How to Source Scrap Railway Track For Sale Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for scrap railway track for sale
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global trade, sourcing scrap railway track for sale poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexities of navigating various suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and ensuring compliance with local regulations can create hurdles that hinder efficient procurement. This comprehensive guide aims to streamline the process by exploring the diverse types of scrap railway tracks available, their applications across industries, and essential supplier vetting strategies.
By delving into the nuances of the scrap railway market, this resource equips buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Vietnam and Germany—with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. The guide will cover crucial aspects such as cost considerations, quality standards, and logistics management, empowering buyers to optimize their supply chains and maximize value.
Whether you are looking to repurpose scrap railway materials for construction projects, infrastructure development, or industrial applications, understanding the global market dynamics is essential. This guide serves as a roadmap, ensuring that you can confidently navigate the intricacies of sourcing scrap railway track, ultimately driving efficiency and success in your business endeavors.
Understanding scrap railway track for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used Steel Rails | Typically sourced from decommissioned rail lines; available in various lengths (e.g., 1.5m) | Industrial transport, temporary tracks, mining | Pros: Cost-effective, readily available. Cons: May require refurbishment or inspection. |
| Heavy Rail | Designed for high load-bearing capacity; usually heavier than 50 kg/m | Mainline railroads, freight transport | Pros: Durable and robust. Cons: Higher upfront costs. |
| Light Rail | Lighter and more flexible; suitable for lower traffic areas | Urban transport, construction sites | Pros: Lower cost, easier to handle. Cons: Not suitable for heavy loads. |
| Crane Rail | Specific design for crane operations; features a larger head width | Ports, warehouses, and heavy machinery areas | Pros: Optimized for crane movement. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Other Track Materials (OTM) | Includes rail fastenings, ties, and other components | Supporting infrastructure for rail systems | Pros: Essential for track stability. Cons: Requires careful selection based on project needs. |
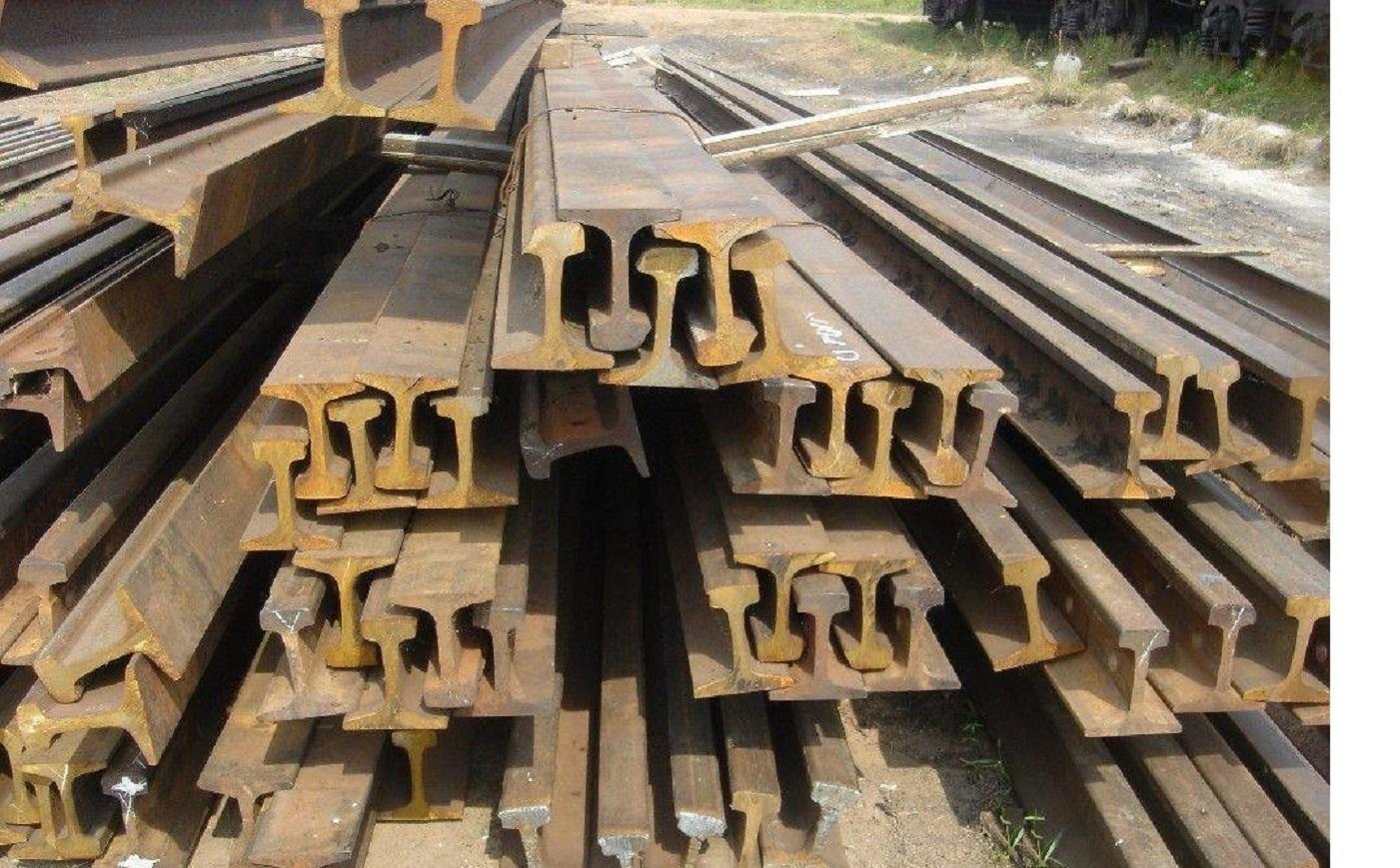
What Are the Characteristics of Used Steel Rails?
Used steel rails are often sourced from decommissioned rail lines, making them an economical choice for businesses looking to repurpose materials. Typically available in lengths such as 1.5 meters, they can be used for industrial transport or temporary tracks in construction and mining applications. Buyers should consider the condition of the rails, as refurbishment or inspection may be necessary to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
How Do Heavy Rails Support Mainline Railroads?
Heavy rails are engineered to support high loads, making them ideal for mainline railroads and freight transport. With weights often exceeding 50 kg/m, these rails offer exceptional durability and resistance to wear. While the initial investment is higher compared to lighter alternatives, their long lifespan and reduced maintenance needs can lead to cost savings over time. B2B buyers should assess their specific load requirements and operational conditions when considering heavy rail options.
