How to Source Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for largest consumer packaged goods companies
Navigating the complex landscape of the largest consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially when seeking to source reliable and innovative products. With fluctuating market dynamics, rising costs, and changing consumer preferences, understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the largest CPG companies, highlighting their product ranges, market strategies, and the latest technological advancements driving their success.
In this resource, we delve into various types of consumer packaged goods, their applications across different sectors, and effective supplier vetting processes. We explore cost considerations, enabling buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Germany and Brazil—to make strategic sourcing choices that align with their business objectives. The insights provided will empower B2B buyers to identify industry leaders, evaluate emerging trends, and navigate the challenges of a rapidly evolving market.
By leveraging this guide, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they align with both local market demands and global best practices. Ultimately, this resource serves as a vital tool for companies looking to thrive in the competitive world of consumer packaged goods, fostering partnerships that drive growth and innovation.
Understanding largest consumer packaged goods companies Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Diverse product range; focus on nutrition and taste; high demand | Retail distribution, food service, e-commerce | Pros: Essential products; strong market demand. Cons: Price sensitivity; supply chain volatility. |
| Personal Care and Beauty | Emphasis on branding and innovation; includes cosmetics and hygiene | Retail partnerships, direct-to-consumer sales | Pros: High margins; brand loyalty. Cons: Intense competition; changing consumer preferences. |
| Household Products | Everyday essentials; focuses on cleaning and maintenance | Wholesale distribution, contract manufacturing | Pros: Steady demand; low seasonality. Cons: Price wars; reliance on consumer trends. |
| Health and Wellness | Products aimed at improving health; growing focus on natural ingredients | Pharmacies, wellness stores, e-commerce | Pros: Rising consumer interest; premium pricing potential. Cons: Regulatory challenges; market saturation. |
| Luxury Goods | High-end products; strong brand identity; exclusivity | High-end retail, boutique partnerships | Pros: High profit margins; brand prestige. Cons: Economic sensitivity; limited customer base. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Food and Beverage Companies?
Food and beverage companies are characterized by their extensive product offerings, which include packaged foods, beverages, and snacks. They often emphasize nutrition, taste, and convenience to appeal to a broad consumer base. For B2B buyers, these companies provide essential products that are consistently in demand across various retail and food service channels. However, buyers must consider price sensitivity and potential supply chain disruptions, especially in times of inflation.
How Do Personal Care and Beauty Companies Stand Out?
Personal care and beauty companies focus on innovative branding and product differentiation, offering a range of cosmetics, skincare, and hygiene products. Their strong emphasis on quality and branding fosters consumer loyalty, making them appealing to B2B buyers looking for high-margin products. However, the intense competition and rapidly changing consumer preferences necessitate that buyers stay informed about market trends to make wise purchasing decisions.
What Defines Household Products in the CPG Sector?
Household products encompass a wide variety of everyday essentials, such as cleaning supplies and paper goods. These products are characterized by their steady demand and low seasonality, making them reliable options for B2B buyers. The primary applications include wholesale distribution and contract manufacturing. However, buyers should be aware of the price wars that can occur in this sector, as well as the need to adapt to evolving consumer preferences.
What is the Focus of Health and Wellness Companies?
Health and wellness companies target the growing consumer interest in health improvement and natural ingredients. Their product lines often include supplements, organic foods, and personal care items designed to promote well-being. B2B buyers can benefit from the rising consumer interest and potential for premium pricing. However, they must also navigate regulatory challenges and a saturated market, making thorough research essential.
How Do Luxury Goods Companies Operate in the CPG Landscape?
Luxury goods companies are defined by their high-end products and strong brand identity, often characterized by exclusivity and premium pricing. These brands cater to a niche market, primarily through high-end retail and boutique partnerships. For B2B buyers, the appeal lies in the high profit margins and brand prestige. However, these companies can be sensitive to economic fluctuations, and their limited customer base may pose challenges in maintaining sales volume.
Key Industrial Applications of largest consumer packaged goods companies
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Supply Chain Optimization | Enhanced efficiency and reduced costs | Reliability of suppliers, local sourcing capabilities, and compliance with food safety regulations. |
| Personal Care Products | Sustainable Packaging Innovations | Improved brand reputation and customer loyalty | Availability of eco-friendly materials and compliance with international packaging standards. |
| Household Goods | AI-Driven Consumer Insights | Better targeting of marketing strategies | Access to robust data analytics tools and understanding of local consumer behavior. |
| E-commerce Solutions | Advanced Digital Marketing Strategies | Increased online sales and market reach | Integration capabilities with existing platforms and data security measures. |
| Health and Wellness | Product Development and Reformulation | Meeting evolving consumer preferences and health trends | Expertise in regulatory compliance and market trends in health products. |
How Do Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies Optimize Supply Chains in the Food and Beverage Sector?
