Everything You Need to Know About 2 Rail Edge Conveyor With Stepper Motor Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
Navigating the complexities of sourcing a 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially in rapidly evolving markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the increasing demand for efficient material handling in sectors like electronics manufacturing, understanding the nuances of these conveyor systems is crucial. This guide aims to illuminate the essential aspects of the 2 rail edge conveyor, exploring various types, their applications, and the critical factors involved in supplier vetting.
As you delve into this comprehensive resource, you will gain insights into the performance capabilities of stepper motors, their integration in conveyor systems, and their role in enhancing operational efficiency. We will cover vital considerations, including cost analysis, maintenance requirements, and the latest technological advancements that align with Industry 4.0 standards. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that not only meet your operational needs but also align with your strategic objectives.
Whether you are looking to streamline production lines in Brazil or enhance logistics efficiency in Saudi Arabia, this guide is designed to serve as your go-to resource for navigating the global market for 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors.
Understanding 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor | Modular design, ESD-safe, customizable lengths, high-speed DC stepper motors | Electronics manufacturing, PCB conveyance | Pros: Durable, customizable; Cons: Higher initial cost |
| GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor | Compact, lightweight, customizable widths and lengths, various drive options | Assembly lines, small parts transport | Pros: Economical, versatile; Cons: Limited load capacity |
| Inline SMT Edge Belt Conveyor | Designed for PCB transport, SMEMA compliant, inspection-friendly features | PCB manufacturing, inspection, buffering | Pros: User-friendly, low maintenance; Cons: Specific to electronics |
| Multi-Stage Edge Conveyor | Multiple stages for enhanced buffering, adjustable height, and speed control | Automated production lines, multi-step processes | Pros: Improved efficiency; Cons: Complexity in setup |
| Portable Edge Belt Conveyor | Lightweight, easy to relocate, flexible in operation modes | Temporary setups, trade shows, mobile manufacturing needs | Pros: Flexibility, ease of use; Cons: Less robust for permanent installations |
What Are the Key Characteristics of the Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor?
The Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor is designed specifically for the electronics industry, featuring a modular structure that allows for customization in length and drive configuration. Its electrostatic dissipative construction ensures safe transport of sensitive materials like PCBs. The high-speed DC stepper motors enable precise control over speed and torque, making it suitable for high-volume production lines. Buyers should consider the initial investment versus the long-term durability and service life, which averages over 15 years.
How Does the GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor Stand Out?
The GUF-P MINI is a compact and lightweight solution ideal for transporting small, lightweight products. Its flexible design accommodates various widths and lengths, making it suitable for tight spaces in assembly lines. With options for different drive motors, including stepper motors, it can adapt to specific operational needs. Buyers should assess the load capacity and integration ease with existing systems, as its lightweight nature may limit its use in heavier applications.
What Are the Benefits of the Inline SMT Edge Belt Conveyor?
The Inline SMT Edge Belt Conveyor is tailored for the PCB manufacturing process, offering features like SMEMA compliance and inspection capabilities. Its design allows for buffering and transporting PCBs between machines efficiently. It is user-friendly and requires minimal maintenance, which is a significant advantage for busy production environments. Buyers should evaluate its suitability for specific PCB sizes and thicknesses to ensure compatibility with their manufacturing processes.
Why Consider a Multi-Stage Edge Conveyor?
Multi-Stage Edge Conveyors are designed to enhance buffering capabilities in automated production lines. They feature adjustable heights and speeds, allowing for flexibility in various production scenarios. This type of conveyor is particularly effective in multi-step processes where efficiency is crucial. Buyers should consider the complexity of setup and maintenance, as the added stages may require more intricate management compared to simpler conveyor systems.
What Makes a Portable Edge Belt Conveyor Ideal for Temporary Needs?
Portable Edge Belt Conveyors are designed for flexibility and ease of relocation, making them perfect for temporary setups at trade shows or mobile manufacturing needs. They offer various operational modes and can be quickly integrated into different workflows. While they provide significant advantages in terms of mobility, buyers should be aware of their limited robustness compared to fixed installations, which may affect long-term performance in high-demand environments.
Key Industrial Applications of 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics Manufacturing | Transporting and buffering Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) | Enhanced efficiency in assembly lines, reducing manual handling and errors. | Compatibility with ESD-sensitive materials, modular design for easy integration. |
| Automotive Industry | Assembly line for automotive components | Streamlined production processes, improved quality control. | Durability under heavy loads, adaptability to various component sizes. |
| Food Processing | Conveying packaged goods through production lines | Increased throughput and reduced labor costs. | Hygiene standards compliance, ease of cleaning and maintenance. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Transporting vials and medical devices during production | Ensures precise handling, reducing contamination risks. | Customization for different vial sizes, compliance with industry regulations. |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Automated sorting and packaging of small parts | Improved accuracy and speed in order fulfillment. | Integration with existing warehouse management systems, flexibility for various product types. |
How is the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor Utilized in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, the 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor is instrumental in transporting and buffering Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) during assembly. This application addresses the need for precision handling of ESD-sensitive materials, minimizing the risk of damage or contamination. Buyers in this sector must consider compatibility with ESD environments, modular design for seamless integration into existing production lines, and the ability to customize conveyor lengths to fit specific workflows.