What Applications Benefit from Light Rails?
Light rails are characterized by their lower weight and flexibility, making them suitable for urban transport systems and construction sites where heavy loads are not a concern. They are more cost-effective and easier to handle compared to heavy rails, which can be advantageous for projects with budget constraints. However, buyers must recognize that light rails are not designed for high-traffic or heavy-load applications, so careful consideration of operational needs is essential.
Why Choose Crane Rails for Heavy Machinery Operations?
Crane rails are specifically designed for environments where cranes operate, featuring a larger head width to facilitate smooth movement. Commonly used in ports and warehouses, these rails provide a stable and efficient runway for heavy machinery. Although they are optimized for specific applications, buyers should evaluate their operational requirements to ensure compatibility and maximize efficiency.
How Do Other Track Materials (OTM) Enhance Railway Infrastructure?
Other track materials (OTM) encompass essential components such as rail fastenings, ties, and other infrastructure elements that support the stability of railway systems. These materials are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and safety of the railways. When purchasing OTM, buyers should consider the specific needs of their projects, including the type of rail and environmental conditions, to select the most suitable components for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of scrap railway track for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of scrap railway track for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Foundation and Structural Support | Provides strong, durable materials for building foundations, reducing costs compared to new steel. | Ensure compliance with local building codes; verify material grades for load-bearing capacity. |
| Mining | Haulage and Transportation Tracks | Enables efficient movement of heavy equipment and materials within mining sites, enhancing operational efficiency. | Assess rail durability and compatibility with existing infrastructure; consider logistics for remote locations. |
| Manufacturing | Crane Runways and Heavy Equipment Tracks | Facilitates the movement of heavy machinery, improving productivity and safety in manufacturing processes. | Check specifications for crane rail compatibility; verify the condition and load ratings of scrap rails. |
| Rail Infrastructure | Track Rehabilitation and Expansion | Cost-effective solution for expanding rail networks or refurbishing existing tracks, supporting increased freight capacity. | Evaluate rail specifications to match existing systems; consider shipping logistics for international buyers. |
| Landscaping and Agriculture | Decorative Elements and Fencing | Enhances aesthetic appeal in landscaping projects while providing durable fencing solutions. | Ensure the aesthetic quality of the rails; consider weight and handling for installation purposes. |
How is Scrap Railway Track Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction sector, scrap railway tracks are often repurposed as foundation and structural support materials. Their inherent strength and durability make them ideal for building robust foundations, particularly in heavy-load applications. For international buyers, especially in regions with developing infrastructure, sourcing scrap rails can significantly reduce costs compared to purchasing new steel. However, buyers must ensure that the materials comply with local building codes and verify the grades to meet specific load-bearing requirements.