Largest consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies in the food and beverage sector leverage advanced supply chain optimization techniques to enhance efficiency and cut costs. By utilizing technology, such as AI and machine learning, these companies can forecast demand more accurately, minimize waste, and manage inventory better. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local sourcing capabilities and ensuring compliance with food safety regulations are crucial for successful partnerships.
What Role Do Sustainable Packaging Innovations Play in Personal Care Products?
In the personal care sector, leading CPG companies are focusing on sustainable packaging innovations to improve their brand reputation and foster customer loyalty. By shifting to biodegradable or recyclable materials, these companies not only meet consumer demand for environmentally friendly options but also comply with increasing regulatory pressures. B2B buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, should consider the availability of eco-friendly materials and the supplier’s ability to meet international packaging standards when sourcing.
How Can AI-Driven Consumer Insights Enhance Marketing Strategies for Household Goods?
AI-driven consumer insights are becoming indispensable for CPG companies in the household goods sector. By analyzing vast amounts of consumer data, these companies can refine their marketing strategies, ensuring they resonate with target audiences effectively. For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Germany and Brazil, it is essential to have access to robust data analytics tools that can provide insights into local consumer behavior and preferences.
How Do Advanced Digital Marketing Strategies Impact E-commerce Solutions for CPG Companies?
Advanced digital marketing strategies are crucial for CPG companies looking to maximize their e-commerce presence. By employing targeted advertising and personalized customer engagement tactics, these companies can significantly boost online sales and expand their market reach. For international B2B buyers, the integration capabilities of digital marketing tools with existing platforms and data security measures should be key considerations when selecting partners.
What Are the Challenges in Product Development for Health and Wellness Applications?
In the health and wellness sector, CPG companies are increasingly focused on product development and reformulation to align with evolving consumer preferences. This involves not only meeting health trends but also navigating complex regulatory landscapes. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who possess expertise in regulatory compliance and are attuned to market trends, particularly in regions with stringent health product regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘largest consumer packaged goods companies’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions in CPG Sourcing
The Problem:
B2B buyers often grapple with unpredictable supply chain disruptions when sourcing from the largest consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, inflationary pressures, and fluctuating commodity prices can lead to delays in product availability and increased costs. For instance, a procurement manager in a retail chain may find that essential products are out of stock or that prices have surged unexpectedly. This situation not only affects inventory levels but can also strain relationships with customers who expect consistency and reliability.
The Solution:
To mitigate these issues, B2B buyers should establish a diversified supplier base that includes multiple CPG companies across different geographical regions. This approach reduces reliance on a single source and creates a buffer against localized disruptions. Additionally, implementing advanced supply chain management software can enhance visibility into inventory levels and supplier performance. Buyers should also engage in regular communication with suppliers to stay informed about potential disruptions and collaboratively develop contingency plans. By leveraging technology and strategic partnerships, procurement teams can maintain stability and responsiveness in their supply chains, ensuring that they can meet customer demands consistently.
Scenario 2: Adapting to Consumer Behavior Shifts
The Problem:
In an ever-evolving market, B2B buyers must stay ahead of changing consumer preferences and behaviors that affect demand for CPG products. For example, a wholesaler may notice a decline in interest for traditional products as consumers increasingly gravitate toward healthier, sustainable options. This shift not only impacts sales forecasts but can also result in excess inventory of products that no longer resonate with consumers, ultimately leading to increased holding costs and wasted resources.
The Solution:
To effectively adapt to these shifts, B2B buyers should conduct regular market research to identify emerging trends in consumer behavior. Collaborating with CPG companies that prioritize innovation and sustainability can provide access to new product lines that align with consumer demands. Additionally, employing data analytics tools can help buyers forecast trends more accurately and optimize inventory levels accordingly. By proactively adjusting their product offerings and collaborating with forward-thinking suppliers, B2B buyers can ensure that their portfolios remain relevant and profitable in a competitive landscape.
Scenario 3: Managing Rising Costs Without Compromising Quality
The Problem:
As inflation continues to affect the global economy, B2B buyers from sectors reliant on CPG products are often challenged with rising procurement costs. This situation can lead to tough decisions regarding pricing, margins, and ultimately, product quality. For instance, a distributor may feel pressured to switch to lower-quality alternatives to maintain profitability, which can alienate customers and damage the brand’s reputation over time.
The Solution:
To navigate rising costs effectively, B2B buyers should focus on negotiating better terms with CPG suppliers while emphasizing long-term partnerships. Buyers can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate discounts or explore bulk purchasing options that reduce unit costs. Additionally, investing in technology such as AI-powered procurement platforms can help identify cost-saving opportunities without sacrificing quality. By maintaining transparency with customers about pricing changes and emphasizing the value of high-quality products, buyers can retain consumer trust while managing costs effectively. Engaging in these practices ensures a balanced approach to cost management, quality assurance, and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for largest consumer packaged goods companies
What Are the Key Materials Used by the Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies?
