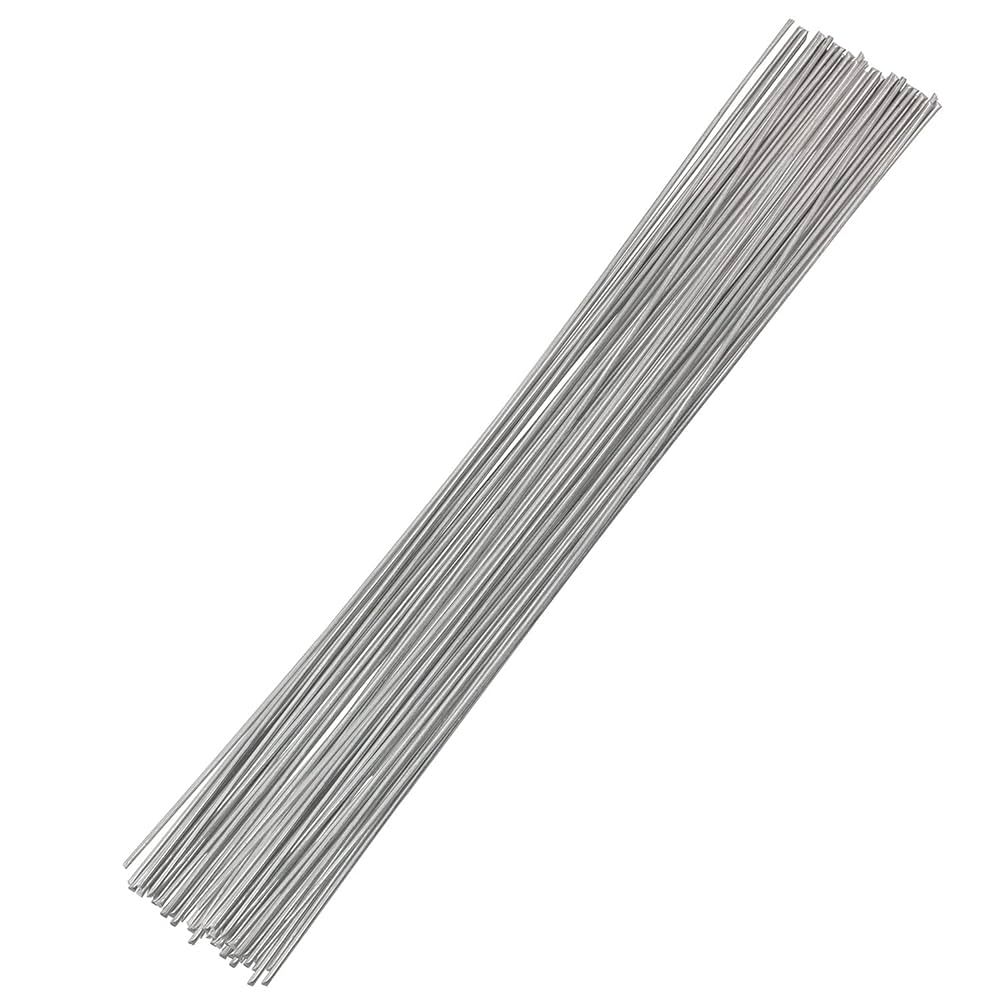
How to Source Galvanised Welding Rods Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for galvanised welding rods
As global industries increasingly prioritize durability and corrosion resistance, sourcing the right galvanised welding rods presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. These rods not only need to withstand harsh environmental conditions but also meet specific application requirements across diverse sectors, from construction to manufacturing. This comprehensive guide addresses the complexities of selecting the ideal galvanised welding rods, covering various types, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By delving into the nuances of galvanised welding rods, this resource empowers international B2B buyers—particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Brazil and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the critical properties of different welding rods, such as their resistance to molten zinc and compatibility with various welding techniques, can help mitigate risks associated with subpar materials that lead to costly repairs and project delays.
In this guide, we will explore not only the technical specifications and best practices for welding with galvanised materials but also strategies for evaluating suppliers and negotiating favorable terms. By equipping buyers with the knowledge they need to navigate the global market effectively, we aim to enhance the efficiency and success of their sourcing efforts, ensuring that their projects are built on a foundation of quality and reliability.