What Role Does Scrap Railway Track Play in Mining Operations?
In mining operations, scrap railway tracks are utilized for creating haulage and transportation systems within the site. These tracks facilitate the movement of heavy machinery and extracted materials, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. For buyers in remote areas of Africa or South America, the durability and compatibility of the scrap rails with existing infrastructure are crucial. It is essential to assess the condition of the rails and their suitability for the specific demands of the mining environment.
How is Scrap Railway Track Beneficial in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often use scrap railway tracks to construct crane runways and heavy equipment tracks. These tracks support the movement of machinery, improving productivity and safety within manufacturing facilities. For B2B buyers in Europe or the Middle East, it is vital to check the specifications of the rails to ensure they meet the required standards for crane operations. Additionally, verifying the load ratings and overall condition of the scrap rails can prevent operational disruptions.
How Can Scrap Railway Track Support Rail Infrastructure Development?
For companies involved in rail infrastructure, scrap railway tracks offer a cost-effective solution for track rehabilitation and expansion. They can be used to refurbish existing rail lines or to support new rail network developments, ultimately increasing freight capacity. International buyers must evaluate the specifications of the scrap rails to ensure compatibility with their existing systems. Logistics considerations are also critical, particularly for buyers in regions with challenging transportation networks.
What Innovative Uses are There for Scrap Railway Track in Landscaping?
In landscaping and agricultural applications, scrap railway tracks can be creatively repurposed as decorative elements or sturdy fencing. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of outdoor spaces but also provides a long-lasting solution for property boundaries. Buyers should ensure that the aesthetic quality of the rails meets their project requirements and consider the weight for ease of handling during installation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘scrap railway track for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Quality Assurance of Scrap Railway Tracks
The Problem: For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions with developing rail infrastructure, the challenge of ensuring the quality of scrap railway tracks is a significant concern. Buyers may encounter tracks that appear structurally sound but have hidden defects due to previous heavy usage or improper storage. This can lead to costly operational failures or safety hazards, especially in projects where load-bearing capacity is critical. Additionally, the lack of consistent quality standards across suppliers can create uncertainty and complicate procurement processes.
The Solution: To mitigate quality assurance issues, buyers should establish a thorough vetting process for suppliers of scrap railway tracks. Begin by requesting detailed documentation regarding the history and condition of the tracks, including inspection reports and compliance with international standards. Implement a sampling strategy where a small batch of tracks is tested for quality before making larger purchases. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers who offer a warranty or guarantee on the materials sold, as this can provide peace of mind regarding their reliability. Collaborating with a trusted third-party inspection service can also help validate the condition of the scrap tracks prior to purchase.
Scenario 2: Complicated Logistics and Transportation Challenges
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face logistical hurdles when sourcing scrap railway tracks, particularly when dealing with large volumes. Shipping heavy materials like railway tracks can involve complex regulations, high freight costs, and potential delays at customs, especially when purchasing from overseas suppliers. Buyers may also struggle to coordinate the timing of shipments with their project schedules, leading to interruptions in their operations.
The Solution: To streamline logistics, buyers should engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive shipping solutions, including the option for CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) pricing. This allows buyers to have a clearer understanding of total costs upfront and reduces the burden of managing transportation logistics. Additionally, establishing a robust communication channel with suppliers to discuss timelines and shipping methods can help ensure that materials arrive when needed. Utilizing local warehouses or distribution centers can also minimize transportation delays and facilitate quicker access to materials as projects progress. Finally, leveraging technology, such as tracking systems, can provide real-time updates on shipments, allowing buyers to plan accordingly.
Scenario 3: Misalignment of Specifications with Project Needs
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the misalignment between the specifications of scrap railway tracks and the actual requirements for their projects. This often arises from unclear communication regarding the intended use of the tracks, leading to purchases that do not meet the necessary dimensions or load capacities. Such discrepancies can cause project delays and increase costs due to the need for modifications or returns.