In the consumer packaged goods (CPG) sector, material selection plays a crucial role in product performance, sustainability, and overall market competitiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials—plastic, glass, metal, and paperboard—highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Plastic Perform in CPG Applications?
Plastic is widely used in packaging due to its versatility and lightweight nature. Key properties include excellent moisture resistance, a wide range of temperature tolerances, and the ability to be molded into various shapes. However, the environmental impact of plastic waste is a growing concern, leading to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulators.
Pros of plastic include low manufacturing costs and high durability, making it suitable for products requiring long shelf life. Conversely, cons involve potential leaching of chemicals into food products and limited recyclability. For international buyers, compliance with regulations such as the European Union’s Plastics Directive is essential, as is adherence to local standards like ASTM and DIN.
What Are the Advantages of Glass in CPG Products?
Glass is another popular material, particularly for food and beverage packaging. Its key properties include excellent barrier protection against oxygen and moisture, high chemical resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures. Glass is also fully recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
The key advantage of glass is its premium feel, which can enhance brand perception. However, it is heavier and more fragile than plastic, leading to higher transportation costs and risks of breakage during handling. International buyers must consider local recycling capabilities and compliance with food safety standards, which can vary significantly across regions.
Why Is Metal a Preferred Choice for Certain CPG Applications?
Metal, particularly aluminum and steel, is commonly used in packaging for beverages and canned goods. Key properties include high strength, excellent barrier properties, and resistance to corrosion. Metals can also withstand high pressure and temperature conditions, making them suitable for various applications.
The advantage of metal is its durability and recyclability, which appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. On the downside, metals can be more expensive than plastics and require complex manufacturing processes. B2B buyers should be aware of international standards for food contact materials and specific regulations in their regions, such as those enforced by the FDA in the U.S. or EFSA in Europe.
How Does Paperboard Fit into the CPG Landscape?
Paperboard is increasingly being used for packaging due to its sustainability and biodegradability. Key properties include lightweight, good printability, and the ability to be formed into various shapes. It is also cost-effective and can be sourced from renewable materials.
The key advantage of paperboard is its eco-friendliness, aligning with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. However, it may not provide the same level of moisture and barrier protection as plastic or metal. International buyers should consider certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and compliance with packaging regulations, which can vary significantly by region.
Summary of Material Selection for CPG Companies
| Material | Typical Use Case for largest consumer packaged goods companies | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Food packaging, beverage bottles, household products | Lightweight and versatile | Environmental concerns and recyclability issues | Medium |
| Glass | Beverage containers, premium food packaging | Excellent barrier and premium feel | Heavier and more fragile | High |
| Metal | Canned goods, beverage cans | Durable and recyclable | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Paperboard | Food packaging, retail boxes, cartons | Eco-friendly and cost-effective | Limited moisture protection | Low |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions regarding material selection in the competitive landscape of consumer packaged goods.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for largest consumer packaged goods companies
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing in Consumer Packaged Goods?
The manufacturing processes of consumer packaged goods (CPGs) are intricate and structured to ensure efficiency and quality. The main stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This stage involves sourcing raw materials, which can range from agricultural products to plastics and metals. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet specified quality standards and regulations. For instance, companies often use quality control processes such as incoming quality control (IQC) to verify the materials before they enter production.
-
Forming: In this stage, raw materials are transformed into usable products through various techniques. Depending on the product type, methods may include extrusion, injection molding, or baking. For example, in the food industry, forming may involve mixing ingredients and shaping them into final products, while in cosmetics, it might involve emulsifying ingredients to create creams or lotions.
-
Assembly: This stage is crucial for products that consist of multiple components. Automated assembly lines are often employed to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. In CPG companies, robotics and conveyor systems are frequently used to streamline the assembly of products like packaged snacks or personal care items.
-
Finishing: The final touches are applied in this stage, which may include packaging, labeling, and quality checks. The packaging process is particularly vital, as it not only protects the product but also serves as a marketing tool. Companies often utilize advanced printing technologies to ensure that labels and packaging meet brand standards and regulatory requirements.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in the Manufacturing of CPGs?
To optimize manufacturing processes, consumer packaged goods companies often adopt several key techniques:
-
Lean Manufacturing: This methodology focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. It is particularly useful in CPGs where margins are tight, and efficiency is paramount.
-
Six Sigma: A data-driven approach that aims to improve quality by identifying and removing causes of defects. This technique is crucial for maintaining high-quality standards in CPG manufacturing, especially in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals.
-
Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: This inventory strategy aims to reduce waste by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process. This technique is beneficial for managing costs and ensuring that inventory levels are kept to a minimum.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for CPG Manufacturers?
Quality assurance in the consumer packaged goods sector is governed by various international and industry-specific standards.
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). CPG companies often seek ISO 9001 certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking signifies that a product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly relevant for consumer goods like electronics and toys.
-
API Standards: In the pharmaceutical sector, adherence to the American Pharmacopoeia (AP) and other similar standards ensures that products meet quality and safety requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CPG Manufacturing?
