Is Your Toll Manufacturing Vs Contract Manufacturing Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of deciding between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing as they seek to optimize their production capabilities. Understanding the nuances of these two outsourcing models is essential for businesses looking to enhance efficiency while managing costs effectively. This guide delves into the intricacies of toll manufacturing versus contract manufacturing, offering insights into their definitions, applications, and operational frameworks.
We will explore key considerations such as supplier vetting processes, cost structures, and the specific advantages and disadvantages of each model. By examining real-world case studies and industry examples, this guide aims to equip businesses—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Brazil and Germany)—with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you’re a startup aiming to scale operations without substantial capital investment or an established enterprise seeking to streamline your supply chain, this comprehensive resource will empower you to navigate the complexities of the global market for manufacturing solutions. With actionable insights and strategic recommendations, you can confidently choose the path that aligns best with your operational goals and market demands.
Understanding toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toll Manufacturing | Client supplies raw materials; toll manufacturer processes them. | Food production, chemicals, electronics | Pros: Cost-effective, control over raw materials. Cons: Requires logistics management. |
| Contract Manufacturing | Manufacturer handles both production and raw material procurement. | Pharmaceuticals, consumer goods | Pros: Simplified process, access to vendor networks. Cons: Less control over inputs. |
| Toll Processing | Specialized processing of raw materials without full manufacturing. | Specialty chemicals, cosmetics | Pros: Tailored processing, expert handling of materials. Cons: Limited to processing only. |
| Private Label Manufacturing | Manufacturer produces goods under the client’s brand. | Retail, beauty products | Pros: Branding control, reduced overhead. Cons: Quality control relies on the manufacturer. |
| Joint Venture Manufacturing | Collaborative arrangement for product development and production. | Automotive, electronics | Pros: Shared resources, innovation potential. Cons: Complexity in management and decision-making. |
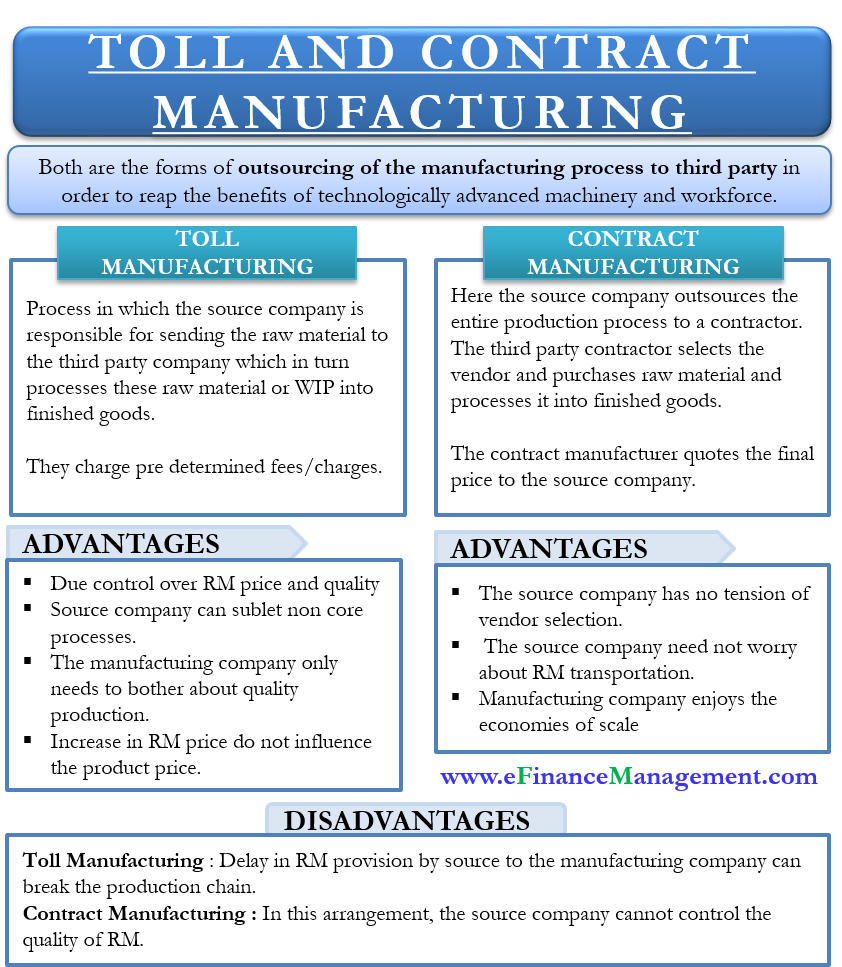
What are the Characteristics of Toll Manufacturing?
Toll manufacturing is characterized by a partnership where the client provides the raw materials, and the toll manufacturer focuses on production. This model is particularly beneficial for businesses that have access to quality raw materials but lack the necessary infrastructure for manufacturing. Industries such as food production and chemicals often leverage this model for its cost-effectiveness and control over material inputs. Buyers should consider their logistics capabilities, as they will be responsible for transporting raw materials to the toll manufacturer.
How Does Contract Manufacturing Differ from Toll Manufacturing?