The Solution: To avoid specification misalignment, buyers must engage in clear and detailed communication with suppliers before making purchases. Create a comprehensive list of project requirements, including dimensions, weight tolerances, and intended use cases (e.g., light rail versus heavy freight). When sourcing materials, ask suppliers for detailed specifications and, if possible, request samples or detailed photographs of the tracks to ensure they meet your needs. Furthermore, consider utilizing suppliers who specialize in custom orders, as they can provide tailored solutions that align with specific project requirements. Implementing a feedback loop where project teams can discuss experiences with various suppliers can also help refine procurement strategies over time, ensuring future purchases are more aligned with actual needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for scrap railway track for sale
What Are the Key Materials Used in Scrap Railway Track for Sale?
When it comes to sourcing scrap railway tracks, understanding the different materials available is crucial for B2B buyers. Various materials exhibit distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact their application in different regions. Below, we analyze four common materials used in scrap railway tracks, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and considerations for international buyers.
Steel Rails: The Backbone of Railway Infrastructure
Steel is the most common material used in railway tracks due to its high tensile strength and durability. Typically, steel rails are designed to withstand heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for both freight and passenger transport.
- Key Properties: Steel rails have excellent tensile strength, typically ranging from 690 to 1179 N/mm², and can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Pros: They offer long service life, high load-bearing capacity, and resistance to wear and fatigue. Steel is also recyclable, which can reduce overall costs.
- Cons: Steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
- Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including heavy freight and high-speed passenger trains.
- Considerations for Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local corrosion factors and treatment options.
Aluminum Rails: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is an alternative material that is increasingly being used in railway applications, particularly where weight reduction is a priority.
- Key Properties: Aluminum offers a lower density compared to steel, making it lighter and easier to handle. It also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance.
- Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can lead to reduced transportation costs and easier installation. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for coastal or humid environments.
- Cons: Aluminum rails are generally less durable under heavy loads compared to steel, which may limit their use in high-traffic applications.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for light rail systems or temporary tracks, aluminum can be particularly effective in regions with less heavy freight traffic.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum rails meet local standards and consider the cost implications of using aluminum in high-load scenarios.
Composite Materials: Innovative Solutions for Modern Railways
Composite materials, which combine different materials to enhance performance, are gaining traction in the railway sector.
- Key Properties: Composites can be engineered to provide specific characteristics such as enhanced strength, reduced weight, and improved corrosion resistance.
- Pros: They offer high durability and can be tailored for specific applications, making them versatile for various environments.
- Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be more complex and costly, which may affect overall pricing.
- Impact on Application: Composites can be particularly effective in specialized applications, such as in areas with extreme weather conditions.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers need to verify the material specifications and compliance with international standards, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Used Rails: Economical and Sustainable Options
Used rails, often sourced from decommissioned tracks, provide a sustainable option for railway construction and maintenance.
- Key Properties: Used rails retain many of the properties of new steel but may show signs of wear and tear.
- Pros: They are typically available at a lower cost compared to new rails and contribute to sustainability efforts by recycling materials.
- Cons: The condition of used rails can vary significantly, requiring careful inspection to ensure suitability for specific applications.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for light rail and industrial applications, used rails can effectively serve in temporary or low-traffic scenarios.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should assess the condition and compliance of used rails with local regulations, particularly in regions with strict safety standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Scrap Railway Track
| Material | Typical Use Case for scrap railway track for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Rails | Heavy freight and passenger transport | High durability and load capacity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum Rails | Light rail systems and temporary tracks | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under heavy loads | High |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications in extreme environments | Tailored properties and versatility | Complex and costly manufacturing | High |
| Used Rails | Light rail and industrial applications | Cost-effective and sustainable | Variable condition and quality | Low |
Understanding these materials and their properties will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing scrap railway tracks, ensuring they select the most suitable options for their specific needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for scrap railway track for sale
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Scrap Railway Track?
The manufacturing process for scrap railway track involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality scrap steel from decommissioned railway tracks or industrial scrap. Suppliers typically assess the material for its chemical composition, ensuring it meets specific mechanical properties essential for rail applications. This step often involves sorting the scrap by grade and size to facilitate efficient processing.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo a forming process. This can include hot rolling, where the scrap steel is heated and shaped into rails. The forming stage is crucial, as it determines the dimensions and structural integrity of the rail. Advanced techniques such as continuous casting or extrusion may also be employed to produce the desired rail profiles, which are vital for compatibility with existing rail infrastructure.
3. Assembly
In some cases, rails may require assembly, especially when creating longer lengths from shorter sections. This stage involves welding or mechanical fastening of rail segments. Proper alignment and secure connections are critical to ensure safety and functionality. Quality assurance protocols are typically implemented at this stage to monitor weld integrity and alignment precision.