Understanding galvanised welding rods Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| E6011 | Versatile for all-position welding; good penetration | General fabrication, repair work | Pros: Good arc stability; works on dirty surfaces. Cons: May require post-weld cleaning. |
| E7014 | Smooth operation; suitable for thin materials; low spatter | Automotive, light structural applications | Pros: Easy to use; good appearance. Cons: Limited in thicker materials. |
| E7018 | Low hydrogen content; excellent strength and ductility | Heavy machinery, structural components | Pros: High strength; good for critical applications. Cons: Requires careful storage to avoid moisture. |
| Silicon Bronze | Non-ferrous; ideal for dissimilar metals; corrosion-resistant | Marine applications, art installations | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance; good for decorative work. Cons: Lower strength compared to steel rods. |
| FCAW (Flux-Cored Arc Welding) | High deposition rates; good for outdoor use | Construction, heavy equipment repair | Pros: Faster welding; less sensitivity to wind. Cons: Higher cost; more complex equipment needed. |
What are the Characteristics and B2B Applications of E6011 Welding Rods?
E6011 welding rods are known for their versatility, allowing for all-position welding and effective penetration into various types of steel, including galvanized materials. They are particularly useful in general fabrication and repair work, making them a staple for many businesses. When purchasing E6011 rods, buyers should consider their ease of use on dirty or rusty surfaces, although post-weld cleaning may be necessary to achieve a smooth finish.
How Does E7014 Differ from Other Galvanised Welding Rods?
E7014 rods are characterized by their smooth operation and suitability for welding thin materials, making them ideal for automotive and light structural applications. They provide a low spatter arc, resulting in a cleaner weld appearance, which is advantageous for projects where aesthetics matter. However, while they are easy to use, buyers should note that E7014 rods may not perform as well on thicker materials.
Why Choose E7018 for Heavy-Duty Applications?
E7018 rods are favored for their low hydrogen content, which provides excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for critical applications in heavy machinery and structural components. These rods require careful storage to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to weld defects. Buyers should prioritize E7018 for projects that demand high strength and reliability, despite the need for meticulous handling.
What are the Benefits of Using Silicon Bronze Welding Rods?
Silicon bronze welding rods are non-ferrous and ideal for applications involving dissimilar metals, particularly in marine environments where corrosion resistance is paramount. They are also popular for artistic and decorative projects due to their aesthetic appeal. While they offer excellent corrosion resistance, buyers should be aware that silicon bronze rods typically have lower strength compared to traditional steel rods.
How Does FCAW Enhance Galvanised Welding Processes?
Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) rods are designed for high deposition rates, making them suitable for outdoor applications and construction projects. They provide a significant advantage in windy conditions, allowing for efficient welding without compromising quality. However, buyers should consider the higher costs associated with FCAW and the need for more complex equipment, which may impact overall project budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of galvanised welding rods
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of galvanised welding rods | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Fabrication of structural steel components | Enhanced corrosion resistance and longevity | Ensure compatibility with local steel standards and regulations |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Repair and assembly of galvanized parts | Improved durability and reduced maintenance costs | Verify specifications for high-temperature resistance |
| Agriculture & Farming | Construction of farm equipment and structures | Increased lifespan of equipment in harsh climates | Assess local availability and transportation logistics |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline construction and repair | Resistance to harsh environments and corrosion | Check for certifications and compliance with industry standards |
| Renewable Energy | Installation of solar panel structures | Long-term performance in outdoor conditions | Evaluate supplier’s track record and delivery capabilities |
How Are Galvanised Welding Rods Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, galvanised welding rods are essential for fabricating structural steel components that are exposed to various environmental conditions. These rods provide enhanced corrosion resistance, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of buildings and infrastructure over time. International buyers should consider sourcing rods that meet local steel standards and regulations to ensure compliance and safety in their projects.
What Role Do Galvanised Welding Rods Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, galvanised welding rods are used for the repair and assembly of parts that are often coated to prevent rust. The use of these rods ensures improved durability and reduced maintenance costs, which are crucial for maintaining vehicle performance. Buyers must verify the specifications of the welding rods to ensure they can withstand high temperatures and provide a strong bond in automotive applications.
Why Are Galvanised Welding Rods Important in Agriculture?
Agriculture relies heavily on robust equipment and structures, such as barns and silos, where galvanised welding rods are employed for construction. These rods offer increased lifespan and durability, particularly in harsh climates where exposure to moisture and chemicals is prevalent. For international buyers, assessing local availability and transportation logistics is essential to ensure timely delivery and efficient project execution.