In contract manufacturing, the third-party manufacturer manages the entire production cycle, including sourcing raw materials. This model is ideal for companies looking for a turnkey solution where they can focus on their core business operations without the complexities of raw material procurement. Common applications include pharmaceuticals and consumer goods. Buyers should evaluate the reliability and quality control measures of potential contract manufacturers, as they will have less oversight over the inputs.
What is Toll Processing and Its Applications?
Toll processing involves specialized processing services where the manufacturer handles specific tasks without taking full responsibility for manufacturing. This arrangement is advantageous for companies dealing with sensitive materials, such as specialty chemicals or cosmetics, as it allows them to utilize expert knowledge without heavy capital investments. Buyers must ensure that the toll processor has the necessary certifications and expertise to handle their specific materials safely.
Why Choose Private Label Manufacturing?
Private label manufacturing allows businesses to produce goods under their own brand name while outsourcing the manufacturing process. This model is prevalent in retail and beauty products, as it provides branding control and minimizes overhead costs. However, buyers must ensure that the manufacturer adheres to quality standards, as the final product reflects their brand reputation. Careful vetting of manufacturers is crucial to maintaining product quality.
What are the Benefits and Challenges of Joint Venture Manufacturing?
Joint venture manufacturing involves a collaborative effort between two or more companies to develop and produce products. This model can be particularly advantageous in industries like automotive and electronics, where shared resources can lead to innovation and cost savings. However, the complexity of managing a joint venture can pose challenges, especially in decision-making and aligning business objectives. Buyers should weigh the potential for innovation against the risks associated with shared management.
Key Industrial Applications of toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Toll manufacturing for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Enhanced control over raw materials and formulations | Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and IP protection |
| Food and Beverage | Contract manufacturing for ready-to-eat meals | Streamlined production and access to specialized facilities | Supplier reliability, food safety certifications |
| Electronics | Toll manufacturing for specialized electronic components | Cost savings and control over component quality | Supplier capabilities, logistics coordination |
| Chemicals | Contract manufacturing for specialty chemicals | Full-service production with raw material procurement | Supplier expertise, scalability, and environmental regulations |
| Cosmetics | Toll manufacturing for custom formulations | Tailored products without heavy capital investment | Ingredient sourcing, formulation expertise, and IP confidentiality |
How Is Toll Manufacturing Used in Pharmaceuticals and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the pharmaceutical sector, toll manufacturing is often utilized for producing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This arrangement allows companies to maintain control over raw materials and formulations, which is crucial for meeting stringent regulatory standards. By outsourcing the manufacturing process, businesses can reduce capital investments while leveraging the toll manufacturer’s expertise in handling complex substances. For international buyers, particularly those in Africa and South America, understanding the regulatory landscape and ensuring compliance with local laws is essential for successful partnerships.
What Are the Benefits of Contract Manufacturing in the Food and Beverage Industry?
Contract manufacturing in the food and beverage industry often involves producing ready-to-eat meals, allowing companies to focus on marketing and distribution while relying on specialized manufacturers for production. This model streamlines operations, reduces lead times, and provides access to advanced food processing technologies. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, supplier reliability and adherence to food safety certifications are critical factors to consider, as they directly impact product quality and consumer trust.
How Is Toll Manufacturing Applied in Electronics and What Advantages Does It Offer?
In the electronics sector, toll manufacturing is employed for specialized components, where companies supply raw materials to manufacturers who process them into finished products. This arrangement provides significant cost savings while allowing businesses to maintain quality control over their components. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, understanding the logistics and coordination of raw material delivery with production schedules is vital to ensure timely product availability and minimize disruptions.
What Role Does Contract Manufacturing Play in the Chemicals Industry?
Contract manufacturing in the chemicals industry often involves specialty chemicals where the contractor manages the entire production process, including raw material procurement. This model offers businesses a full-service solution, enabling them to scale operations without the burden of managing complex supply chains. For buyers in South America and Europe, evaluating the supplier’s expertise and compliance with environmental regulations is crucial for maintaining sustainability and product integrity throughout the manufacturing process.
How Does Toll Manufacturing Benefit the Cosmetics Sector?
Toll manufacturing is particularly beneficial in the cosmetics industry for creating custom formulations tailored to specific market demands. Companies can provide their proprietary ingredients while leveraging the toll manufacturer’s capabilities without heavy capital investments in production facilities. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, ensuring ingredient sourcing aligns with local regulations and maintaining IP confidentiality are key considerations to protect brand integrity and foster trust in the marketplace.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Raw Material Control Challenges
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the chemical industry faces difficulties when deciding between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing due to concerns over raw material control. The buyer has access to high-quality raw materials but fears that a contract manufacturer may not uphold the same standards, leading to inconsistent product quality. This challenge is exacerbated by the complex supply chain dynamics, which can result in elevated costs and potential production delays.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, the buyer should consider toll manufacturing, where they retain control over raw material sourcing. This approach allows them to select only the highest-quality inputs, ensuring consistent product quality. To effectively implement this, the buyer should conduct thorough due diligence on potential toll manufacturers. This includes evaluating their processing capabilities, quality control measures, and experience in handling similar materials. Establishing a comprehensive toll manufacturing agreement is crucial; this should outline specifications, quality standards, and penalties for non-compliance. Regular audits and communication with the toll manufacturer can further enhance oversight, ensuring that the final products meet the buyer’s stringent quality expectations.