4. Finishing
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing. This includes surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Common techniques involve galvanizing or applying protective coatings. Finishing is vital as it prolongs the lifespan of the rails, especially in harsh environmental conditions typical in many regions where these products are utilized.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Scrap Railway Track Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of scrap railway tracks. It ensures that the products meet both international standards and the specific requirements of B2B buyers.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
B2B buyers should be aware of the international standards governing the quality of railway materials. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures consistent quality and continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API specifications for North America may apply depending on the intended use of the railway tracks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several critical checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Tests may include chemical analysis and physical inspections to ensure the steel meets required specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections and tests are performed at various stages, including material forming and assembly. This helps identify defects early in the process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the manufacturing process is complete, a thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted. This includes dimensional checks, surface inspections, and mechanical property tests to ensure compliance with specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Scrap Railway Tracks?
To ensure the quality and safety of scrap railway tracks, several testing methods are commonly employed:
-
Tensile Testing: This determines the strength of the steel and its ability to withstand loads without failure.
-
Impact Testing: This assesses the toughness of the material, particularly important for tracks that must endure dynamic forces.
-
Ultrasonic Testing: This non-destructive method detects internal flaws or inconsistencies within the steel, ensuring structural integrity.
-
Magnetic Particle Inspection: This technique is used to identify surface and near-surface defects in the rail.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality management systems. During an audit, buyers can review documentation related to quality control, observe production practices, and assess compliance with international standards.
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Buyers should always request quality control reports that detail the results of inspections and tests conducted throughout the manufacturing process. These reports should include information on material properties, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct audits and inspections to verify compliance with international standards and provide unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s quality control practices.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have varying standards for railway materials. Understanding local regulations and ensuring that suppliers comply with these standards is crucial for project success.
-
Import Regulations: Buyers must be aware of the import regulations in their countries, which may require specific certifications or compliance with international quality standards.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Different markets may have varying expectations regarding quality. Effective communication with suppliers about quality expectations can help bridge these gaps.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for scrap railway tracks is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing and the importance of quality control, buyers can ensure that they partner with reliable suppliers who meet international standards and deliver high-quality products. Through diligent verification practices, including audits and third-party inspections, buyers can safeguard their investments and ensure the successful implementation of their railway projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘scrap railway track for sale’
To successfully procure scrap railway tracks, it is essential to follow a structured approach that ensures quality, compliance, and value for your investment. This guide outlines the critical steps involved in sourcing scrap railway tracks, helping you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications required for the scrap railway tracks, including dimensions, weight, and material grade. Understanding your needs upfront will facilitate smoother negotiations and ensure that the materials you acquire meet the operational standards of your projects. Be specific about the type of rail (e.g., heavy rail vs. light rail) and any other requirements pertinent to your applications.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in scrap railway tracks. Look for companies with a robust online presence, positive reviews, and a history of successful transactions in your target region. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online marketplaces to compile a list of potential vendors who can meet your sourcing needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Verify their credibility by checking for certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate compliance with quality management systems.
- Check customer reviews: Look for testimonials or feedback from other businesses that have purchased scrap from the supplier.
- Assess their experience: Suppliers with extensive experience in the railway materials market are often more reliable.
Step 4: Request Samples and Assess Quality
Always request samples of the scrap railway tracks to assess their quality before making a bulk purchase. This step is vital as it allows you to verify that the material meets your specifications and is suitable for your intended use. Pay attention to signs of wear, corrosion, or structural integrity that could affect performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and assessed the quality of their products, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms of sale. Be clear about your budget constraints and any logistical considerations, such as shipping and delivery timelines. Ensure that you discuss payment terms, warranty conditions, and any return policies in case the materials do not meet your expectations.
Step 6: Confirm Compliance with Local Regulations
Before finalizing your purchase, confirm that the scrap railway tracks comply with local regulations and environmental standards in your region. This is particularly important in international transactions, where standards may vary significantly. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as certificates of compliance or material safety data sheets.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Contract
Finally, draft a detailed contract that outlines all agreed-upon terms, including specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. A well-defined contract protects both parties and minimizes the risk of misunderstandings. Ensure that both you and the supplier have a copy of the signed agreement for future reference.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing scrap railway tracks, ensuring that you secure high-quality materials that align with your operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for scrap railway track for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Scrap Railway Track Pricing?