How Do Galvanised Welding Rods Benefit the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, galvanised welding rods are critical for pipeline construction and repair, providing resistance to corrosion in harsh environments. The longevity and reliability of these rods help prevent costly repairs and downtime, which is vital for maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers should check for certifications and compliance with industry standards to guarantee the quality and safety of the welding materials.
What Advantages Do Galvanised Welding Rods Offer in Renewable Energy Projects?
For renewable energy installations, particularly solar panel structures, galvanised welding rods are used to ensure long-term performance in outdoor conditions. The corrosion-resistant properties of these rods contribute to the overall durability of the installations, supporting the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions. Evaluating a supplier’s track record and delivery capabilities is crucial for international buyers to ensure reliable sourcing and project success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘galvanised welding rods’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Welding Rod for Galvanized Steel
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of choosing the appropriate welding rods for galvanized steel applications. The presence of zinc can lead to issues such as porosity and poor weld quality if the wrong electrode is used. Many buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the variety of options available, unsure of which rods will provide optimal results without compromising the integrity of the weld. This confusion can result in wasted resources and time, as poorly executed welds can lead to structural failures and increased costs for rework.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, it is crucial to understand the specifications of the welding rods suitable for galvanized materials. Buyers should look for electrodes that have been specifically designed for welding galvanized steel, such as E6011 or E7014, which are known for their compatibility with zinc-coated surfaces. When sourcing these rods, it is advisable to consult manufacturers’ technical data sheets that detail the performance characteristics and recommended applications of each electrode.
Additionally, conducting a small-scale test weld before commencing a larger project can help assess the suitability of the chosen welding rod, allowing for adjustments to be made if necessary. Buyers should also consider collaborating with experienced welding professionals or suppliers who can provide insights into the best practices for welding galvanized materials. This proactive approach can save time and reduce the likelihood of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Corrosion Resistance Post-Welding
The Problem:
A prevalent concern among B2B buyers is the corrosion resistance of welds made on galvanized steel. After welding, the heat can alter the protective zinc coating, leading to areas that are more susceptible to rust and corrosion. This issue is particularly critical in industries where structural integrity is paramount, such as construction and manufacturing. Buyers may worry that their projects will not meet longevity and safety standards due to inadequate corrosion protection.
The Solution:
To address this concern, buyers should prioritize using welding rods that maintain a similar corrosion resistance to the base metal. Selecting electrodes with low silicon content, such as those in the E6027 category, can help create welds that have a corrosion rate comparable to the surrounding galvanized material. Furthermore, applying a post-weld treatment, such as a cold galvanizing spray or a protective coating, can enhance the corrosion resistance of the weld area.
Buyers should also ensure that proper pre-welding procedures are followed, including cleaning the surface to remove any contaminants and ensuring the base metal is adequately prepared. This preparation can significantly improve the integrity of the weld and its resistance to corrosion. Engaging with suppliers who can offer guidance on suitable post-weld treatments is also recommended.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Welding Techniques on Galvanized Steel
The Problem:
Welding galvanized steel poses unique challenges due to the presence of zinc, which can create harmful fumes during the welding process and affect the weld quality. B2B buyers may find that traditional welding techniques do not yield satisfactory results, leading to difficulties in achieving strong, reliable welds. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions where skilled labor may be limited, and the available workforce may not have the necessary training to handle galvanized materials effectively.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, buyers should invest in training programs for their welding teams that focus specifically on techniques for working with galvanized steel. This training should cover the importance of using the right equipment and settings, such as adjusting the amperage and using appropriate filler materials to minimize the adverse effects of zinc during welding.
Moreover, employing techniques like weaving or stringer beads can help manage heat input, reducing the risk of zinc vaporization and weld defects. Providing access to quality safety equipment, including respirators and fume extraction systems, is essential to protect welders from harmful fumes. Buyers should also consider leveraging technology, such as automated welding solutions, which can enhance precision and consistency when working with galvanized materials. By fostering a well-trained workforce and investing in the right technology, companies can improve their welding outcomes and ensure the longevity and safety of their projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for galvanised welding rods
When selecting the appropriate welding rods for galvanized materials, it is crucial to consider various factors such as corrosion resistance, compatibility with the base metal, and the specific requirements of the application. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in galvanised welding rods, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of E6011 Welding Rods?
E6011 welding rods are designed for all-position welding and are particularly effective for welding galvanized steel. They exhibit good penetration and can handle dirty or rusty surfaces, making them versatile in various environments.