Quality control in CPG manufacturing is typically segmented into several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. The goal is to ensure that all materials meet predefined quality specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks are performed to monitor the production process. This includes testing samples at various stages to detect any deviations from quality standards early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once products are finished, they undergo a thorough inspection before packaging. FQC ensures that the final product meets all specifications and is ready for distribution.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are several strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request audit reports and certifications to assess compliance with recognized standards like ISO 9001.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including test results and corrective actions taken for any non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. This can be especially beneficial for buyers looking to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware of Regarding QC and Certification?
When sourcing from international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control and certification:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Differences: Attitudes towards quality control can vary significantly by region. Buyers should approach negotiations with an understanding of these cultural differences to foster better relationships with suppliers.
-
Documentation and Certification: Ensuring that suppliers possess the necessary certifications is crucial. Buyers should verify that all documentation is current and valid to mitigate risks related to product quality.
By understanding the complexities of manufacturing processes and quality assurance in the consumer packaged goods sector, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and forge successful partnerships with suppliers globally.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘largest consumer packaged goods companies’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement process for products from the largest consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies requires a strategic approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to source effectively from leading CPG firms. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they are making informed decisions that align with their business goals and consumer needs.
Step 1: Identify Your Product Requirements
Clearly define what products you need, including specifications such as size, packaging, and quality standards. This step is vital as it sets the foundation for your sourcing strategy, ensuring that you target suppliers who can meet your specific needs. Consider the preferences of your target market, such as eco-friendly packaging or organic ingredients.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify the largest CPG companies that align with your product requirements. Utilize industry reports, market analysis, and trade publications to gather insights on potential suppliers. Pay special attention to their market reputation, product range, and ability to meet international standards, especially if you’re sourcing from different regions.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with industry regulations. This includes food safety certifications (like ISO 22000 or HACCP) and sustainability certifications (such as Fair Trade or Rainforest Alliance). Ensuring compliance is crucial to mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety, particularly when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 4: Assess Financial Stability
Review the financial health of potential suppliers to gauge their reliability and capacity to fulfill orders. Look for financial reports, credit ratings, and market share insights. A financially stable supplier is more likely to handle fluctuations in demand and maintain consistent product availability, which is essential for your supply chain continuity.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Quality Testing
Always request product samples before finalizing any agreements. This allows you to assess the quality, packaging, and overall suitability of the products for your market. Conduct quality testing in accordance with your defined specifications to ensure the products meet your standards and those of your consumers.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms, including pricing, payment schedules, and delivery timelines. This step is critical for aligning supplier capabilities with your business objectives. Ensure clarity on any penalties for late deliveries or quality issues to protect your interests.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Develop a robust communication strategy with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing collaboration. Regular updates on order status, inventory levels, and market trends can help build a strong partnership. Effective communication is key to addressing any potential issues proactively and ensuring a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing efficiency, reduce risks, and foster strong relationships with leading consumer packaged goods companies.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for largest consumer packaged goods companies Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing from the Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies?
When considering sourcing from the largest consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Raw materials represent a significant portion of total production costs. CPG companies are often influenced by global commodity prices, which can fluctuate due to supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events. Buyers should consider sourcing materials from suppliers with stable pricing agreements or those who can provide alternative materials to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region. In countries with higher labor standards and costs, such as Germany or the UK, buyers may face increased pricing. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs, like parts of South America, may offer more competitive pricing but could come with challenges related to quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting pricing positively. Buyers should inquire about the operational efficiencies of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for production, including molds and machinery, can be a significant upfront cost. This cost is typically amortized over the volume of products produced. Buyers should negotiate tooling costs when discussing larger volumes, as economies of scale can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is crucial for maintaining brand reputation. Companies invest in QC processes, which can add to the overall cost. Buyers should evaluate suppliers’ QC certifications and processes to ensure they align with their quality requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are vital considerations, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as shipping routes, Incoterms, and local tariffs can greatly affect overall pricing. Buyers should assess the logistical capabilities of suppliers to ensure timely delivery and cost-efficiency.
-
Margin: CPG companies typically mark up their costs to achieve profitability. Understanding the margin expectations of potential suppliers can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence pricing in the CPG sector:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders usually lead to better pricing. Buyers should assess their demand forecasts and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capabilities to leverage volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom products often come with higher costs due to additional tooling and production complexity. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and specific certifications (e.g., organic, fair trade) can elevate costs. Buyers should prioritize essential certifications that align with their brand values and consumer expectations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and capabilities of suppliers can impact pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing through loyalty and collaboration.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical for cost management. Incoterms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk, influencing the total landed cost of goods.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating with CPG Suppliers?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to optimize their sourcing:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate not just on price but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies. Flexibility in these areas can lead to cost savings.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the full lifecycle costs associated with sourcing products, including shipping, handling, and potential tariffs, rather than just the initial purchase price.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Different regions have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, labor costs, and material availability. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East should conduct thorough market research and consider local suppliers to reduce logistical costs.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and transparency about your needs can foster a mutually beneficial partnership.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for consumer packaged goods can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and order specifics. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing largest consumer packaged goods companies With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies
In the realm of consumer packaged goods (CPG), businesses often seek effective solutions to meet their operational needs. While the largest CPG companies provide a wealth of resources and established products, alternatives exist that can also address specific market demands. This analysis explores two viable alternatives: private label brands and direct-to-consumer (DTC) e-commerce platforms. Each alternative offers unique benefits and challenges that B2B buyers must consider in relation to their specific business objectives.