What Role Does the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, these conveyors are critical for the assembly of various components, such as engine parts and electronic systems. The stepper motor allows for precise speed control, ensuring that components are delivered at the right pace for assembly. This leads to enhanced production efficiency and improved quality control. International buyers should prioritize durability to withstand heavy loads and consider the conveyor’s adaptability to different component sizes and weights.
How is the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor Beneficial in Food Processing?
In food processing, the 2 rail edge conveyor facilitates the transportation of packaged goods through various production stages. This application is vital for increasing throughput while reducing manual labor costs. For businesses in this sector, sourcing considerations include compliance with hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and the ability to handle various packaging types without damaging them.
What Advantages Does the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor Provide in Pharmaceuticals?
The pharmaceutical industry utilizes the 2 rail edge conveyor for transporting vials and medical devices during production. This ensures precise handling, which is crucial for maintaining product integrity and minimizing contamination risks. Buyers should focus on customization options for different vial sizes and compliance with strict industry regulations to ensure safety and efficacy in their operations.
How Does the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor Enhance Logistics and Warehousing Operations?
In logistics and warehousing, the 2 rail edge conveyor is used for automated sorting and packaging of small parts. This enhances accuracy and speed in order fulfillment processes, which is essential for meeting customer demands in a timely manner. Key sourcing considerations for international buyers include the conveyor’s ability to integrate with existing warehouse management systems and its flexibility to accommodate various product types and sizes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Adjusting Conveyor Speed for Varying Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to adjust the speed of 2 rail edge conveyors to accommodate different products. In industries such as electronics manufacturing, where precision and timing are crucial, a conveyor that cannot easily adjust its speed can lead to inefficient operations. This may result in production bottlenecks, increased wear and tear on machinery, or even damage to delicate items like printed circuit boards (PCBs).
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing conveyors with advanced stepper motor technology that offers precise control over speed settings. When specifying a conveyor, look for models that include multiple preset speeds and adjustable speed controls. Additionally, integrating a programmable logic controller (PLC) can enhance the system’s flexibility, allowing for seamless adjustments during operation. Training staff on how to effectively use these controls will further optimize the conveyor’s performance, ensuring that the speed can be adjusted quickly to meet varying production requirements.
Scenario 2: Managing ESD Sensitivity in Electronics Manufacturing
The Problem: In sectors dealing with electronic components, static electricity can pose a serious risk, potentially damaging sensitive materials like PCBs. B2B buyers are particularly concerned about ensuring that their conveyor systems are designed to handle electrostatic discharge (ESD) safely. Failure to manage ESD can lead to costly product defects and increased warranty claims, affecting the bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate ESD risks, buyers should select 2 rail edge conveyors specifically designed with ESD-safe materials and features. Look for conveyors that incorporate electrostatic dissipative (ESD) belts and grounding options, such as wrist strap receptacles for operators. It’s crucial to evaluate the entire conveyor system’s design to ensure it minimizes static build-up, including the frame materials and operational environment. Regular training on ESD protocols for employees operating the conveyor will also help reinforce safe practices, ultimately protecting sensitive components throughout the manufacturing process.
Scenario 3: Limited Flexibility in Conveyor Design and Integration
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges with the rigidity of conveyor systems, particularly when trying to integrate them into existing production lines or when needing to modify their layout. A lack of flexibility can lead to increased costs and operational downtime, especially in industries where production lines frequently change to accommodate new products or processes.
The Solution: Buyers should seek out modular 2 rail edge conveyors that can be easily customized in terms of length, width, and configuration. Choose systems that allow for easy integration with other equipment and offer features such as adjustable in-feed tips and bi-directional operation. Consulting with manufacturers about future needs during the purchasing process can also help ensure that the conveyor system can evolve alongside the business. Additionally, considering options that allow for quick assembly and disassembly will facilitate faster layout changes, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
What are the Key Materials for a 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor?
