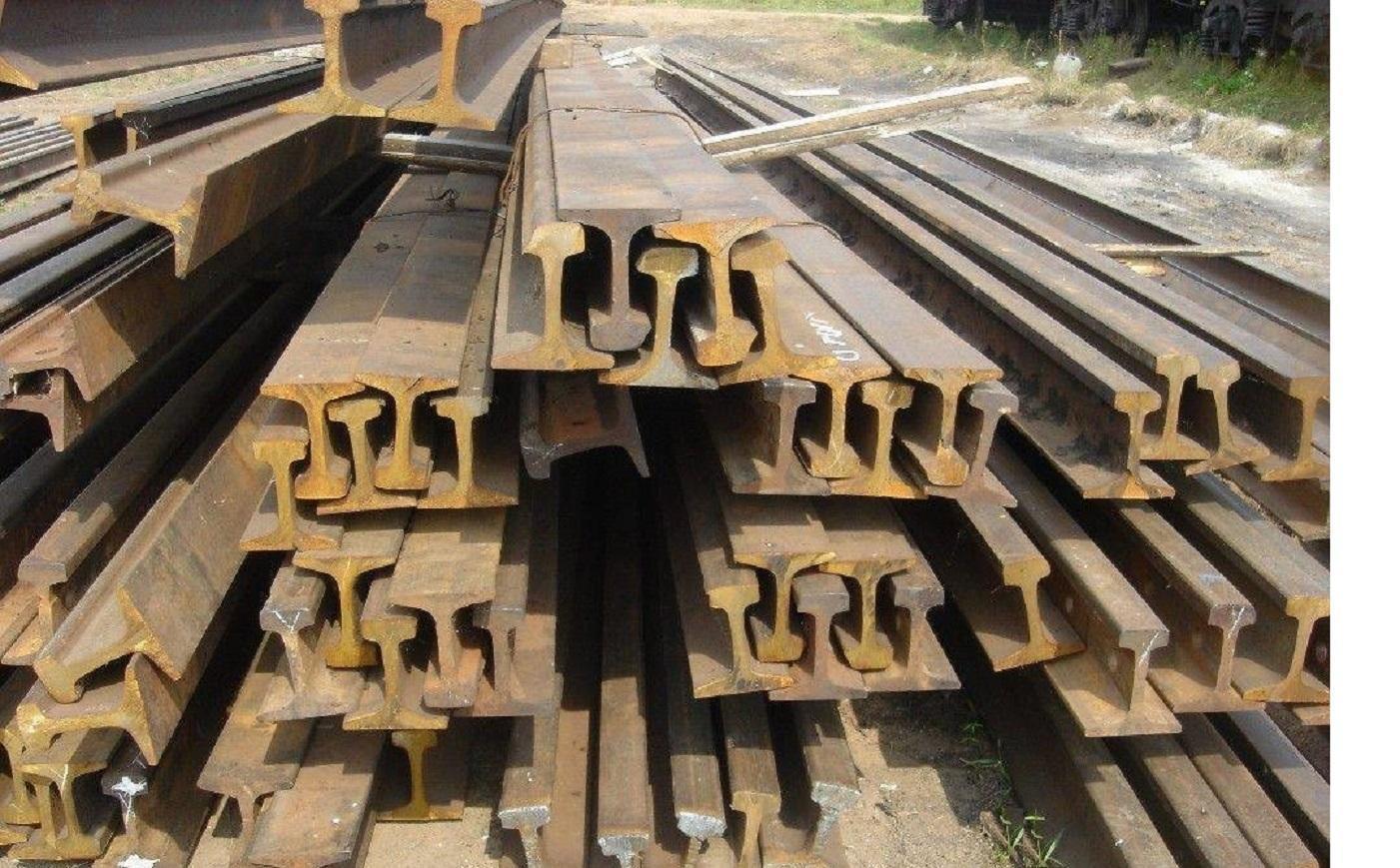
1. Railroad Rails – Used Rail Type 43kg & 50kg
Domain: railroadrails.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Used Rail Type: 43kg, 50kg
Material: 50Mn, 45Mn
Standard: GB 2585-2007
Description: Used rail refers to the railroad track that has been previously used on busy lines and is now being reused in light transport industrial areas. It should have a neat appearance, no bending fractures, and no scars. It is mainly used for temporary transportation lines, light locomotive lines, crane tracks, and drivin…
2. Railroad Track Pieces – Sourcing Options
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Railroad track pieces can be sourced from various locations: 1. Local railroad authorities may have old or dead rail available for purchase, with prices mentioned around $30 per meter. 2. Scrap yards or individuals working in railroad yards may have scrap pieces available, sometimes for a small fee. 3. Specific vendors like Cohen Steel in Concord, NH, offer railroad track sections for $20 per one-…
3. Welding Web – Railroad Track Scrap
Domain: weldingweb.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Railroad track available legally at local scrapyards; price is approximately 15¢ per pound; can be cut into desired lengths, typically available in small (3′) pieces; availability may occur one or two times a year.
4. Accio – Used Railroad Rails
Domain: accio.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used Railroad Rails: Quality & Bulk Supply Options; Bulk Suppliers: FERM ENTERPRISE COMPANY LIMITED, Shandong Baotai Steel Co., Ltd., R AND K TRADING CO., LTD., Shandong Henghai Materials Co., Ltd., Zhejiang Zhongding Iron And Steel Co., Ltd., AMI (Tianjin) New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong Huajin Metal Products Co., Ltd., Hdt Tubing Co., Ltd., Shandong Bailida Metal Products Co., Ltd.,…
5. Savona Equipment – Rail and Accessories
Domain: savonaequipment.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: New and Used Rail and Accessories for Sale by Savona Equipment – Reconditioned Rail and Accessories Available.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for scrap railroad rail for sale
In the evolving landscape of scrap railroad rail sourcing, international buyers must recognize the critical importance of strategic sourcing to enhance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the diverse types of used rail available, including various weights and conditions, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific project needs. Engaging with reputable suppliers who provide transparent pricing and quality guarantees is essential to securing reliable materials.
Moreover, the reuse of scrap rail offers not only significant cost savings but also contributes to sustainability efforts in the industry. As global demand for recycled materials increases, sourcing scrap railroad rail presents a unique opportunity to improve both environmental and financial outcomes.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage these insights to build robust supply chains that prioritize quality and sustainability. As you navigate your sourcing strategy, consider reaching out to established suppliers for tailored solutions that meet your operational requirements. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your procurement processes and drive your business forward in a competitive marketplace.