| Comparison Aspect | Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies | Private Label Brands | Direct-to-Consumer E-commerce Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Established reputation and quality standards, extensive distribution networks | Varies by manufacturer; can match quality but often lacks brand recognition | High potential for quality and consumer engagement, but reliant on brand marketing |
| Cost | Higher due to brand investment and marketing costs | Generally lower; cost-effective for retailers and consumers | Variable; initial setup can be high, but lower long-term operational costs possible |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy for established retailers due to existing partnerships | Requires negotiation with manufacturers, but often straightforward | Requires significant marketing efforts and tech integration for success |
| Maintenance | Continuous R&D and marketing investment necessary | Lower maintenance; relies on retailer for marketing and distribution | Ongoing need for digital marketing, customer engagement, and tech upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for businesses needing reliable, well-known products | Best for retailers looking to offer competitive pricing without brand loyalty issues | Suitable for brands wanting direct customer relationships and control over branding |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Private Label Brands?
Private label brands, often produced by manufacturers for retailers, offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional CPGs. The primary advantage is lower pricing, making them attractive to budget-conscious consumers. Retailers can also tailor these products to meet local tastes and preferences, fostering customer loyalty. However, the challenge lies in brand recognition. Without the established reputation of major CPG companies, private labels may struggle to attract consumers who prioritize brand trust. Additionally, quality can vary significantly, which may impact consumer perception.
How Do Direct-to-Consumer E-commerce Platforms Work?
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) e-commerce platforms represent a modern approach to product distribution, allowing brands to sell directly to consumers via online channels. This model enables brands to maintain control over their marketing, pricing, and customer relationships. The benefits include higher profit margins and the ability to gather direct feedback from consumers, which can inform product development. However, the initial investment in technology and marketing can be substantial, and success is heavily dependent on effective digital marketing strategies. Brands must also be prepared for competition, as the online space is increasingly crowded.
Making the Right Choice: Which Solution Is Best for Your Business?
When considering alternatives to the largest consumer packaged goods companies, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs and market conditions. If a business prioritizes cost and local consumer preferences, private label brands may be the most suitable option. Conversely, if building a direct relationship with consumers is crucial, investing in a DTC e-commerce platform could yield significant long-term benefits. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s strategic goals, market positioning, and resource availability, ensuring that the chosen solution effectively supports growth and customer engagement.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for largest consumer packaged goods companies
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Consumer Packaged Goods Companies?
Understanding the critical technical properties in the consumer packaged goods (CPG) industry is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some vital specifications that play a significant role in product quality and operational efficiency.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in product manufacturing. In the CPG sector, this can include plastics, metals, or organic materials. For example, food packaging often requires materials that are food-safe and can withstand various environmental conditions. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for compliance with safety regulations and ensuring product longevity, which directly impacts customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance in manufacturing indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or property. In CPG, maintaining precise tolerances is vital for product consistency and functionality. For instance, in food processing, slight deviations in ingredient measurements can alter taste and quality. Understanding tolerance levels helps B2B buyers ensure that suppliers can meet their specifications, thereby reducing the risk of product recalls and maintaining quality assurance.
3. Shelf Life
Shelf life denotes the period during which a product remains safe and effective for consumption or use. For perishable goods, knowing the shelf life is critical for inventory management and supply chain logistics. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide clear shelf life information to minimize waste and ensure product availability aligns with consumer demand.
4. Packaging Standards
Packaging standards encompass the specifications related to the materials and methods used for packaging products. This includes considerations for recyclability, durability, and compliance with international regulations. Adhering to packaging standards is essential for marketability and sustainability, especially as consumers increasingly favor eco-friendly products. Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers align their sourcing strategies with market trends.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in the CPG Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is critical for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B environment. Here are several key terms that are frequently used in the consumer packaged goods sector.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CPG context, an OEM might supply components for packaged goods, such as packaging materials or ingredients. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure high-quality components while also optimizing costs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts inventory management and cost considerations. Suppliers with high MOQs may require buyers to invest more upfront, which can strain cash flow, particularly for smaller businesses.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to invite suppliers to bid on providing specific products or services. Including details about quantities, specifications, and delivery timelines, an RFQ helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better terms. For international buyers, a well-structured RFQ can streamline procurement processes and lead to cost savings.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and risk management during the transportation of goods. Proper use of Incoterms can mitigate disputes and enhance supply chain efficiency.
5. SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
SKU is a unique identifier for each distinct product and service that can be purchased. In the CPG sector, SKUs are vital for inventory tracking, sales analysis, and supply chain management. Understanding SKU management can help B2B buyers optimize their stock levels and improve order fulfillment rates.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the consumer packaged goods sector can make more informed decisions, fostering stronger supplier relationships and enhancing their overall operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the largest consumer packaged goods companies Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies?
The consumer packaged goods (CPG) sector is currently navigating a complex landscape shaped by global drivers such as inflation, supply chain disruptions, and evolving consumer preferences. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must remain vigilant to these changes. Companies are increasingly adopting technology-driven solutions to enhance operational efficiency and consumer engagement. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics is becoming prevalent, with firms using these tools to streamline processes, optimize inventory management, and tailor marketing strategies to local markets.
Emerging trends also point to a shift towards sustainable and ethical sourcing practices. Consumers are increasingly favoring brands that prioritize environmental responsibility, leading CPG companies to invest in greener technologies and alternative materials. For B2B buyers, this presents an opportunity to align their procurement strategies with suppliers that emphasize sustainability, thus enhancing their brand reputation in diverse markets. Furthermore, as e-commerce continues to grow, companies are revamping their digital platforms to improve customer experiences, making it crucial for buyers to stay informed about the latest technological advancements and consumer engagement strategies.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping B2B Relationships in the CPG Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations in the CPG industry, significantly impacting B2B relationships. As environmental concerns rise, companies are under pressure to minimize their ecological footprints, leading to increased investments in sustainable practices. This encompasses everything from sourcing raw materials responsibly to implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes. For international buyers, partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability not only meets consumer demand but also mitigates risks associated with regulatory compliance and reputational damage.
Certifications such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, and various eco-labels are becoming vital in establishing credibility and trust among consumers. B2B buyers can leverage these certifications to differentiate themselves in competitive markets, particularly in regions where consumers are more environmentally conscious. Additionally, the shift towards circular economy practices—where companies aim to reduce waste and reuse materials—presents further opportunities for businesses to collaborate on innovative solutions that meet both economic and environmental goals.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Evolution of the CPG Sector?
The evolution of the consumer packaged goods sector dates back to the late 19th century, marked by the rise of mass production and the establishment of iconic brands. The introduction of packaged goods revolutionized how products were marketed and distributed, paving the way for modern retail environments. Over the decades, the industry has adapted to various economic shifts, technological advancements, and changing consumer behaviors.
In recent years, the focus has shifted from merely providing products to creating value through innovation and consumer engagement. As the global marketplace continues to evolve, the largest CPG companies are now more than just suppliers; they are strategic partners that must align with the values and expectations of their B2B clients and end consumers alike. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding market dynamics and sourcing trends, which are critical for international buyers aiming to make informed decisions in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of largest consumer packaged goods companies
-
How do I choose the right consumer packaged goods supplier for my business?
Selecting the right supplier involves assessing their reputation, financial stability, and product quality. Start by reviewing their track record in your specific market and check for certifications that indicate compliance with industry standards. Engage in discussions to understand their production capacity, lead times, and customer service approach. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Lastly, consider their willingness to accommodate your specific needs, such as customization options and minimum order quantities (MOQs). -
What is the best way to negotiate payment terms with consumer packaged goods companies?
Negotiating payment terms requires a clear understanding of your cash flow needs and the supplier’s policies. Start by proposing terms that work for you, such as net 30 or net 60 days, and be open to compromise. It’s beneficial to build a relationship based on trust; consistent, timely payments can lead to more favorable terms over time. Inquire about discounts for early payments or bulk purchases, and ensure that all agreements are documented to avoid future disputes. -
How can I ensure product quality when sourcing from large consumer packaged goods companies?
To ensure product quality, request detailed specifications and quality assurance processes from potential suppliers. Consider conducting factory audits or requesting third-party inspections before placing large orders. Establish clear quality standards in your contract and include clauses for penalties in case of non-compliance. Additionally, maintain open lines of communication with your supplier throughout production, and consider implementing a sampling process to review products before full shipment. -
What are the typical logistics challenges when importing consumer packaged goods?
Logistics challenges may include customs delays, shipping costs, and ensuring compliance with local regulations. To mitigate these issues, work with experienced freight forwarders who understand the nuances of international trade. Ensure all documentation is accurate and complete to avoid customs complications. Additionally, consider the mode of transport that best balances cost and delivery speed, and stay informed about potential disruptions due to geopolitical factors or global supply chain issues. -
What should I know about minimum order quantities (MOQs) when dealing with CPG suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary widely among suppliers and can impact your purchasing strategy. Some large companies may impose higher MOQs due to production efficiencies, while smaller firms might offer more flexible terms. Discuss your specific needs upfront, as some suppliers may be willing to negotiate MOQs for new partnerships or trial orders. Be prepared to balance the cost benefits of larger orders against your inventory management capabilities and cash flow considerations. -
How do I assess the sustainability practices of consumer packaged goods companies?