- Key Properties: E6011 rods have a low hydrogen content, allowing them to perform well in high-humidity conditions. They are suitable for both AC and DC welding, providing flexibility in equipment use.
- Pros: They are cost-effective and widely available, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Their ability to weld through contaminants adds to their utility.
- Cons: The welds may not be as strong as those made with other rods, such as E7018. Additionally, they can produce more spatter, which may require additional cleanup.
- Impact on Application: E6011 rods are ideal for general fabrication and repair work where surface cleanliness cannot be guaranteed.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local welding standards (e.g., AWS) is essential. Buyers should also be aware of regional preferences for specific rod types, as some markets may favor E7018 for its superior strength.
How Does E7018 Compare for Galvanized Welding?
E7018 rods are known for their high strength and low hydrogen content, making them suitable for structural applications.
- Key Properties: They provide excellent ductility and toughness, with a high tensile strength rating. E7018 rods are best used in applications requiring strong, durable welds.
- Pros: The welds produced are smooth and have a low likelihood of cracking. They are suitable for high-stress applications, making them a preferred choice for structural work.
- Cons: E7018 rods require a dry environment and must be stored properly to avoid moisture absorption, which can lead to hydrogen-induced cracking.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for structural applications, E7018 rods are commonly used in construction and heavy fabrication where strength is paramount.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the rods meet ASTM specifications and consider the availability of storage facilities to maintain rod quality.
What are the Benefits of Using Silicon Bronze Welding Rods?
Silicon bronze rods are often used for welding galvanized steel due to their excellent corrosion resistance.
- Key Properties: These rods have a lower melting point and excellent fluidity, making them suitable for welding thin materials.
- Pros: Silicon bronze rods do not react with zinc, reducing the risk of weld degradation in galvanized applications. They also provide a clean finish and are less prone to spatter.
- Cons: The strength of silicon bronze welds is lower than that of steel welds, which may limit their use in load-bearing applications.
- Impact on Application: These rods are ideal for applications where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in marine environments or chemical processing.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local standards and consider the specific application requirements when choosing silicon bronze rods.
Why Choose E6013 Welding Rods for Galvanized Steel?
E6013 rods are known for their versatility and ease of use, making them a popular choice for various welding applications.
- Key Properties: These rods are designed for all-position welding and provide a smooth, stable arc with minimal spatter.
- Pros: E6013 rods are user-friendly and can be used on thin materials, making them suitable for light fabrication and repair work.
- Cons: They may not penetrate as deeply as other rods, which can be a disadvantage in thicker materials or high-stress applications.
- Impact on Application: Best suited for light to medium fabrication, E6013 rods are often used in automotive and household repairs.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that E6013 rods meet relevant welding standards and consider local market preferences for rod selection.
Summary Table of Galvanised Welding Rods
| Material | Typical Use Case for galvanised welding rods | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E6011 | General fabrication and repair | Cost-effective and versatile | Weaker welds with more spatter | Low |
| E7018 | Structural applications | High strength and ductility | Requires dry storage | High |
| Silicon Bronze | Marine and chemical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| E6013 | Light to medium fabrication | User-friendly and smooth arc | Limited penetration on thick materials | Low |
This guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding the selection of welding rods for galvanized materials, ensuring compliance with local standards and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for galvanised welding rods
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Galvanised Welding Rods?
The manufacturing of galvanised welding rods involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the rods meet the rigorous demands of welding applications. Here’s a breakdown of the main processes involved:
How Is Material Prepared for Galvanised Welding Rods?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality steel is selected as the base material due to its strength and weldability. The steel is then subjected to various treatments, including:
-
Cleaning: The steel is cleaned to remove any surface contaminants, such as oils, dust, and rust. This is typically done using solvents or abrasive techniques to ensure a clean surface for coating.
-
Cutting: The steel is cut into specific lengths, depending on the type of welding rod being produced. Precision in this step is crucial, as it influences the final product’s performance.
-
Alloying: Depending on the specific application, alloying elements may be added to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance and strength. For galvanised welding rods, maintaining a balance of elements is vital to ensure compatibility with the galvanisation process.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Assembly?
After material preparation, the forming and assembly stage begins. This stage typically includes:
-
Drawing: The steel is drawn through a series of dies to achieve the desired diameter and shape. This process can be done cold or hot, depending on the specifications required.