When selecting materials for a 2 rail edge conveyor with a stepper motor, it is crucial to consider properties such as durability, compatibility with the transported media, and environmental factors. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these conveyors: aluminum, stainless steel, plastic composites, and mild steel.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it easy to handle and install, reducing overall shipping costs. However, it may not be suitable for high-load applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel. Additionally, while aluminum is relatively cost-effective, it can be more expensive than some plastics.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring frequent adjustments or mobility, as its lightweight nature allows for easy modifications. It is compatible with ESD-sensitive materials, making it suitable for electronics manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum grades. In regions like Africa and South America, where corrosion from humidity may be a concern, selecting anodized aluminum can enhance durability.
Stainless Steel: Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, which is beneficial in industrial settings.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long service life, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run. However, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum and plastics, which may increase shipping and installation costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective in food processing and pharmaceutical applications where hygiene is critical. Its non-reactive nature makes it suitable for transporting sensitive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with hygiene standards (e.g., FDA, USDA) is essential for buyers in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe. Buyers should also consider the specific grades of stainless steel that meet local regulations.
Plastic Composites: Cost-Effective and Lightweight
Key Properties: Plastic composites are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into various shapes. They are generally less durable than metals but offer good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic composites is their low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads, limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are suitable for light-duty applications and environments where chemical exposure is a concern. They are often used in packaging and light assembly processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic composites meet relevant chemical resistance standards, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. Certifications such as ISO may be required in various regions.
Mild Steel: Economical but Less Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Mild steel is strong and cost-effective but is prone to rust and corrosion if not properly treated. It can handle heavy loads and is suitable for structural applications.
Pros & Cons: The affordability of mild steel makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Mild steel is often used in heavy-duty applications where strength is prioritized over corrosion resistance. It is suitable for environments where exposure to moisture is minimal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in humid regions like Brazil and parts of Africa should consider protective coatings or galvanization to enhance corrosion resistance. Compliance with local standards for structural integrity is also crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor
| Material | Typical Use Case for 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Electronics manufacturing, ESD-sensitive materials | Lightweight and easy to handle | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceutical applications | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Plastic Composites | Packaging, light assembly processes | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited temperature and load capacity | Low |
| Mild Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Economical and strong | Prone to corrosion | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials available for 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor?
The manufacturing process for a 2 rail edge conveyor with a stepper motor involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets both performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The initial stage focuses on selecting high-quality materials suitable for the conveyor’s operational demands. Common materials include aluminum for the frame, fiberglass-reinforced belts, and durable plastics for components like guides and covers. These materials undergo inspection to verify that they meet specified standards, including strength, flexibility, and resistance to electrostatic discharge (ESD), particularly vital for electronics manufacturing. -
Forming
In this phase, the raw materials are shaped into their final forms. This includes cutting the aluminum extrusions to length, molding plastic components, and preparing the conveyor belt. Advanced techniques such as CNC machining and laser cutting are often employed to achieve precise dimensions and finishes. This accuracy is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and minimizing wear during conveyor use. -
Assembly
The assembly stage integrates all components into a functional conveyor system. This process typically involves mounting the stepper motor, attaching the conveyor belt, and installing the control systems, including PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). Workers or automated systems perform quality checks at this stage to ensure proper fit and function. For example, alignment of the motor and belt is critical to prevent jams and maintain speed. -
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves testing and refining the conveyor system. This includes applying protective coatings, conducting functional tests, and adjusting settings for speed and torque. The finishing process ensures that the conveyor not only meets aesthetic standards but also operates efficiently under load.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in the Production of 2 Rail Edge Conveyors?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of manufacturing, especially for equipment used in critical applications such as electronics assembly. Manufacturers often adhere to international standards, such as ISO 9001, to ensure consistent quality.
-
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
Adhering to ISO 9001 helps manufacturers establish a quality management system (QMS) that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. In addition to ISO, other certifications like CE mark for European compliance and specific industry standards like IPC SMEMA 9851 for electronics are also essential. These standards ensure that the conveyor systems are safe, reliable, and suitable for their intended applications. -
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process and typically includes several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to catch any issues early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to verify that it meets all operational and safety standards. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Verification?
Testing methods may include:
– Functional Testing: Ensures that the conveyor operates as intended, including speed and load capacity tests.
– Stress Testing: Evaluates the conveyor’s performance under maximum load conditions to ensure durability.
– Electrical Testing: Confirms that electrical components function correctly and safely.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers.
-
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and QC measures in place. Buyers should look for suppliers who allow on-site audits or provide detailed documentation of their quality management systems. An audit can help identify potential risks in the supply chain and ensure compliance with international standards. -
What Documentation and Reports Should Be Requested?
Buyers should request quality assurance documentation, including:
– Certificates of Compliance: Verification that products meet relevant standards.
– Test Reports: Detailed results from functional and stress testing.