Assessing sustainability practices involves reviewing the company’s commitment to environmental responsibility, such as sourcing materials sustainably, reducing waste, and minimizing carbon footprints. Look for certifications like ISO 14001 or initiatives like the UN Global Compact that indicate a commitment to sustainability. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain practices to ensure ethical sourcing and labor standards. Engage with suppliers on their sustainability goals to align your brand values with theirs. -
What are effective strategies for customizing products from large CPG suppliers?
To customize products effectively, begin by clearly defining your requirements and the desired outcomes. Engage in open discussions with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and limitations regarding customization. Some suppliers may offer modular products that allow for variations without extensive retooling. Establish a collaborative relationship where you can share market insights, enabling the supplier to tailor products that meet your specific consumer needs while maintaining quality and cost-effectiveness. -
How can I mitigate risks when sourcing from international consumer packaged goods companies?
Mitigating risks involves thorough due diligence, including researching supplier backgrounds and financial health. Establish clear contracts that outline terms, responsibilities, and quality standards to protect your interests. Diversify your supplier base to avoid dependence on a single source, and consider using escrow services for payments to secure transactions. Regular communication and relationship building can also help address issues proactively and foster a smoother collaboration.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
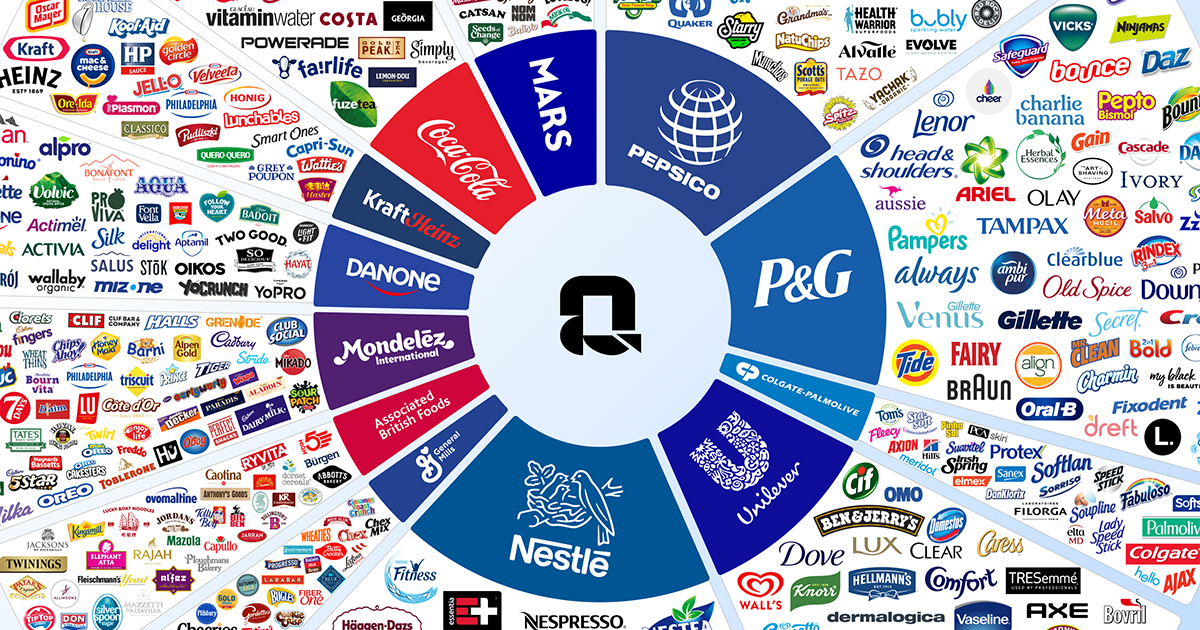
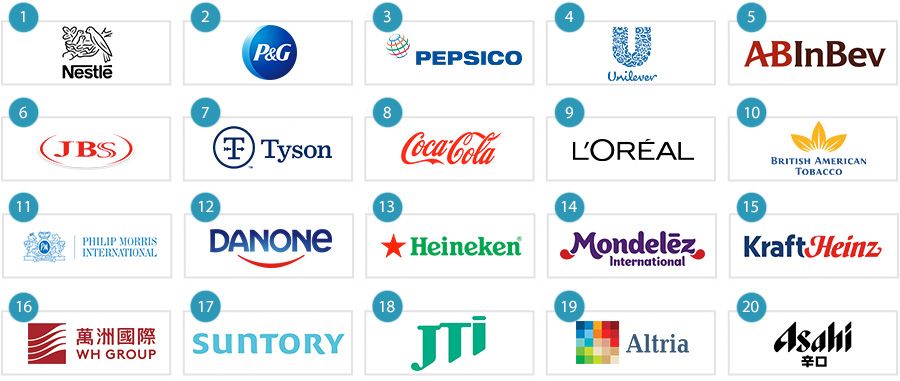
Top 9 Largest Consumer Packaged Goods Companies Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top Consumer Goods Brands – Market Cap Leaders
Domain: companiesmarketcap.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Top Consumer Goods Brands – Market Cap Leaders, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. ChannelWill – Post-Purchase Experience Solutions
Domain: channelwill.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Post-Purchase Order Tracking: Deliver an unmatched post-purchase tracking experience. Returns & Exchanges: Turn satisfied shoppers into vocal fans of your brand. Shipping Protection: Ensure ‘Worry-Free Delivery’ and give customers peace of mind. Retention Reviews & UGC: Turn satisfied shoppers into vocal fans of your brand. Loyalty & Rewards: From ‘Like it’ to ‘Love it’ with our all-in-one loyalty…
3. CPG Market – Key Players
Domain: marketsandmarkets.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The consumer packaged goods (CPG) market is estimated at USD 3,450.12 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4,235.01 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2025 to 2030. Major companies in the market include Procter & Gamble (US), Unilever, Nestlé, PepsiCo, and The Coca-Cola Company. Procter & Gamble offers products across personal care, home care, hygiene, and baby care, with brands like…
4. Unilever – Key Product
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Unilever – Key Product, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Procter & Gamble – Pampers, Tide, Crest; Colgate-Palmolive – Colgate, Palmolive, Speed Stick