-
Coating: The rods undergo a galvanisation process, where they are coated with a layer of zinc. This is usually done through hot-dip galvanising, where the rods are immersed in molten zinc, providing a robust protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance.
-
Cooling: After galvanisation, the rods are cooled in a controlled environment to ensure that the zinc coating adheres properly and maintains its integrity.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Galvanised Welding Rod Production?
Finishing processes enhance the properties of the welding rods and prepare them for packaging and distribution. Key finishing techniques include:
-
Inspection: Each rod is inspected for uniformity in coating thickness and surface defects. This step ensures that any imperfections are identified before the product reaches the customer.
-
Packaging: The rods are then bundled and packaged, often with protective materials to prevent damage during transport. Proper packaging is essential, especially for international shipping, to ensure that the rods arrive in optimal condition.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Galvanised Welding Rods?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for galvanised welding rods. It ensures that the products meet international and industry-specific standards, which is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What International Standards Apply to Galvanised Welding Rods?
Manufacturers of galvanised welding rods often adhere to several international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, this marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers supplying the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that the products meet the stringent requirements of that sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. This includes checking the chemical composition and physical properties of the steel.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters such as temperature, coating thickness, and mechanical properties are monitored to ensure they remain within specified limits.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, the finished rods undergo a final inspection to verify that they meet all specifications, including dimensional accuracy and coating quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of galvanised welding rods, including:
- Tensile Testing: This measures the strength and ductility of the rods, ensuring they can withstand the stresses encountered during welding.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Specialized tools are used to measure the thickness of the zinc coating, as insufficient coating can lead to premature corrosion.
- Visual Inspections: Trained inspectors conduct visual checks to identify surface defects or inconsistencies in the coating.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, especially those from international markets, should implement measures to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can provide insights into their adherence to international standards.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for documentation of their quality assurance processes, including test results and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product reliability.
-
Certifications Verification: Ensure that suppliers hold the necessary certifications (ISO, CE, API) and verify their authenticity. This helps in confirming the credibility of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Differences in regulatory requirements and standards across regions can impact product quality and compliance. Buyers should be aware of:
-
Regional Standards: Familiarize themselves with the specific standards and regulations applicable in their region. For example, buyers in Europe may need to prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on compliance with local regulations.
-
Cultural and Operational Differences: Recognize that manufacturing practices can vary by region, which may affect quality control methods. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better understanding and compliance.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce risks, such as damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling protocols to mitigate these risks.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing galvanised welding rods, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘galvanised welding rods’
Introduction
Sourcing high-quality galvanised welding rods is essential for businesses engaged in metal fabrication and construction. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring that they select the right materials and reliable suppliers. By following these steps, you can enhance your operational efficiency and ensure the longevity of your welding projects.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensuring that the welding rods meet your project’s requirements. Consider factors such as the type of steel being welded, the thickness of the materials, and the desired welding process (e.g., stick welding, TIG, or MIG). Specific requirements for silicon content and compatibility with molten zinc should also be noted, as these can significantly affect weld quality.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Standards
Verify that the galvanised welding rods comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This includes checking for compliance with AWS (American Welding Society) specifications or equivalent standards in your region. Compliance ensures that the rods meet safety and performance benchmarks, which is especially important when operating in industries such as construction or manufacturing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it is vital to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, product samples, and references from other businesses in your industry. Assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and delivery timelines to ensure they can meet your needs consistently.
- Check Reviews and Testimonials: Look for feedback from previous customers regarding product quality and service reliability.
- Assess Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure that the supplier provides clear information about their sourcing and manufacturing processes.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Always request samples of the galvanised welding rods before placing a bulk order. Testing the samples in your specific welding conditions allows you to assess their performance, ease of use, and compatibility with your equipment. This step minimizes the risk of costly errors in production.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing, payment terms, and delivery options. Keep in mind that the lowest price does not always equate to the best value; consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential import duties. Look for suppliers that offer favorable payment terms and bulk purchase discounts.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
Choose a supplier that provides robust after-sales support and warranty options. This ensures that you can receive assistance with any issues that arise post-purchase, such as product defects or performance concerns. A solid warranty can also protect your investment, giving you peace of mind regarding the quality of the welding rods.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you’ve found a reliable supplier, consider establishing a long-term partnership. Building a strong relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products or technologies. Regular communication and feedback can enhance collaboration and ensure that your evolving needs are met effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for galvanised welding rods Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing Galvanised Welding Rods?