– Quality Management System Documentation: Information about the supplier’s adherence to ISO 9001 or other relevant certifications. -
Are Third-Party Inspections Beneficial?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct thorough assessments of the manufacturing process and final products, providing unbiased reports to buyers. This is particularly important for international transactions, where buyers may not have the ability to conduct on-site inspections themselves.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific quality control nuances to ensure their procurement processes are robust.
-
How Do Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements that affect product quality. For example, CE marking is mandatory in Europe, while specific certifications may be required in South America or the Middle East. Understanding these regional differences is critical for compliance and market entry. -
What Role Does Cultural Understanding Play in Supplier Relationships?
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers often involves understanding cultural differences in business practices and communication. Buyers should be aware of these nuances to foster collaboration and ensure that quality standards are upheld throughout the supply chain. -
How Can Buyers Ensure Ongoing Quality After Purchase?
Buyers should establish a feedback loop with suppliers to address any quality issues that may arise post-purchase. Regular communication, performance reviews, and collaborative problem-solving can help maintain high-quality standards over time.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices surrounding 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors are critical for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure high-quality equipment for their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor’
Introduction
In the quest for efficient material handling solutions, sourcing a 2 rail edge conveyor with a stepper motor is a critical decision for B2B buyers. This guide serves as a practical checklist to help you navigate the procurement process, ensuring you select a conveyor system that meets your operational needs while adhering to industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of your conveyor system. Consider factors such as load capacity, dimensions, speed, and specific applications (e.g., conveying printed circuit boards). Understanding these specifications helps in selecting a conveyor that aligns with your operational goals and minimizes the risk of underperformance.
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum weight the conveyor will transport.
- Speed Requirements: Specify the speed at which materials need to be moved.
Step 2: Research Available Features
Familiarize yourself with the available features of 2 rail edge conveyors. Many models come equipped with advanced capabilities such as adjustable speed controls, emergency stop mechanisms, and integrated communication protocols like SMEMA.
- Stepper Motor Benefits: Look for precision control over velocity and torque, which enhances operational efficiency.
- Modularity: Ensure the conveyor can be customized in terms of length and drive sections to fit your specific setup.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request documentation such as company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies relevant to your industry.
- Certifications: Verify that the suppliers meet international standards and have the necessary certifications for quality assurance.
- Reputation: Investigate the supplier’s track record in your region, particularly in markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Reach out to shortlisted suppliers for detailed quotations. This should include pricing, delivery timelines, and terms of service.
- Comparative Analysis: Use these quotes to compare not only prices but also the value-added services offered, such as installation and after-sales support.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure that the warranty terms are clear and that the supplier provides reliable customer support.
Step 5: Assess Compatibility with Existing Systems
Evaluate how the new conveyor will integrate with your current manufacturing processes. This step is crucial to avoid disruptions and ensure a seamless operation.
- Communication Protocols: Check compatibility with existing PLCs and other automation systems.
- Physical Space: Measure your available installation area to ensure the conveyor fits without compromising workflow.
Step 6: Conduct a Final Review
Before making a final decision, conduct a comprehensive review of all gathered information. This includes a re-evaluation of supplier reliability, product specifications, and overall alignment with your operational needs.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks associated with the procurement and integration of the conveyor.
- Stakeholder Input: Involve key stakeholders in the review process to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Make Your Purchase Decision
After thorough evaluation and review, proceed with your purchase decision. Ensure that all contractual obligations are clear and that you have a plan for installation and training.
- Documentation: Confirm that all agreements are documented, including delivery schedules and payment terms.
- Training: Plan for adequate training of your staff on the new system to maximize its benefits.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for a 2 rail edge conveyor with a stepper motor, ensuring a choice that enhances productivity and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing a 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor?
When considering the procurement of a 2 rail edge conveyor with a stepper motor, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved. The primary elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in constructing the conveyor significantly affect costs. High-strength aluminum for the frame, specialized fiberglass-reinforced belts, and reliable stepper motors are common materials that ensure durability and performance but come at a higher price point.
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and installation, which can add to the total cost.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, but they can still represent a significant portion of the overall expense.
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can increase initial costs. However, investing in appropriate tooling can lead to better long-term performance and reduce maintenance needs.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each conveyor meets industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes, which incur additional costs. However, these expenses are crucial for maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees can vary based on the destination, particularly for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms is essential, as they define responsibilities regarding shipping costs, insurance, and liability.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the level of competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of a 2 Rail Edge Conveyor?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost components. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQs) play a critical role; larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Custom specifications—such as conveyor length, width, and additional features—can significantly impact pricing.
The quality and certifications of the materials used also affect the price. Conveyors that comply with international standards may command higher prices, but they provide assurance of quality and reliability.