Domain: newsweek.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Procter & Gamble: Brands include Pampers, Tide, Crest, Febreze; charitable initiatives include mobile laundry and shower services for tornado victims, P&G Good Everyday rewards program. Colgate-Palmolive: Brands include Colgate toothpaste, Palmolive soap, Speed Stick, Irish Spring, Hill’s Pet Nutrition; initiatives include free oral health education, pet food donations, youth programs in Mexico. S…
6. PageFly – CPG Solutions
Domain: pagefly.io
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Consumer packaged goods (CPG) are daily products that consumers use regularly and purchase frequently. Examples of CPG include food, beverages, clothing, tobacco, cosmetics, and household products. CPG products typically generate low profits with high sales volumes due to competition, price sensitivity, economies of scale, brand loyalty, and consumer expectations. Types of CPG include: 1. Food (e….
7. Unilever – Dove
Domain: quartr.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: The consumer goods sector includes a range of products such as food, beverages, personal care items, and household goods. Key brands owned by major companies include: Unilever (Dove, Lipton, Ben & Jerry’s, Knorr), PepsiCo (Pepsi, Doritos, Cheetos, Gatorade, Tropicana), The Coca-Cola Company (Coca-Cola, Schweppes, Powerade, Sprite), and Procter & Gamble (Pampers, Head & Shoulders, Gillette). The se…
8. CPG – Everyday Essentials
Domain: investopedia.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Consumer packaged goods (CPG) are everyday items used regularly by consumers that must be replaced frequently. Examples include food, beverages, cosmetics, and cleaning products. The CPG sector in the U.S. is valued at approximately $2 trillion and is led by companies like Coca-Cola, Procter & Gamble, and L’Oréal. CPGs have a short shelf life and are designed for immediate consumption, contrasting…
9. Nestlé – Nescafé, KitKat, Maggi; Procter & Gamble – Pampers, Gillette, Tide; Coca-Cola – Coca
Domain: medium.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Nestlé Group: Sales: $105 Billion, Brands: Nescafé, KitKat, Maggi, Nestea. Procter & Gamble: Sales: $90 Billion, Brands: Pampers, Gillette, Tide. The Coca-Cola Company: Sales: $40 Billion, Brands: Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Fanta, Sprite. PepsiCo: Sales: $75 Billion, Brands: Pepsi, Lay’s, Gatorade. Unilever: Sales: $65 Billion, Brands: Dove, Lipton, Ben & Jerry’s. Johnson & Johnson: Sales: $80 Billion,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for largest consumer packaged goods companies
In navigating the complexities of the consumer packaged goods (CPG) landscape, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal component for success. As demonstrated by the top performers, such as Nestlé and Procter & Gamble, leveraging innovative technologies and operational efficiencies is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. By adopting digital tools and embracing artificial intelligence, these companies have not only streamlined their operations but also enhanced consumer engagement, allowing them to adapt swiftly to market changes and consumer preferences.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. It offers the opportunity to forge resilient supply chains, optimize costs, and ensure product availability in an increasingly volatile market. Buyers are encouraged to focus on partnerships with leading CPG companies that prioritize sustainability and innovation, thereby aligning with global trends and consumer expectations.
Looking ahead, the CPG sector is poised for continued evolution. By embracing strategic sourcing initiatives, international buyers can position themselves for growth, ensuring they remain responsive to market dynamics and consumer demands. Engage proactively with industry leaders to unlock new opportunities and drive mutual success.