When sourcing scrap railway tracks, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of the scrap rail itself is the most significant factor. Prices can fluctuate based on the quality and source of the steel, ranging from around $200 per metric ton for lower-grade scrap to higher amounts for more premium materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve the workforce required for dismantling, sorting, and preparing the scrap for sale. Skilled labor may command higher wages, especially in regions with labor shortages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead expenses.
-
Tooling: Specific tools and machinery are needed to cut and process scrap tracks, which adds to the overall cost. Investment in high-quality, durable tools can lead to long-term savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the scrap meets industry standards requires additional investment in quality assurance processes. Certificates of compliance can enhance the value of the scrap track.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly depending on the distance from the supplier to the buyer and the mode of transport used. Incoterms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) influence who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin to cover their risks and profit. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Scrap Railway Track Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of scrap railway tracks, impacting the final cost for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their expected volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as specific lengths or grades, can increase costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality scrap that meets international standards will command higher prices. Certifications can also affect resale value, making it essential for buyers to consider quality when sourcing.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their assurance of quality and timely delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding terms of trade is vital. Buyers should consider whether prices are quoted FOB (Free On Board) or CIF, as this affects who is responsible for shipping costs and risks.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Secure Better Prices?
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can employ several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Leverage Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Frequent communication fosters trust and potential for negotiation.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the purchase price but also associated costs such as shipping, handling, and potential downtime caused by delays. A lower upfront cost might not always equate to savings in the long run.
-
Market Research: Conducting thorough research on current market trends, prices, and supplier capabilities can empower buyers during negotiations. Being informed allows for more strategic discussions.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: If buyers can be flexible with their specifications or delivery timelines, they may be able to negotiate better pricing or terms.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers should be aware that pricing for scrap railway tracks can vary widely based on regional market conditions. Factors such as local demand, economic stability, and currency fluctuations can influence prices. It’s essential to request indicative prices and understand that these are subject to change based on market dynamics.
In conclusion, navigating the landscape of scrap railway track sourcing requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies. By being informed and strategic, buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and achieve better value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing scrap railway track for sale With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Scrap Railway Track for Sale
When evaluating options for railway infrastructure projects, it’s essential to consider various solutions that meet specific operational needs. While scrap railway track offers a cost-effective and sustainable option for certain applications, other alternatives may provide different advantages. This analysis compares scrap railway track for sale against two viable alternatives: New Steel Rails and Recycled Composite Track Systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Scrap Railway Track For Sale | New Steel Rails | Recycled Composite Track Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability; suitable for light to medium loads | High durability; ideal for heavy loads | Good durability; designed for specific applications |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; variable pricing based on condition | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost; varies by system and application |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires additional processing and transport logistics | Simple installation; widely available | Installation may require specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance due to wear and tear | Low maintenance; high reliability | Low maintenance; resistant to environmental factors |
| Best Use Case | Temporary tracks, light industrial use | Heavy freight lines, main railways | Urban transit systems, environmentally sensitive areas |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of New Steel Rails?
New steel rails are engineered for high performance and longevity. They are made from high-grade steel, ensuring they can withstand the rigorous demands of heavy freight transport. The initial investment is significantly higher than scrap railway tracks, but the long-term savings on maintenance and downtime can justify the cost. New steel rails are readily available and can be quickly installed, making them an excellent choice for new railway construction. However, their higher cost may be prohibitive for projects with limited budgets.
How Do Recycled Composite Track Systems Compare?
Recycled composite track systems represent an innovative approach to railway infrastructure, combining materials like plastic and rubber to create durable tracks. These systems are particularly advantageous in urban areas where environmental considerations are paramount. They offer good durability and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for light rail and transit systems. However, their installation may require specialized knowledge, and their performance under heavy loads may not match that of steel rails. Additionally, the cost can be moderate, depending on the specific requirements of the project.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Railway Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate railway solution involves a thorough assessment of project requirements, budget constraints, and operational goals. Scrap railway track for sale can be an excellent choice for temporary applications or where budget limitations exist. In contrast, new steel rails are better suited for high-traffic, heavy-load environments, while recycled composite track systems provide a sustainable option for urban applications. By analyzing the specific needs of a project and considering the pros and cons of each alternative, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and financial strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for scrap railway track for sale
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Scrap Railway Track for Sale?