Supplier factors, including their reputation, experience, and service offerings, can influence pricing as well. A well-established supplier might charge more for their products, but they often provide better support and warranty options.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for International B2B Purchases?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to optimize costs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and shipping costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and operation costs. A cheaper conveyor might lead to higher long-term costs if it requires frequent repairs or has lower efficiency.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations, currency fluctuations, and potential tariffs or duties that can affect the final cost.
-
Utilize Incoterms Effectively: Familiarize yourself with Incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping and delivery. This understanding can help you avoid unexpected costs.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Engage with multiple suppliers to gather quotes, which can provide leverage in negotiations and help you identify competitive pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While indicative prices for 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors can range from $3,850 to $4,850, actual costs may vary based on customization, supplier, and market conditions. It is advisable to consult with suppliers directly for precise quotations tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor With Other Solutions
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing and logistics, selecting the right conveyor system is crucial for optimizing productivity and efficiency. B2B buyers often face the challenge of choosing between various technologies that can transport materials effectively. This section provides a comparative analysis of the ‘2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor’ against two viable alternatives: the ‘Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor’ and the ‘GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor’.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 2 Rail Edge Conveyor With Stepper Motor | Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor | GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed transport, precise control | High-speed, modular, ESD-sensitive | Economical, flexible, low-speed |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled installation | Modular design allows easy integration | Easy integration with low height |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, service-free motors | Low maintenance, long service life | Moderate maintenance, accessible design |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for precision applications | Best for electronics manufacturing | Suitable for lightweight, small products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor
The Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor is specifically designed for handling ESD-sensitive materials, making it ideal for electronics manufacturing environments. Its modular design allows for customization in length and drive configuration, accommodating various production needs. With a robust build and the use of high-quality DC stepper motors, this conveyor system offers reliable performance with minimal maintenance. However, the initial investment is relatively higher, which might be a consideration for cost-sensitive buyers.
GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor
The GUF-P MINI Small Conveyor is a compact solution tailored for transporting small and lightweight products. It is particularly beneficial in environments where space is limited, thanks to its low installation height. The conveyor supports various drive options, including stepper motors, and can operate in reverse or accumulation modes. While it offers a lower initial cost and ease of integration, it is not designed for high-speed applications, making it less suitable for scenarios requiring rapid transport of heavier items.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Conveyor Solution
When selecting the right conveyor system, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including the type of materials being transported, the speed and precision needed, and the available budget. The 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor excels in precision and speed, making it suitable for high-tech manufacturing processes. In contrast, the Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor offers robust performance for ESD-sensitive environments, albeit at a higher cost. Meanwhile, the GUF-P MINI provides an economical solution for lightweight products but may not meet the demands of high-speed applications. Careful evaluation of these factors will ensure that the chosen conveyor system aligns with both immediate and long-term business objectives.
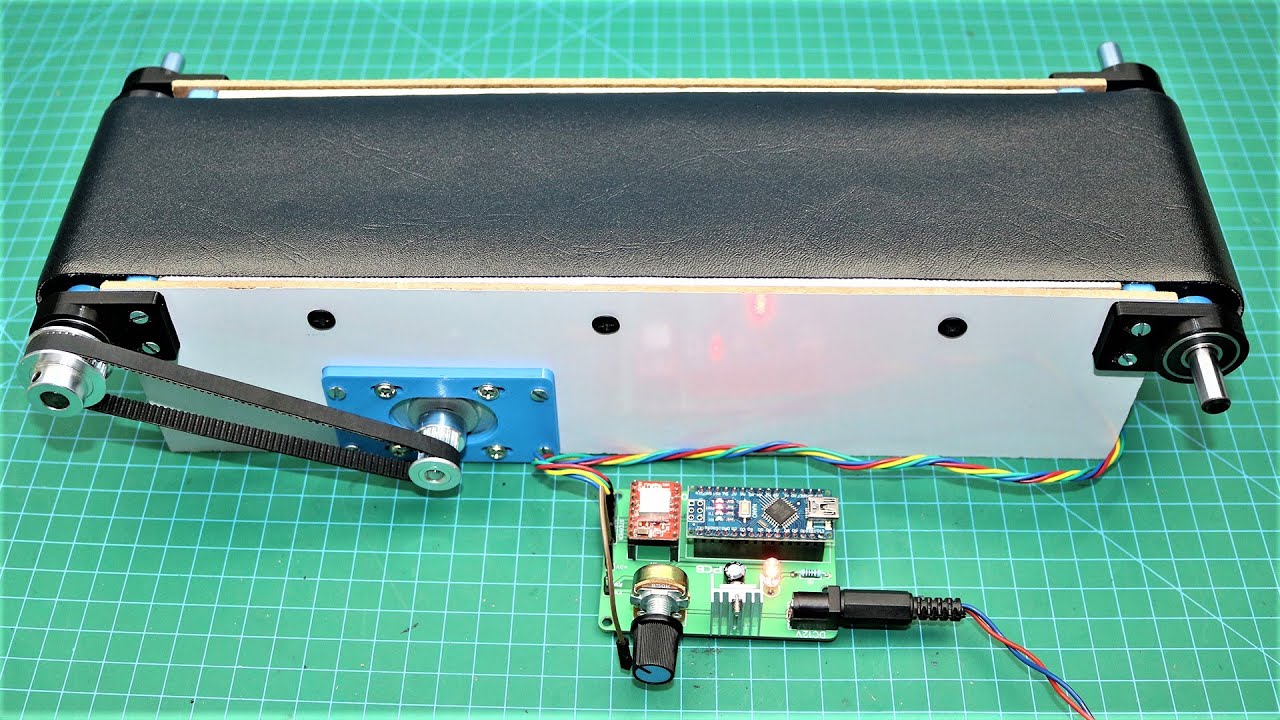
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor?