When considering the procurement of galvanised welding rods, understanding the various cost components is essential for effective budgeting. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of raw materials significantly influences the cost. High-grade steel and zinc coatings are crucial for durability and performance. Suppliers often offer different grades, which can affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages for workers involved in the manufacturing process. This includes skilled labor for welding and quality control checks.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses that support production but are not directly tied to any one unit of output.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific welding rod designs, particularly for rods with unique specifications or features. This upfront investment can affect initial pricing but may lead to lower costs per unit in large-scale production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that welding rods meet industry standards and certifications requires investment in quality control processes. This can include testing for tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and shipping conditions. International buyers should be aware of these costs, as they can significantly impact the overall price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market competition. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, reliability, and product quality.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Galvanised Welding Rods?
Several factors influence the pricing of galvanised welding rods, particularly for international B2B buyers. Key influencers include:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate for lower prices based on their order size.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or unique requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality rods that meet specific industry certifications typically command a premium price. Buyers should verify certifications to ensure they are getting the best value.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed Incoterms is crucial, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This affects the total landed cost of the products.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices on Galvanised Welding Rods?
International B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing galvanised welding rods:
-
Research and Compare: Gather pricing data from multiple suppliers to understand the market rate. This knowledge will strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the welding rods, including maintenance and replacement. Sometimes a higher upfront cost can lead to lower overall expenses.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Regular communication and feedback can foster loyalty and encourage favorable negotiations.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local demand, availability, and economic conditions. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions.
Conclusion
While sourcing galvanised welding rods, it’s essential to consider the intricate cost structure and various price influencers. By understanding these elements, international B2B buyers can negotiate better deals, enhance cost efficiency, and ultimately make informed purchasing decisions. Always remember to approach suppliers with a clear understanding of your requirements and the current market conditions to achieve optimal pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing galvanised welding rods With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to Galvanised Welding Rods
In the welding industry, selecting the right materials can significantly impact the quality and durability of the final product. While galvanised welding rods are a popular choice due to their resistance to corrosion, several alternative solutions may offer distinct advantages depending on the specific application and environment. This analysis compares galvanised welding rods with two viable alternatives: Silicon Bronze Welding Rods and Stainless Steel Welding Rods.
| Comparison Aspect | Galvanised Welding Rods | Silicon Bronze Welding Rods | Stainless Steel Welding Rods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for mild steel; performs well with minimal surface prep | Excellent for dissimilar metals; lower heat input required | High strength and corrosion resistance; suitable for various environments |
| Cost | Moderate; often more affordable than specialized rods | Higher initial cost; often more expensive than galvanised rods | Typically high; costs vary based on grade and application |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some surface prep; effective with proper technique | Easier to work with; less fume generation | Requires advanced skills; may need specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required to prevent corrosion | Low maintenance; good for long-term applications | Low maintenance; highly durable |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for outdoor structures and general fabrication | Best for marine applications, art, and dissimilar metal welding | Suitable for high-stress environments, food processing, and medical applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Silicon Bronze Welding Rods
Silicon bronze welding rods are particularly advantageous when welding dissimilar metals or when a lower heat input is required. They produce less fume, making them suitable for applications where air quality is a concern. However, their initial cost is typically higher than that of galvanised rods, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Despite this, their excellent corrosion resistance makes them a long-term investment, especially in marine or humid environments.
Stainless Steel Welding Rods
Stainless steel welding rods are renowned for their strength and exceptional resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. They are suitable for demanding applications, such as in the food processing or medical industries, where hygiene and durability are critical. However, they require skilled welders and specialized equipment, which may increase overall project costs. Additionally, the higher price point can be a barrier for some buyers, but the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a welding solution, B2B buyers must consider the specific requirements of their projects, including material compatibility, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Galvanised welding rods offer a balanced combination of cost and performance for general applications, while silicon bronze and stainless steel rods provide specialized benefits for unique situations. Ultimately, the choice should align with the project’s long-term goals, ensuring durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness in the welding process. By weighing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for galvanised welding rods
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Galvanised Welding Rods?
When selecting galvanised welding rods, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and durability in applications. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the welding rod based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades for galvanised welding rods include E6011 and E7014. The choice of material grade impacts the rod’s suitability for different welding conditions, including the ability to withstand corrosion from molten zinc. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for achieving strong, reliable welds that meet project specifications.
