Top 5 Scrap Copper For Sale Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for scrap copper for sale
In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade, sourcing high-quality scrap copper for sale presents both opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers. With fluctuating market prices, varying purity standards, and a multitude of suppliers, navigating this global market can be daunting. This guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge and tools needed to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that you can confidently engage in the scrap copper marketplace, whether you are operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various types of scrap copper available, including Bare Bright Wire, #1 and #2 Copper, and specialized alloys. We will explore their applications across industries, from electrical manufacturing to plumbing, highlighting the importance of selecting the right type for your needs. Furthermore, we will provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, enabling you to identify reliable partners who can meet your quality and compliance standards.
Additionally, we will analyze cost factors, including pricing trends and the impact of global demand on scrap copper values. By arming yourself with this critical information, you will enhance your negotiating power and optimize your purchasing strategies, ultimately leading to better business outcomes in your operations. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the industry, this guide will serve as your essential resource for navigating the complex world of scrap copper.
Understanding scrap copper for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Bright Copper Wire | Stripped, shiny wire with no insulation | Electrical applications, wiring | Pros: High purity, excellent conductivity. Cons: Higher cost compared to other types. |
| #1 Copper Tubing | Clean, unpainted, and free from contaminants | Plumbing, HVAC systems | Pros: Versatile, good resale value. Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid damage. |
| #2 Copper Tubing | May contain minor contaminants, such as paint or solder | Construction, electrical applications | Pros: Lower cost, still useful in many applications. Cons: Reduced resale value due to impurities. |
| Insulated Copper Wire | Copper wire coated with insulation | Electrical installations, appliances | Pros: Widely available, suitable for many projects. Cons: Requires stripping to sell as pure copper. |
| Copper Scrap from Radiators | Copper and brass mixed, often with steel ends | Recycling, automotive industry | Pros: Commonly available, can yield high copper content. Cons: Requires sorting and cleaning for maximum value. |
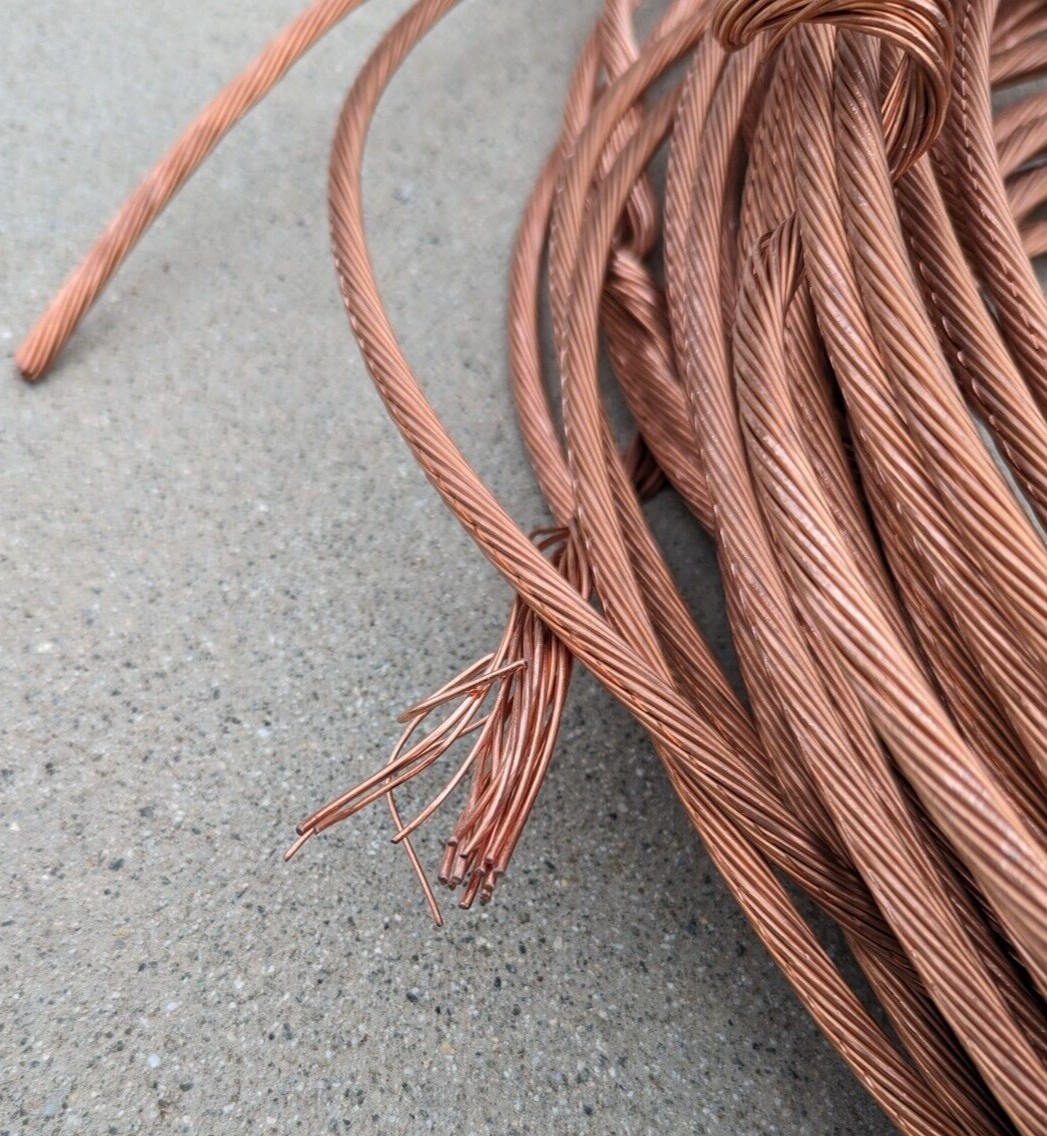
What Are the Characteristics of Bare Bright Copper Wire?