Scenario 2: Managing Logistics and Supply Chain Synchronization
The Problem: An electronics manufacturer in Europe is struggling with the logistics of toll manufacturing, where they provide the raw materials to a third-party manufacturer. The complexities of coordinating the timely delivery of these materials with the production schedule of the toll manufacturer have led to production delays and increased transportation costs. The manufacturer finds themselves in a bind, as any hiccup in this chain can lead to missed deadlines and lost revenue.
The Solution: To streamline logistics, the manufacturer should invest in advanced supply chain management software that facilitates real-time tracking of raw material shipments and production schedules. Additionally, establishing a strong partnership with the toll manufacturer is essential; regular communication regarding production timelines and material availability can help mitigate delays. The manufacturer should also consider implementing a just-in-time inventory strategy, which reduces excess inventory while ensuring that materials are available precisely when needed. By enhancing collaboration and utilizing technology, the manufacturer can effectively synchronize their logistics, minimizing downtime and optimizing production efficiency.
Scenario 3: Weighing Cost-Effectiveness vs. Quality Assurance
The Problem: A food processing company in South America is evaluating the cost implications of toll manufacturing versus contract manufacturing. While toll manufacturing offers lower upfront costs, the buyer is concerned about the long-term implications on product quality and the potential need for rigorous quality control measures. The fear is that cutting costs could compromise their brand reputation, especially in a market that values quality.
The Solution: To address these concerns, the buyer should perform a thorough cost-benefit analysis that includes not just immediate financial implications but also long-term quality considerations. It may be beneficial to pilot a small batch production using toll manufacturing to assess the quality of the final product before committing to larger orders. During this trial phase, the buyer should establish strict quality benchmarks and closely monitor outcomes. Additionally, building a robust quality assurance framework, including regular inspections and third-party audits, can help ensure that the products consistently meet the expected standards. By taking a strategic approach to evaluate both cost-effectiveness and quality, the buyer can make an informed decision that supports their brand integrity while optimizing production costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
What Are the Key Materials for Toll Manufacturing vs. Contract Manufacturing?
When considering toll manufacturing versus contract manufacturing, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in determining the overall efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and quality of the final products. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in these manufacturing processes, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Metals Perform in Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Metals such as aluminum, steel, and titanium are known for their high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent durability, and resistance to wear and tear. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons: Metals offer exceptional durability and can be recycled, which is a significant advantage in sustainability-focused markets. However, they can be costly to source and process, particularly high-performance alloys. Additionally, the complexity of metal fabrication can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Metals are often used in automotive, aerospace, and construction applications where structural integrity is paramount. The material’s compatibility with specific media, such as corrosive environments, must be assessed to ensure longevity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM for metals. Understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is also essential.
What Role Do Polymers Play in Manufacturing Processes?
Key Properties: Polymers like polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be engineered for specific applications, including flexibility and temperature resistance.
Pros & Cons: Polymers are generally more cost-effective than metals and offer greater design flexibility. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals, which can limit their applications in certain industries.
Impact on Application: Polymers are widely used in packaging, consumer goods, and automotive components. Their compatibility with various chemicals and environments is crucial for product performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional regulations regarding plastic use and recycling, particularly in Europe, where stringent environmental laws are in place. Familiarity with standards like DIN for polymers can aid in compliance.
How Do Ceramics Compare in Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Ceramics are known for their hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion. They can operate effectively at high temperatures and are often used in specialized applications.
Pros & Cons: Ceramics provide excellent wear resistance and thermal insulation, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. However, they can be brittle and prone to cracking under stress, which limits their use in some scenarios.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are commonly used in electronics, aerospace, and biomedical applications. Their compatibility with extreme environments must be evaluated to ensure they meet performance requirements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sourcing of raw materials for ceramics, as they may vary significantly by region. Compliance with international standards, such as JIS for ceramics, is essential for quality assurance.
What Are the Benefits of Composites in Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, combine the properties of different materials to achieve superior strength, lightweight characteristics, and resistance to environmental factors.
Pros & Cons: Composites offer high performance and customization options, making them suitable for specialized applications. However, they can be expensive to produce and may require advanced manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be informed about the specific certifications required for composite materials in their respective markets. Understanding compliance with standards like ASTM for composites can help in making informed sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Considerations
| Material | Typical Use Case for Toll Manufacturing vs Contract Manufacturing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Automotive parts, aerospace components | High durability | High sourcing costs | High |
| Polymers | Packaging, consumer goods | Cost-effective and flexible | Limited temperature resistance | Medium |
| Ceramics | Electronics, aerospace applications | Excellent thermal stability | Brittle and prone to cracking | High |
| Composites | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive production | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions when choosing between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing, ensuring that they select the most suitable materials for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
The manufacturing processes for toll and contract manufacturing share several similarities but also have key distinctions that impact how products are developed and produced.