2. Silicon Content
Silicon content is a critical factor in determining how well a welding rod performs when welding galvanised steel. A lower silicon percentage (typically less than 0.25%) is recommended, as it reduces the risk of excessive reaction with molten zinc. This property ensures that the weld does not erode quickly, providing longevity and reducing maintenance costs. For businesses, this means fewer repairs and less downtime.
3. Welding Process Compatibility
Welding rods can be compatible with various welding processes, including Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), and Submerged Arc Welding (SAW). Each process has its unique advantages and is suited for different applications. Understanding the compatibility of a welding rod with specific processes helps businesses choose the right equipment and methods, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
4. Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength refers to the ability of the weld to withstand loads and stresses. This property is measured in terms of tensile strength and yield strength. High mechanical strength is essential for structural applications where safety and reliability are paramount. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the welding rods used can meet or exceed the required mechanical strength is crucial to maintaining quality standards in production.
5. Diameter and Length
The diameter and length of welding rods affect their usability and the type of welding tasks they can perform. Common diameters range from 1/16 inch to 1/8 inch. The size must match the welding application to ensure optimal heat input and penetration. For businesses, selecting the correct rod size can lead to improved weld quality and reduced material waste.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Galvanised Welding Rod Industry?
Navigating the world of galvanised welding rods also involves understanding industry-specific terminology. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of welding rods, understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality standards in production.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and ensuring that sufficient stock is available for ongoing projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers of galvanised welding rods, an RFQ enables them to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing of welding rods, as they clarify aspects like shipping costs, risk, and delivery obligations.
5. Welding Electrode Classification
This classification system, established by the American Welding Society (AWS), categorizes welding rods based on their properties and applications. Familiarity with these classifications helps buyers select the right welding rods for specific projects, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the technical properties and trade terminology related to galvanised welding rods is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge aids in making informed purchasing decisions, optimizing project outcomes, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the galvanised welding rods Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Galvanised Welding Rods in International B2B?
The global market for galvanised welding rods is experiencing a surge driven by the increasing demand for durable and corrosion-resistant materials across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand, the need for reliable welding solutions has become paramount. In particular, emerging economies like Brazil and Nigeria are witnessing rapid industrial growth, which fuels the demand for high-quality welding materials. Additionally, technological advancements in welding processes, such as automated welding and improved electrode formulations, are reshaping sourcing trends. International B2B buyers are increasingly turning to suppliers who offer innovative products that enhance welding efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Moreover, the shift towards online sourcing platforms and digital marketplaces is making it easier for buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products. The use of data analytics in procurement processes is helping businesses to make informed decisions based on market trends and supplier performance. As environmental regulations become stricter, the demand for welding rods that comply with sustainability standards is also on the rise, prompting suppliers to innovate and adapt their offerings accordingly.
How Does Sustainability Influence the Sourcing of Galvanised Welding Rods?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers of galvanised welding rods. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, including high energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to seek out suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. The adoption of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, is increasingly important in supplier selection. Buyers are looking for materials that not only meet their performance requirements but also contribute to reducing their carbon footprint.
Furthermore, the integration of recycled materials in the production of galvanised welding rods is gaining traction. Suppliers who can demonstrate responsible sourcing and production methods are more likely to attract international buyers who are committed to corporate social responsibility. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are pushing industries towards greater sustainability. By prioritizing ethical supply chains, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers and partners.
What Has Been the Evolution of Galvanised Welding Rods in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of galvanised welding rods can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for corrosion-resistant materials became evident in industrial applications. Initially, the focus was primarily on enhancing the mechanical properties of welding rods to withstand harsh environments. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and coating technologies have significantly improved the performance and durability of these rods.
The introduction of specialized electrodes designed for welding galvanized steel has further refined the market. These innovations have addressed challenges such as zinc-related weld degradation and ensured that welds maintain integrity over time. Today, the landscape is characterized by a diverse range of products tailored for specific applications, including those that comply with modern environmental standards. As global demand continues to rise, the galvanised welding rods sector is poised for ongoing innovation, driven by both technological advancements and evolving market needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of galvanised welding rods
-
How do I select the right galvanised welding rods for my project?
Selecting the right galvanised welding rods involves considering the base materials and the application requirements. Look for rods specifically designed for welding galvanized steel, such as E6011 or E7014, which are known for their compatibility and performance. Additionally, assess the thickness of the materials being welded and the position of the weld (overhead, vertical, etc.). Consulting technical specifications and supplier recommendations can further ensure you choose rods that will yield strong, durable joints while minimizing issues like spatter and poor penetration. -
What is the best welding rod for welding galvanized steel?