When evaluating scrap railway tracks for purchase, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and operational requirements. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of scrap railway track typically refers to the type of steel used, which significantly influences durability and load-bearing capacity. Common grades include R50 to R65, indicating the rail’s strength and suitability for heavy loads. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is vital, as it affects the longevity and safety of the rail system. -
Length and Weight
Scrap railway tracks are often sold in standardized lengths, commonly around 1.5 meters, and their weight can vary based on the rail type (light, heavy, or crane rails). Understanding the weight per meter (e.g., 56.9 kg/m for 115RE rail) aids in calculating transportation costs and ensuring that the existing railbed can support the new track. This information is essential for logistics planning and budget considerations. -
Tensile Strength
This property indicates the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. For scrap railway tracks, tensile strength is typically measured in N/mm² (Newton per square millimeter) and can range from 690 to 1179 N/mm². High tensile strength is crucial for tracks that will endure heavy traffic and environmental stressors, making it a key factor in procurement decisions. -
Corrosion Resistance
Given that railway tracks are often exposed to harsh weather conditions, corrosion resistance is an important property. This can be influenced by the quality of the steel and any protective coatings applied. Buyers should assess the condition of scrap tracks to avoid future maintenance costs related to rust and degradation, ensuring a longer lifespan for their investment. -
Compliance with Standards
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that scrap railway tracks must meet, such as those set by the American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association (AREMA) or the International Union of Railways (UIC). Compliance ensures that the tracks are safe for use and can be integrated seamlessly into existing networks.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Scrap Railway Track Transactions?
Understanding industry terminology is equally important for navigating the purchasing process of scrap railway tracks. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of scrap railway tracks, an OEM may supply components that need to fit specific specifications or compatibility with existing rail systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For scrap railway tracks, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively, especially when dealing with large-scale projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific quantities of products. This process is vital for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing on scrap railway tracks. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of pre-defined international rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to navigate shipping costs, risks, and obligations associated with the purchase of scrap railway tracks. -
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)
This Incoterm indicates that the seller is responsible for the costs, insurance, and freight needed to transport goods to a specified destination. For buyers, understanding whether a quote is CIF can significantly impact total purchasing costs and liability during transportation.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing scrap railway tracks, ensuring they meet their operational requirements while optimizing costs and logistics.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the scrap railway track for sale Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Scrap Railway Track Market?
The scrap railway track market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by various global factors. A key driver is the rising demand for sustainable materials, particularly in developing regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure projects are booming. These regions are increasingly focusing on repurposing scrap materials to reduce costs and environmental impact. Additionally, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a growing trend towards modernization of rail networks, leading to an uptick in the availability of scrap tracks as old systems are upgraded.
Emerging technologies in sourcing, such as digital marketplaces and blockchain, are reshaping how buyers interact with suppliers. Digital platforms allow international B2B buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and negotiate better terms. Moreover, blockchain technology enhances transparency in transactions, ensuring the authenticity of materials and improving supply chain efficiency. This shift towards technology-driven sourcing is crucial for buyers looking to streamline procurement processes and mitigate risks associated with traditional methods.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Scrap Railway Track Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern B2B procurement, especially in the scrap railway track sector. The environmental impact of sourcing and utilizing scrap materials is significant, as it reduces the need for new raw materials and minimizes waste. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are acquired and processed in ways that respect both environmental standards and local communities.
Green certifications play a crucial role in this context. Suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or those that follow strict recycling standards are becoming more attractive to international buyers. These certifications not only validate the sustainability claims of suppliers but also provide assurance that the materials being sourced are environmentally friendly. For B2B buyers, investing in scrap railway tracks from certified suppliers aligns their procurement strategies with corporate sustainability goals and enhances their brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context of Scrap Railway Track Sourcing?
The sourcing of scrap railway tracks has evolved significantly over the years. Historically, railway tracks were predominantly made from iron and later transitioned to steel, reflecting advancements in material science and engineering. The introduction of electric and high-speed trains necessitated stronger and more durable materials, which led to an increase in the production of high-grade steel rails.
As rail systems aged, the practice of recycling scrap tracks gained traction, driven by both economic and environmental considerations. In the late 20th century, the focus shifted towards using recycled materials as a cost-effective solution for new projects. Today, the scrap railway track market is characterized by a blend of traditional procurement practices and modern technological advancements, positioning it as a vital component in the global push for sustainable infrastructure development.