1. Material Preparation
In both models, the initial stage involves preparing raw materials. In contract manufacturing, the contractor typically sources and prepares the materials, benefiting from established supply chains and vendor relationships. Conversely, in toll manufacturing, the client provides the raw materials. This direct control allows the client to choose suppliers that align with their quality and cost expectations.
2. Forming
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into intermediate or finished products. This can include processes such as molding, casting, or machining. In contract manufacturing, the contractor employs advanced machinery and skilled labor to optimize production efficiency and quality. Toll manufacturers, on the other hand, focus on processing the client-supplied materials using their specialized equipment, which may be tailored to specific applications, enhancing the potential for customized outputs.
3. Assembly
Assembly is crucial, particularly for complex products. In contract manufacturing, the contractor handles assembly, which can include integrating various components and systems. This approach allows for streamlined processes and reduced lead times. In toll manufacturing, the assembly process may be limited to the components supplied by the client, potentially allowing for more rigorous control over critical aspects of the product.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes, such as painting, coating, or packaging, are essential for product presentation and functionality. Contract manufacturers often have the capability to provide a full range of finishing services, ensuring consistency and quality across all products. Toll manufacturers may also offer finishing services, but the final responsibility for quality assurance lies with the client, who must ensure that the finishing meets their specifications.
What Are the Quality Control Standards for Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of both toll and contract manufacturing. However, the approach to quality control (QC) can differ significantly based on the responsibilities of each party involved.
International Standards and Industry-Specific Regulations
Both contract and toll manufacturing must adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. For specific industries, additional certifications may be necessary. For instance, pharmaceutical manufacturers may require Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) compliance, while electronics manufacturers may need to adhere to CE marking requirements in Europe.
Key QC Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the initial checkpoint where raw materials are inspected before production begins. In toll manufacturing, clients must ensure that their supplied materials meet their quality standards, whereas, in contract manufacturing, the contractor typically handles this.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, continuous monitoring is essential. Both manufacturing types should implement IPQC to catch potential issues early. Contract manufacturers often have robust processes in place due to their experience and established protocols.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before products are shipped. In contract manufacturing, the contractor is responsible for ensuring that finished products meet the agreed specifications. In toll manufacturing, the client must verify that the processing aligns with their standards, which can involve additional testing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Manufacturing Quality Control?
Testing methods are critical in ensuring product quality in both contract and toll manufacturing settings.
-
Material Testing: This includes physical, chemical, and mechanical testing of raw materials. Techniques such as spectrometry or chromatography may be employed to verify material compositions.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and gauges to ensure that products meet specified dimensions is a common practice in both manufacturing types.
-
Functional Testing: This assesses whether the final product performs as intended. For instance, electronics may undergo electrical testing to ensure proper functionality.
-
Stress Testing: This method evaluates how products perform under extreme conditions, providing insights into durability and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their manufacturing partners, regardless of whether they choose toll or contract manufacturing.
Audits and Inspections
Conducting thorough audits of potential suppliers is essential. Buyers should evaluate the manufacturer’s facilities, equipment, and quality control processes. This can include reviewing certifications, inspection reports, and previous audit outcomes.
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Manufacturers should provide documentation that outlines their quality assurance processes. This includes details on testing methods, results from past quality checks, and compliance with relevant standards. Buyers should look for consistency and transparency in these reports.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality control processes. These services can conduct random inspections at various stages of production, ensuring that products meet the required standards before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial.
Regional Compliance Requirements
Different regions may have specific regulations governing product quality and safety. Buyers must ensure that their manufacturing partners comply with local laws and international standards to avoid regulatory issues. For example, products entering the European market must often meet CE marking requirements.
Cultural and Communication Barriers
Cultural differences can impact how quality control processes are perceived and executed. B2B buyers should foster open communication with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding of quality expectations.
Supply Chain Transparency
Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chain management. This includes clear documentation of sourcing practices, production processes, and any third-party certifications that may be relevant to their industry.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in both toll and contract manufacturing, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing’
Introduction
Navigating the decision between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing can significantly impact your business operations and profitability. This step-by-step checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through the essential considerations and actions needed to make an informed choice that aligns with your production goals, cost management, and quality control requirements.
1. Identify Your Production Needs
Start by clearly defining what you need from the manufacturing process. Consider the volume of production, specific technical requirements, and timelines.
– Assess your capacity: Determine whether your current capabilities are sufficient or if outsourcing is necessary.
– Establish product specifications: Outline the materials, processes, and quality standards required for your products.
2. Evaluate Control Preferences Over Raw Materials
Decide how much control you want over the raw materials. This will help you determine whether toll or contract manufacturing aligns better with your strategy.
– Toll manufacturing: You maintain raw material control, which can be beneficial if you have proprietary materials or specific sourcing relationships.
– Contract manufacturing: If you prefer to simplify logistics and leverage the contractor’s supply chain, this option might be more suitable.
3. Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research on potential toll or contract manufacturers. Look for companies that specialize in your industry to ensure they have the necessary expertise and equipment.
– Check their track record: Investigate their history, client testimonials, and case studies to gauge their reliability and quality.
– Visit facilities: If possible, visit manufacturing sites to assess capabilities and compliance with industry standards.
4. Assess Cost Structures and Pricing Models
Analyze the cost implications of both manufacturing options. Understanding the pricing structure is crucial for budgeting and financial planning.
– Toll fees vs. contract rates: Compare the flat fees of toll manufacturing against the potentially higher costs of contract manufacturing, which includes raw material procurement.
– Long-term financial impact: Consider not just upfront costs but also the ongoing expenses related to quality control, logistics, and potential price fluctuations of raw materials.
5. Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers meet relevant industry standards and certifications. This is vital for maintaining product quality and regulatory compliance.
– Request documentation: Ask for certifications like ISO, GMP, or any industry-specific approvals that validate their manufacturing processes.
– Evaluate their quality control measures: Understand their quality assurance protocols to ensure they align with your standards.
6. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected potential manufacturers, it’s time to negotiate the terms of your agreement. Clear contracts can prevent misunderstandings and protect your interests.
– Outline responsibilities: Specify who is responsible for raw materials, quality assurance, and logistics.
– Include confidentiality clauses: If you’re sharing proprietary information, ensure there are adequate protections in place.
7. Establish Communication Protocols
Effective communication is key to a successful manufacturing partnership. Set up clear channels and protocols for ongoing dialogue.
– Regular updates: Schedule consistent check-ins to discuss production progress, address issues, and make adjustments as necessary.
– Feedback mechanisms: Create a system for providing and receiving feedback to enhance collaboration and continuous improvement.
By following this checklist, you can make a well-informed decision between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing, ensuring that your chosen approach aligns with your business strategy and operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Toll Manufacturing vs Contract Manufacturing?
When evaluating toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing, understanding the cost components is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: In toll manufacturing, the buyer supplies raw materials, which can lead to cost savings if the buyer has better access or lower costs than the manufacturer. In contrast, contract manufacturing includes the cost of materials in the overall price, which can vary significantly based on the contractor’s procurement strategies and supplier relationships.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs in toll manufacturing are typically lower as toll manufacturers often specialize in specific processes, leading to greater efficiency. However, buyers must ensure that the toll manufacturer has adequate skilled labor to meet quality standards. Contract manufacturing generally involves higher labor and overhead costs due to the contractor managing the entire production process and associated facilities.
Tooling and QC: Tooling costs can be a significant factor, especially in contract manufacturing where the contractor invests in specialized equipment. Conversely, in toll manufacturing, buyers may incur initial tooling costs but can negotiate these based on volume. Quality control is essential in both models, but buyers should consider that toll manufacturing places more responsibility on them to ensure material quality, while contract manufacturers often have established QC processes.
Logistics: Logistics costs can be more complex in toll manufacturing since the buyer must manage the transportation of raw materials to the toll manufacturer. This adds an extra layer of coordination and potential costs. In contrast, contract manufacturing typically includes logistics in the final pricing, simplifying the process for the buyer.
Margin: Profit margins can vary between the two models. Toll manufacturers often operate on lower margins due to their focus on processing and efficiency, while contract manufacturers might have higher margins to cover the comprehensive services they provide.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Toll Manufacturing and Contract Manufacturing Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in both toll and contract manufacturing, including volume or minimum order quantities (MOQ), specifications and customization, material quality and certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
Volume/MOQ: Higher volumes generally lead to reduced per-unit costs in both manufacturing types. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to ensure they can achieve favorable pricing while meeting their production needs.
Specifications and Customization: Customized products can incur additional costs, particularly in contract manufacturing, where the contractor may need to invest in new tooling or processes. In toll manufacturing, buyers have more control over specifications, potentially leading to cost efficiencies if they can provide the necessary materials.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can significantly impact costs. In contract manufacturing, the contractor’s sourcing strategy can lead to variations in material costs. Buyers should ensure that they specify their quality requirements clearly, regardless of the manufacturing model.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and capabilities of the manufacturer can influence pricing. Established contract manufacturers may charge a premium for their experience and reliability, while toll manufacturers may offer competitive pricing to attract business.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics, impacting overall costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk and maximize cost efficiency.
What Buyer Tips Should Be Considered for Cost-Efficiency in Manufacturing?
To maximize cost-efficiency, international B2B buyers should consider several strategies. First, conduct a thorough Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis that includes all relevant costs, not just the initial price. This analysis should encompass logistics, QC, and any potential hidden costs related to delays or quality issues.
Second, leverage negotiation techniques to achieve better pricing. Understanding the cost structure of both toll and contract manufacturing can empower buyers to negotiate more effectively.