The best welding rod for galvanized steel often depends on the specific requirements of the project. E7014 and E6011 rods are commonly recommended due to their ability to perform well in various positions and with minimal cleanup. For thin materials, rods with a lower amperage rating may be beneficial to prevent burning through. It’s crucial to consider the welding process (SMAW, FCAW, etc.) and the environment in which you are working, as these factors can influence rod selection. -
What are the common challenges when welding galvanized steel?
Welding galvanized steel presents challenges such as zinc fumes, which can be hazardous if inhaled. The zinc coating can also cause poor weld quality if not adequately managed, leading to issues like porosity or lack of fusion. To mitigate these challenges, pre-clean the weld area to remove zinc, use appropriate ventilation, and select the right welding rod. Understanding the properties of the materials involved and following best practices in welding will help overcome these challenges. -
What should I consider when sourcing galvanised welding rods internationally?
When sourcing galvanised welding rods internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, product certifications, and compliance with local standards. Evaluate the quality control processes in place to ensure consistent product quality. Additionally, assess the supplier’s ability to meet your demand in terms of minimum order quantities (MOQs) and delivery timelines. Understanding import regulations and potential tariffs in your country is also crucial for budgeting and logistics planning. -
How can I vet suppliers of galvanised welding rods?
Vetting suppliers requires thorough research into their credentials, industry experience, and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate product quality and performance before placing a larger order. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, certifications (such as ISO), and compliance with international standards. Establishing communication with previous customers can also provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality. -
What are typical payment terms for international orders of galvanised welding rods?
Payment terms for international orders can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific agreement. Common terms include letters of credit (LC), advance payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect your interests while ensuring the supplier’s commitment. Be sure to clarify currency exchange considerations and transaction fees, as these can impact overall costs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for galvanised welding rods?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for galvanised welding rods typically varies by supplier and can depend on factors such as manufacturing capabilities and shipping logistics. Many suppliers may set MOQs to cover production costs and ensure profitability. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with suppliers, as some may offer flexibility or tiered pricing based on volume, which could be beneficial for large-scale projects. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of galvanised welding rods?
Logistics and shipping play a critical role in the procurement process of galvanised welding rods, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and customs clearance can affect delivery schedules and costs. It’s vital to work closely with suppliers to understand their shipping options and choose the most reliable and cost-effective method. Additionally, consider local regulations regarding imports and any potential tariffs that could impact your overall budget.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Galvanised Welding Rods Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. WeldingWeb – Best Stick Electrodes for Galvanized Steel
Domain: weldingweb.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Best stick electrodes for welding galvanized steel include: 6011, 6010, 7016, and E6022. 6011 and 6010 are commonly recommended for their effectiveness. E6022 is noted for puddle welding galvanized decking but is not suitable for out-of-position welding. Safety precautions include wearing a respirator to avoid zinc fume exposure.
2. Hobart – Welding Galvanized Pipe to Sucker Rod
Domain: weldtalk.hobartwelders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Welding galvanized pipe to sucker rod for a farm gate. Recommended welding rods: 7018 (1/8 and 3/32), with a preference for 3/32 at about 100 amps. It is advised to grind off the galvanized coating before welding. Sucker rod may contain high carbon or chrome-moly steel.
3. Central Mobile Welding – 7018 Welding Rod for Galvanized Steel
Domain: centralmobilewelding.ca
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Best welding rod for galvanized steel: 7018. Important note: Grind off the zinc coating before welding and apply cold-galvanizing spray after welding.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for galvanised welding rods
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of galvanised welding rods is essential for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and ensure product longevity. By selecting the right welding materials, particularly those with optimal silicon content and corrosion resistance, companies can prevent costly repairs and maintain the integrity of their projects. Understanding regional preferences and local market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is crucial for effective procurement.
As the demand for galvanised steel applications continues to grow, international buyers must prioritize suppliers who offer quality, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Emphasizing relationships with manufacturers who can deliver innovative solutions and tailored support will further enhance your competitive edge.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies and align with partners that can meet evolving industry needs. By investing in the right welding materials and fostering strong supplier relationships, businesses can position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected marketplace. Engage with your suppliers today to explore opportunities that can drive your success in the galvanised welding rod sector.