Bare Bright Copper Wire is one of the highest grades of copper scrap, recognized for its shiny, stripped appearance. This wire is devoid of any insulation, making it highly sought after for electrical applications where conductivity is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the purity level when purchasing, as it directly influences pricing and usability in high-performance electrical systems. While it commands a premium price due to its quality, the investment can yield significant returns in projects demanding high conductivity.
How Does #1 Copper Tubing Stand Out in the Market?
1 Copper Tubing is characterized by its clean, unpainted surface, free from any contaminants. This type of copper is commonly used in plumbing and HVAC systems, making it a staple in construction projects. Buyers should prioritize sourcing this type of copper for applications where reliability and performance are critical. Although it may come at a higher cost, the durability and versatility of #1 Copper Tubing justify the investment, especially for long-term projects.
What Should Buyers Know About #2 Copper Tubing?
2 Copper Tubing is slightly less pure than #1, often containing minor contaminants such as paint or solder. Despite this, it remains a valuable resource for various applications, particularly in construction and electrical work where cost-effectiveness is essential. Buyers should be aware that while #2 Copper Tubing offers lower pricing, it may result in a reduced resale value. However, its affordability makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Why Choose Insulated Copper Wire for Electrical Projects?
Insulated Copper Wire is prevalent in electrical installations, providing essential conductivity while ensuring safety through its protective coating. This type is widely available, making it a convenient choice for various projects. However, B2B buyers should consider the additional step of stripping the insulation to realize its full copper value. Despite this extra effort, its versatility and abundance in the market make it a practical choice for many electrical applications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Copper Scrap from Radiators?
Copper Scrap from Radiators typically consists of a mixture of copper and brass, often with steel ends attached. This type of scrap is especially common in the automotive industry and recycling sectors. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing this material as it can yield a high copper content, although it requires sorting and cleaning to maximize value. Its availability makes it a viable option for businesses looking to capitalize on copper recycling efforts while maintaining cost efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of scrap copper for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of scrap copper for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Manufacturing | Production of electrical components | Enhances conductivity and reduces production costs | Ensure high purity levels and compliance with standards |
| Construction | Plumbing and roofing applications | Durable and corrosion-resistant materials | Verify scrap quality and origin to meet building codes |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of radiators and wiring | Improves vehicle efficiency and performance | Source from reputable suppliers to ensure quality |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine and solar panel components | Supports sustainability goals and energy efficiency | Assess recycling processes for environmental compliance |
| Telecommunications | Wiring for communication systems | Ensures reliable transmission of signals | Consider insulation type and scrap condition for safety |
How is scrap copper used in electrical manufacturing, and what benefits does it provide?
In the electrical manufacturing sector, scrap copper is primarily utilized for producing various electrical components such as wires, connectors, and circuit boards. The inherent properties of copper, including high electrical conductivity and thermal resistance, enhance the performance of these components. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-purity scrap copper is crucial, as impurities can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. Additionally, adhering to international standards ensures compliance and reliability in electrical applications.
What role does scrap copper play in construction applications?
Scrap copper is widely used in the construction industry for plumbing systems and roofing materials. Its resistance to corrosion and durability make it an ideal choice for long-lasting installations. Businesses engaged in construction projects must ensure that the sourced scrap copper meets specific quality standards to comply with building codes. For international buyers, verifying the origin and purity of the scrap is essential to avoid legal complications and ensure the safety and longevity of structures.
How does the automotive industry benefit from scrap copper?
In the automotive sector, scrap copper is essential for manufacturing components such as radiators, wiring harnesses, and electronic systems. The use of recycled copper helps reduce production costs while maintaining high performance and efficiency in vehicles. For B2B buyers, sourcing from reputable suppliers is vital to guarantee the quality of scrap copper, which directly impacts vehicle safety and reliability. Understanding the specific requirements for copper grades and types ensures compliance with industry standards.
Why is scrap copper important for renewable energy applications?