When evaluating a 2 rail edge conveyor equipped with a stepper motor, several technical specifications are critical for ensuring operational efficiency and compatibility with specific production needs. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Load Capacity: This refers to the maximum weight the conveyor can handle without compromising performance. Understanding the load capacity is vital for B2B buyers to ensure that the conveyor can transport the intended materials, such as Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) or other delicate components, without risk of failure.
-
Belt Material: The composition of the conveyor belt significantly affects its durability and performance. Common materials include fiberglass-reinforced polymers, which provide strength and resistance to wear. Selecting the right belt material is crucial for minimizing maintenance costs and extending the conveyor’s lifespan, particularly in high-demand environments.
-
Motor Specifications: Stepper motors are often chosen for their precision and control over speed and torque. Key specifications to consider include the motor’s voltage rating (e.g., 24V, 48V) and maximum speed (measured in meters per minute). These factors influence the conveyor’s ability to maintain consistent movement, essential for processes that require high accuracy.
-
Adjustability Features: Features such as hand-crank width adjustments and variable speed controls allow for customization based on specific operational requirements. These adjustments enable the conveyor to accommodate different product sizes and weights, enhancing versatility and efficiency in diverse applications.
-
Communication Protocols: Industry 4.0 readiness is becoming increasingly important, with many conveyors featuring communication capabilities such as SMEMA (Surface Mount Equipment Manufacturers Association) standards. This facilitates seamless integration with other machinery and systems, allowing for improved process automation and data exchange.
-
Frame Construction: The framework material and design, often made from extruded aluminum, affect the conveyor’s overall weight, stability, and ease of integration into existing systems. A robust yet lightweight frame is essential for minimizing installation challenges and enhancing mobility within manufacturing environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 2 Rail Edge Conveyors?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms related to 2 rail edge conveyors:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce components or equipment that are then marketed by another company. For buyers, working with OEMs can ensure that they receive high-quality components that meet specific industry standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for buyers to plan their inventory and budget accordingly, especially when dealing with specialized equipment like conveyors.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed quote for specific products or services. This process is essential for buyers to compare prices and services from different vendors, ensuring they get the best value for their investment.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are predefined commercial terms used in international trade that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and risks in global transactions.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays.
-
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge): This term describes the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects. In electronics manufacturing, conveyors designed with ESD protection are essential for preventing damage to sensitive components, making it a key consideration for buyers in the electronics sector.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor Sector?
The global market for 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes, particularly in electronics and automotive sectors. As industries seek to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs, these conveyor systems have emerged as integral components in production lines, especially for handling sensitive materials like printed circuit boards (PCBs). Key trends include the shift towards modular and customizable conveyor systems that allow for easy integration into existing setups, catering to varied production needs. Furthermore, with the rise of Industry 4.0, there is a growing emphasis on smart conveyor solutions equipped with advanced communication technologies, such as PLC integrations and IoT capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and control.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are also witnessing a surge in sourcing trends favoring localized suppliers. This shift is a response to the need for more reliable supply chains that can adapt to geopolitical changes and logistical challenges. The demand for energy-efficient models is rising, as buyers prioritize long-term operational cost savings over initial investment. Additionally, the introduction of sustainable practices in sourcing and manufacturing processes is becoming a focal point for many companies, influencing their purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor Market?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a crucial aspect of the B2B landscape, including the 2 rail edge conveyor sector. Companies are recognizing the environmental impact of their operations and are actively seeking solutions that minimize waste and energy consumption. The use of eco-friendly materials and processes in the manufacturing of conveyors not only reduces carbon footprints but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Green Seal are becoming essential for suppliers, demonstrating their commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining prominence as buyers become more aware of the social implications of their purchasing decisions. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations is now a standard expectation. B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating their supply chains for transparency and accountability, favoring manufacturers that prioritize ethical sourcing. This trend not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the values of a growing segment of consumers who prioritize sustainability in their purchasing choices.