In summary, the scrap railway track market is not just about sourcing materials; it’s about navigating complex dynamics influenced by global trends, sustainability imperatives, and historical practices that shape the current landscape. International buyers must remain agile and informed to leverage opportunities in this evolving sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of scrap railway track for sale
-
How do I ensure the quality of scrap railway track before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of scrap railway track, conduct a thorough supplier vetting process. Request samples and test reports that confirm the material’s specifications, including tensile strength and chemical composition. Engaging a third-party inspection service can also provide an unbiased assessment. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and certifications, which can give insight into their reliability and adherence to industry standards. -
What is the best type of scrap railway track for industrial applications?
The best type of scrap railway track for industrial applications typically depends on the specific requirements of the project. For heavy-load scenarios, consider high-grade rails such as UIC60 or 115RE, known for their strength and durability. If the application involves lighter loads, lighter rail sections may suffice. Always align the rail type with the intended use, considering factors like load capacity and environmental conditions. -
How can I verify the legitimacy of a scrap railway track supplier?
Verifying a supplier’s legitimacy involves several steps. Start by checking their business registration and certifications to ensure they comply with local and international trade regulations. Look for customer testimonials and case studies that demonstrate their track record. Additionally, request references from past clients and investigate their online presence, including reviews and ratings on industry-specific platforms. -
What are the common payment terms in international scrap railway track transactions?
Payment terms in international transactions can vary, but common practices include upfront deposits, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It is crucial to negotiate terms that protect both parties. Using secure payment methods and platforms can also reduce the risk of fraud. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid disputes later on. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for scrap railway track?
Minimum order quantities for scrap railway track can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of rail being purchased. Some suppliers may have a MOQ of a few tons, while others might require larger volumes to ensure cost-effectiveness. Discussing your specific needs with the supplier can lead to more flexible arrangements, especially for larger projects. -
How does logistics work for shipping scrap railway track internationally?
Logistics for shipping scrap railway track involves several steps, including customs clearance, freight forwarding, and selecting the right mode of transport. Collaborate with logistics partners experienced in handling heavy materials to ensure compliance with international shipping regulations. Discuss timelines, costs, and any potential duties or tariffs in advance to avoid unexpected delays or expenses. -
What customization options are available for scrap railway track?
Customization options for scrap railway track often include cutting lengths, surface treatment, and coating applications to enhance durability and corrosion resistance. Suppliers may also offer modifications to the rail profile to meet specific project requirements. Discussing your needs with the supplier can lead to tailored solutions that align with your operational goals. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of scrap railway track?
To ensure timely delivery, establish clear communication with your supplier about lead times and shipping schedules. Confirm the availability of the required materials before placing an order. Using reliable logistics partners with a proven track record in timely deliveries can also help. It’s advisable to build a buffer time into your project schedule to accommodate any unforeseen delays in the supply chain.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 2 Scrap Railway Track For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Railroad Track – Blacksmith Tools
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Railroad Track for sale on eBay, featuring various brands and refinements such as Anvil, VEVOR, Craftsman, and Picard. Popular items include blacksmith tools like hammers, tongs, and forges, with prices ranging from $35.04 to $168.77. Related searches include antique railroad track, railroad steel track, and model train tracks.
2. Best Metal Trade – Used Rail Scrap R50-R65
Domain: bestmetaltrade.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Used Rail Scrap R50-R65”, “Price”: “$280.00 per MT”, “Specifications”: {“R50”: {“Weight”: “51.67 Kg/M”, “GOST”: “7173-75”}, “R65”: {“Weight”: “64.72 Kg/M”, “GOST”: “8165-75”}}, “Chemical Composition”: {“Carbon”: “0.54 – 0.82%”, “Silicon”: “0.18 – 0.40%”, “Manganese”: “0.60 – 1.05%”, “Sulphur”: “0.04% Max”, “Phosphorus”: “0.035% Max”, “Arsenic”: “0.01% Max”}, “ISRI Codes”: {“27”: …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for scrap railway track for sale
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of scrap railway track presents a unique opportunity for international buyers. By leveraging reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure not only the quality of materials but also favorable pricing structures. The demand for scrap railway track, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, highlights the necessity for sustainable sourcing practices that align with environmental standards.
Key takeaways from this guide emphasize the importance of understanding local market conditions and regulations, as well as establishing strong relationships with suppliers who can provide transparent and timely service. The versatility of scrap railway track—ranging from heavy-duty applications to lighter industrial uses—offers buyers a range of options tailored to their specific needs.
Looking ahead, the global market for scrap railway track is poised for growth, driven by infrastructure development and sustainability initiatives. For B2B buyers, now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers and explore innovative sourcing strategies that can enhance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Start building those connections today to secure your competitive advantage in the evolving railway landscape.