Lastly, keep in mind the pricing nuances specific to regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and regional regulations can all impact pricing and should be factored into any pricing discussions.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary widely based on specific circumstances, including but not limited to production scale, material costs, and supplier negotiations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own research and obtain quotes tailored to their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Toll Manufacturing and Contract Manufacturing
In today’s competitive market, businesses are often faced with critical decisions regarding their manufacturing strategies. While toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing are popular choices, various alternative solutions can also meet production needs. This section examines these alternatives, providing a comparative analysis to guide B2B buyers in selecting the most suitable approach for their operations.
| Comparison Aspect | Toll Manufacturing Vs Contract Manufacturing | In-House Manufacturing | Joint Ventures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High quality control; dependent on supplier capabilities | Full control over quality and production processes | Shared expertise can enhance product quality |
| Cost | Generally lower due to flat-rate fees; no investment in infrastructure | High initial investment in equipment and facilities | Shared costs but potential for complex financial arrangements |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires coordination of raw materials and schedules | High; requires significant planning and resources | Moderate; involves negotiation and partnership setup |
| Maintenance | Low; maintenance handled by the toll manufacturer | High; ongoing maintenance of equipment and facilities | Moderate; shared responsibilities can ease burden |
| Best Use Case | When raw material control is essential, and production expertise is needed | When complete control over the production process is desired | When entering new markets or sharing risks is beneficial |
What Are the Pros and Cons of In-House Manufacturing?
In-house manufacturing offers complete control over production processes, allowing companies to maintain strict quality standards and oversee every aspect of manufacturing. This option is beneficial for businesses with specialized products or proprietary processes that require confidentiality. However, it often involves significant upfront capital investment in machinery and facilities, which can strain resources, particularly for smaller companies. Additionally, in-house operations require a skilled workforce and ongoing maintenance, which can further complicate logistics and management.
How Does a Joint Venture Work as an Alternative?
A joint venture involves two or more companies collaborating to achieve a common goal, often pooling resources to share risks and benefits. This approach can be advantageous for companies looking to enter new markets or leverage complementary expertise without bearing all the costs alone. Joint ventures can enhance innovation and efficiency, as partners contribute their strengths. However, they can also introduce complexity in management and decision-making, and potential disagreements may arise between partners, impacting operations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Manufacturing Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing strategy is crucial for optimizing production and maintaining competitive advantage. B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including the level of control required, cost constraints, and the complexity of implementation. While toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing provide distinct benefits, alternatives like in-house manufacturing and joint ventures may better align with certain business objectives. By carefully evaluating these options, companies can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and drive growth in their respective markets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Toll Manufacturing and Contract Manufacturing?
When deciding between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the quality and specifications of the raw materials used in manufacturing. Different grades can impact the final product’s performance and compliance with industry standards.
– B2B Importance: Ensuring the correct material grade is essential for product durability and reliability, particularly in industries like automotive and electronics. Buyers must communicate their requirements clearly to avoid costly mistakes. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or property in the manufacturing process. It is a measure of precision in production.
– B2B Importance: In sectors such as aerospace or medical devices, tight tolerances are critical for safety and functionality. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers assess whether a manufacturer can meet their specifications. -
Batch Size
– Definition: Batch size refers to the quantity of product produced in a single manufacturing run. This can vary significantly between toll and contract manufacturing.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the optimal batch size helps buyers manage inventory and costs. Smaller batch sizes may be more suitable for custom products, while larger batches can reduce per-unit costs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the total time from the initiation of a manufacturing order to the delivery of the finished product. This includes production time and any necessary logistics.
– B2B Importance: For businesses operating in fast-paced markets, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and maintaining supply chain efficiency. Buyers should inquire about lead times during negotiations to ensure timely delivery. -
Quality Control Standards
– Definition: Quality control standards are the protocols and procedures established to ensure that products meet specific quality criteria throughout the manufacturing process.
– B2B Importance: High-quality standards are non-negotiable in many industries. Buyers should verify the quality control measures in place to mitigate risks associated with defects or non-compliance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate more effective communication and negotiations. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are sold under another company’s brand name.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers evaluate their options for both toll and contract manufacturing, particularly in terms of branding and product customization. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a manufacturer is willing to produce.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. It can influence a buyer’s decision on whether to engage in toll or contract manufacturing based on their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs can streamline the sourcing process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms effectively between different manufacturers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global transactions, particularly regarding shipping and logistics.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international B2B transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, helping to prevent disputes. -
Toll Fee
– Definition: The toll fee is the charge paid by a company to a toll manufacturer for processing raw materials.
– Importance: Understanding toll fees helps buyers calculate the total cost of outsourcing manufacturing and assess the financial viability of toll manufacturing versus contract manufacturing options.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when navigating the complexities of toll and contract manufacturing.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Impacting Toll Manufacturing and Contract Manufacturing?
The global manufacturing landscape is undergoing significant transformations influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, economic shifts, and evolving consumer demands. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
One notable trend is the increased adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, which enhance operational efficiency and provide real-time data analytics. This trend is particularly beneficial for contract manufacturing, where managing supply chains and quality control processes can become complex. In contrast, toll manufacturing allows companies to retain control over raw materials, which is increasingly important as businesses seek to mitigate supply chain disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions and pandemics.