How Has the 2 Rail Edge Conveyor with Stepper Motor Technology Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor technology has been marked by significant advancements in automation and materials handling. Initially designed for basic conveyance tasks, these systems have transformed into sophisticated solutions tailored for specific applications, such as the transport of ESD-sensitive components in electronics manufacturing. Over the years, the integration of stepper motors has enhanced the precision and reliability of these conveyors, enabling finer control over speed and torque, which is vital for delicate operations.
With the ongoing digital transformation in manufacturing, the introduction of Industry 4.0 technologies has further revolutionized the sector. Modern conveyors now feature advanced PLC controls and IoT connectivity, allowing for seamless integration with other automated systems. This evolution not only improves operational efficiency but also supports data-driven decision-making, paving the way for smarter manufacturing environments. As the technology continues to evolve, B2B buyers can expect even greater flexibility and customization options in the design and functionality of edge conveyors, solidifying their role as essential components in contemporary production lines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
-
How do I choose the right 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor for my application?
Selecting the appropriate conveyor depends on your specific operational requirements. Consider the dimensions of the products being transported, weight capacity, and the necessary speed of operation. Evaluate the conveyor’s design features, such as its ESD sensitivity for electronics or its ability to integrate with existing systems. Additionally, assess the motor specifications, including torque and acceleration, to ensure they meet your production line needs. -
What are the advantages of using a stepper motor in edge conveyors?
Stepper motors provide precise control over the conveyor’s speed and position, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate product handling, such as electronics manufacturing. Their virtually maintenance-free operation enhances reliability, while the ability to adjust velocity, torque, and acceleration allows for flexibility in production processes. Furthermore, stepper motors can facilitate smooth transitions between different operational modes, such as inspection and buffering. -
What customization options are available for 2 rail edge conveyors?
Many manufacturers offer extensive customization options for edge conveyors. These may include adjustable lengths and widths, various drive configurations, and the integration of additional features like inspection stations or product stops. It’s essential to discuss your specific requirements with the supplier to ensure the conveyor meets your operational needs. Customization may also extend to the control systems, allowing you to choose PLC options that align with your existing machinery. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 2 rail edge conveyors?
The MOQ for 2 rail edge conveyors can vary significantly among suppliers. While some manufacturers may accept small orders for standard models, others might require a higher MOQ for custom configurations. It’s advisable to inquire directly with potential suppliers about their MOQ policies and any associated pricing tiers. This will help you determine the feasibility of your purchase based on your production volume and budget. -
How do I vet suppliers for international sourcing of edge conveyors?
When sourcing internationally, vetting suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching their reputation through customer reviews and testimonials. Request references and verify their experience in manufacturing edge conveyors. Additionally, assess their compliance with international quality standards and certifications. Engaging in direct communication can also help gauge their responsiveness and customer service capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing edge conveyors internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include upfront deposits, progress payments during manufacturing, and final payment upon delivery. It’s important to clarify these terms before finalizing your order. Consider utilizing secure payment methods or letters of credit to mitigate risks associated with international transactions, especially in regions with fluctuating currencies. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in edge conveyor suppliers?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that the conveyors meet industry standards and perform reliably. Look for suppliers who implement rigorous testing protocols, including performance testing and material inspections. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management practices. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies and after-sales support to ensure you have recourse in case of defects or operational issues. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of edge conveyors?