Another key driver is the growing demand for customization and short production runs. Buyers are increasingly looking for manufacturers who can adapt quickly to changing market needs, making toll manufacturing an attractive option. Companies can leverage toll manufacturers’ specialized capabilities while maintaining control over the quality and sourcing of raw materials. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a significant consideration, with many buyers seeking partners who prioritize environmentally friendly practices.
The market is also seeing a rise in strategic partnerships, as companies look to leverage the strengths of both contract and toll manufacturers. These collaborations enable firms to optimize their production capabilities while managing risks associated with sourcing and logistics.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Future of Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have emerged as critical factors in the decision-making process for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing practices is under scrutiny, and companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain’s ecological footprint. This shift is pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices, whether through energy-efficient processes, waste reduction initiatives, or sustainable sourcing of raw materials.
For toll manufacturing, buyers can take advantage of their control over raw materials to select eco-friendly inputs, thus promoting sustainability in their final products. Additionally, many toll manufacturers are now pursuing certifications for sustainable practices, making it easier for companies to align their production methods with their environmental goals.
On the other hand, contract manufacturers are responding to this demand by implementing sustainable practices across their operations. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, waste recycling programs, and sustainable packaging solutions. Buyers should look for manufacturers with recognized ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 or LEED, to ensure their partners are committed to sustainability.
Ultimately, companies that prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainability in their manufacturing processes are likely to gain a competitive edge. This alignment with consumer values can enhance brand loyalty and open new market opportunities, particularly in regions like Europe, where eco-consciousness is particularly strong.
What Is the Historical Context of Toll and Contract Manufacturing?
The concepts of toll and contract manufacturing have evolved significantly over the last few decades. Initially, contract manufacturing emerged as a response to the growing need for companies to outsource production to reduce costs and focus on core competencies. This model allowed businesses to benefit from the expertise and capabilities of specialized manufacturers without heavy capital investments.
Toll manufacturing, on the other hand, gained traction as companies recognized the need for more control over their raw materials while still leveraging external manufacturing capabilities. This model became particularly popular in industries where proprietary materials or formulations were essential, such as pharmaceuticals and food production.
As globalization expanded, both manufacturing models adapted to meet the demands of international markets. Today, they are integral to supply chains across various sectors, providing businesses with the flexibility and efficiency needed to thrive in a rapidly changing economic landscape. Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers as they navigate their manufacturing options and seek partnerships that align with their strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
-
How do I determine whether to choose toll manufacturing or contract manufacturing for my business?
Choosing between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing depends on your specific needs and capabilities. If you have reliable access to quality raw materials and want to maintain control over them, toll manufacturing might be the better option. Conversely, if you’re looking for a streamlined process where the manufacturer handles everything from sourcing to production, contract manufacturing could be more suitable. Evaluate your logistics, production scale, and the level of control you wish to retain to make the best decision. -
What are the key differences between toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing?
The primary difference lies in raw material management. In toll manufacturing, you provide the raw materials and pay a fee for processing, allowing you to control quality and costs. In contrast, contract manufacturing includes the entire production cycle, where the manufacturer sources materials and handles production. This can simplify the process but may reduce your control over input quality and pricing. Understanding these distinctions helps align your choice with your business strategy and operational needs. -
What are the typical payment terms for toll manufacturing agreements?
Payment terms in toll manufacturing agreements can vary but typically include upfront fees for production services and may incorporate a per-unit toll fee based on the volume processed. It’s common to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs, such as partial payments before production and final payments upon completion. Ensure that these terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid disputes and facilitate smooth transactions. -
What should I consider when vetting a toll manufacturer or contract manufacturer?
When vetting potential manufacturers, assess their industry experience, facility certifications, and production capabilities. Review their quality assurance processes and any previous client testimonials to gauge reliability. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, especially if you are importing materials from different regions. Establishing clear communication regarding your quality standards and expectations is also crucial for a successful partnership. -
How does customization work in toll manufacturing versus contract manufacturing?
Customization in toll manufacturing allows you to dictate the specifications of your raw materials and production processes, giving you greater control over the final product. This flexibility is beneficial for unique formulations or proprietary products. In contract manufacturing, while customization is possible, it may be more limited as the manufacturer has established processes and supply chains. Discuss your customization needs upfront to ensure the chosen model can accommodate your requirements. -
What are the logistics considerations when using toll manufacturing?
Logistics play a critical role in toll manufacturing since you are responsible for supplying raw materials to the manufacturer. This requires careful planning to synchronize material deliveries with production schedules to avoid delays. Consider the transportation costs, timeframes, and any potential customs issues if importing materials. Establishing a strong logistics plan can mitigate risks and ensure that production runs smoothly and efficiently. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) typically associated with toll and contract manufacturing?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between toll and contract manufacturing. Toll manufacturers may offer more flexibility in MOQs since you control the raw materials, which can accommodate smaller batch sizes. However, contract manufacturers often have set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness and efficient production. Discuss your volume needs with potential partners to find a suitable arrangement that aligns with your production goals. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in both toll and contract manufacturing?