Logistics for international orders typically involve coordinating shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Discuss with your supplier the available shipping options, such as sea freight or air freight, and their associated costs. Ensure that the supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs, including invoices and certificates of origin. Understanding the lead times for production and shipping will help you plan effectively and minimize disruptions to your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 2 2 Rail Edge Conveyor With Stepper Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
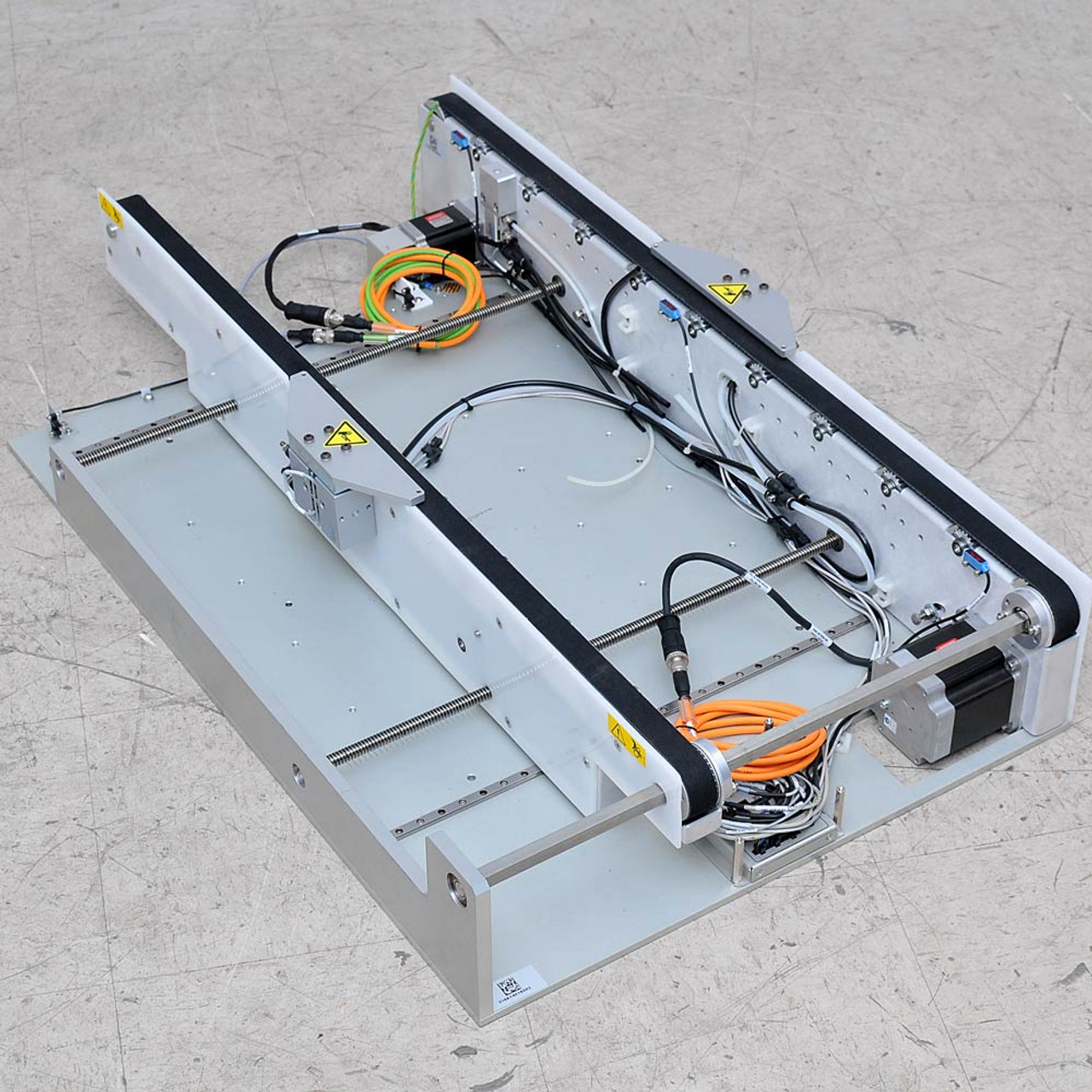
1. Simplimatic – Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor
Domain: simplimatic.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Cimtrak® Edge Belt Conveyor is a modular standalone conveyor designed for conveying ESD-sensitive materials by their edges, primarily used for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and electronic assemblies. Key features include:
– Solid non-spliced, fiberglass-reinforced transmission belts for strength
– Reliable DC stepper motors for precise adjustments
– Premium rail design with zero gaps to elimina…
2. MK Group – Modular Belt Conveyors
Domain: mk-group.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Belt Conveyors with a Modular, Profile-Based Design suitable for transporting both packaged and unpackaged piece goods. Features include:
– Widths: 50-2000 mm
– Lengths: 300-20000 mm
– Total load: typically up to 200 kg
– Speed: up to 80 m/min
– Options: dual-line, incline, curved, INOX.
Specific models include:
1. GUF-P MINI: Small conveyor for low volume and weight products.
2. GUF-P 20…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 2 rail edge conveyor with stepper motor
In the evolving landscape of industrial automation, the strategic sourcing of 2 rail edge conveyors with stepper motors presents a compelling opportunity for B2B buyers across diverse regions. These conveyor systems, designed for precision and efficiency, are essential for transporting sensitive materials like Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in manufacturing environments. Their modular design and adaptability to various production lines make them invaluable assets for companies aiming to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Investing in high-quality edge conveyors not only minimizes downtime through reliable performance but also maximizes return on investment with their impressive service life. Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 capabilities allows for seamless communication and control, positioning businesses to capitalize on future technological advancements.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe assess their procurement strategies, prioritizing suppliers that offer customizable solutions and robust support can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your production capabilities by sourcing cutting-edge conveyor technology that meets your specific needs. Engage with reputable suppliers today to ensure your business remains competitive in a rapidly changing market.