Quality assurance is crucial in both manufacturing models. In toll manufacturing, you retain control over raw materials, allowing you to establish quality standards for inputs. Implement regular inspections and testing protocols to monitor production quality. In contract manufacturing, ensure that the manufacturer has robust quality control processes in place, including certifications and compliance with industry standards. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and conduct regular audits to maintain standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Toll Manufacturing Vs Contract Manufacturing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toll Manufacturing – Key Functions and Risks
Domain: transferpricingweb.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Toll manufacturing: Functions – Manufacturing only; Risks – Limited volume and restructuring risks; Intangibles – Limited process know-how; Inventory – No title to inventory; Transaction structure – Rendering of a production service; Typical remuneration – A cost based remuneration, excluding the value of the raw materials. Contract manufacturing: Functions – Procurement and manufacturing; Risks -…
2. Sierra Coating – Toll and Contract Manufacturing Services
Domain: sierracoating.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Sierra Coating offers toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing services, providing customers with valuable ways to save time and capital on product line development. Toll manufacturing allows customers to supply raw materials or semi-finished goods to Sierra Coating, which then processes them using its facilities and equipment, eliminating the need for customers to invest in manufacturing ope…
3. Toll Manufacturing – Contract Processing Services
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Toll manufacturing, also known as toll processing, is a type of contract manufacturing where the customer provides raw materials, formulas, and specifications to the manufacturer, who processes them into finished or semi-finished products. The manufacturer charges a fee for the service but does not own the materials or products. The customer retains full ownership and control over intellectual pro…
4. Synerlogic Chemicals – Contract & Toll Manufacturing Services
Domain: synerlogic-chemicals.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Synerlogic Chemicals offers contract manufacturing and toll manufacturing services in the chemical industry. Contract manufacturing involves an external manufacturer producing products according to client specifications, managing the entire production process including sourcing raw materials, production, packaging, and delivery. Key benefits include flexibility in production capacity, economies of…
5. Elchemy – Contract Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: elchemy.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Contract manufacturing involves outsourcing the entire production process to a third-party manufacturer who sources raw materials, handles production, and packages the final product under the client’s brand name. It is popular in industries like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food and beverage, and consumer goods. Toll manufacturing, on the other hand, is a limited form of outsourcing where the hirin…
6. M&M Automatic Products – Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: mmautomatic.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: M&M Automatic Products offers three types of manufacturing entities: Toll Manufacturer, Contract Manufacturer, and Full-Fledged Manufacturer. Toll Manufacturers provide the plant, machinery, and labor while the client supplies all materials and assumes selling risks. Contract Manufacturers own the plant and machinery, provide labor, and source materials, with the client assuming selling risks. Ful…
7. Worthen Industries – Custom Adhesives & Coatings
Domain: worthenind.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Toll manufacturing, adhesives and coatings, coated products, extruded products, custom adhesives & coatings, film extrusion, web coating, adhesive coated products, co-polyester products, laminating adhesives & coatings, foam fabricating adhesives, footwear products, paper converting adhesives, performance coated fabrics, performance coatings & adhesives, printable fabric solutions, specialty adhes…
8. Capital Resin – Specialty Chemicals & Custom Manufacturing
Domain: capitalresin.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Products offered by Capital Resin include: Acetoguanamine, Alkylated Phenols, Amino Resin, Aromatic Sulfonic Acids, Formaldehyde, Phenolic and Resorcinol Resins, Polyurethanes & Polyurethane Dispersions. Services include Custom Chemical Contract Manufacturing, Chemical Blending, Bulk Storage, Shipping, Packaging, and Labeling, Packaged Materials Storage, Contract Research & Development, Chemical A…
9. Custom Processing Services – Toll Processing Solutions
Domain: customprocessingservices.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Toll processing is a segment of contract manufacturing that involves partnering with a third-party manufacturer to process or manufacture a product, component, or ingredient. It provides access to advanced equipment, increased capacity, expertise, and technical skills without major capital investments. Toll processing typically does not include turnkey manufacturing or procurement of raw materials…
10. AJAW – Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: ajawmrp.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: This company, AJAW – Manufacturing Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for toll manufacturing vs contract manufacturing
In navigating the complexities of toll manufacturing and contract manufacturing, businesses must weigh their specific needs against the advantages each model offers. Toll manufacturing provides greater control over raw materials, often resulting in cost savings and tailored production processes, making it an attractive option for companies with unique material requirements or proprietary technologies. Conversely, contract manufacturing streamlines operations by outsourcing both production and material sourcing, simplifying logistics and accelerating time to market.
Strategic sourcing is vital in this decision-making process, as it enables companies to align their manufacturing approach with their operational goals, market demands, and financial constraints. By understanding the nuances of each manufacturing model, international B2B buyers can make informed choices that enhance their competitive edge.
Looking ahead, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage these insights to optimize their sourcing strategies. As global supply chains continue to evolve, the ability to adapt and select the right manufacturing partner will be crucial for sustained growth and innovation. Embrace these opportunities to refine your manufacturing processes and drive your business forward in an increasingly interconnected marketplace.