The renewable energy sector utilizes scrap copper in the production of components for wind turbines and solar panels. Copper’s excellent conductivity contributes to the efficiency of energy conversion and transmission. As sustainability becomes a priority globally, sourcing recycled copper supports environmental goals while reducing costs. International buyers should evaluate the recycling processes used to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and promote sustainable practices in their operations.
How is scrap copper utilized in telecommunications, and what are the sourcing considerations?
In telecommunications, scrap copper is primarily used for wiring in communication systems, ensuring reliable signal transmission. The quality of copper, including insulation type and overall condition, significantly affects performance. For international B2B buyers, it’s crucial to ensure that the sourced scrap meets safety standards and is free from contaminants. Establishing a reliable supply chain with transparent sourcing practices can mitigate risks associated with quality and compliance in telecommunications applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘scrap copper for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Pricing Transparency for Scrap Copper
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant challenges when trying to determine fair pricing for scrap copper. Due to market volatility, prices can fluctuate daily, and without a reliable benchmark, buyers may end up overpaying or receiving less value for their scrap. This uncertainty can lead to distrust in suppliers and a sense of frustration, especially when trying to negotiate bulk deals. Buyers operating in regions with less access to up-to-date market information may find themselves at a distinct disadvantage, impacting their profit margins and operational budgeting.
The Solution: To navigate pricing transparency, B2B buyers should leverage multiple resources to establish a fair market value for scrap copper. Utilize reputable online platforms that provide real-time pricing data, such as the London Metal Exchange (LME) or industry-specific websites. Additionally, engaging with local recycling centers and scrap yards can provide insights into current local pricing trends. Establishing relationships with several suppliers can also help create a competitive environment, ensuring better price negotiations. Documenting price trends over time will empower buyers to make informed decisions and anticipate market movements.
Scenario 2: Quality Variability in Scrap Copper Materials
The Problem: Quality variability is a significant pain point for B2B buyers in the scrap copper market. Buyers often receive materials that do not meet the expected quality standards, resulting in additional costs for sorting and processing. This issue is particularly prevalent when purchasing from multiple suppliers or when sourcing materials from different regions, leading to discrepancies in purity and usability. Such challenges can hinder production schedules and impact overall operational efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate quality variability, B2B buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process that includes quality assurance protocols. Establish clear specifications for the types of copper required, including purity levels and acceptable contaminants. Before finalizing purchases, consider conducting sample tests or requesting certifications that indicate the quality of the scrap. Building long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who consistently deliver high-quality materials can also reduce the risk of variability. Additionally, investing in technology for sorting and quality assessment at the point of receipt can streamline operations and ensure that only suitable materials are processed.
Scenario 3: Logistical Challenges in Transporting Scrap Copper
The Problem: Transporting scrap copper poses logistical challenges that can be particularly daunting for B2B buyers, especially those dealing with large volumes. Issues such as high transportation costs, delays, and the risk of damage during transit can create complications that affect profitability and project timelines. Buyers may struggle with finding reliable carriers who understand the unique requirements of handling scrap metal, leading to additional stress and potential financial loss.
The Solution: To overcome logistical challenges, B2B buyers should consider partnering with specialized logistics providers experienced in scrap metal transportation. These companies can offer tailored solutions that address specific needs, such as weight limits, packaging requirements, and compliance with local regulations. Implementing a just-in-time delivery system can also help minimize inventory costs and improve cash flow. Additionally, buyers can explore the option of consolidating shipments to maximize transport efficiency and reduce costs. Utilizing tracking technology can provide visibility throughout the shipping process, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing the likelihood of damage or loss. By strategically planning logistics and choosing the right partners, buyers can enhance operational efficiency and maintain steady supply chains.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for scrap copper for sale
What Are the Key Properties of Common Scrap Copper Materials?
When evaluating scrap copper for sale, it is essential to understand the different materials involved, their properties, and their implications for various applications. Here, we will analyze four common types of scrap copper materials: Bare Bright Copper Wire, #1 Copper, #2 Copper, and Copper Alloys. Each material has distinct characteristics that can influence performance in various applications, particularly for international B2B buyers.
What Makes Bare Bright Copper Wire a Preferred Choice?
Bare Bright Copper Wire is recognized for its high conductivity and purity, making it ideal for electrical applications. With a minimum copper content of 99%, it exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. This wire is typically used in electrical wiring, motors, and transformers.
Pros: Its high conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, while its durability allows for long-term use in demanding environments.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other copper types, which may not be suitable for all budgets. Additionally, its softness can make it prone to physical damage if not handled properly.
Impact on Application: Bare Bright Copper Wire is particularly compatible with high-temperature and high-pressure environments, making it a preferred choice for electrical components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers provide certification to meet local regulations.
How Does #1 Copper Compare in Terms of Performance?
1 Copper is characterized by its clean, unalloyed copper content, typically used in plumbing and electrical applications. It is slightly less pure than Bare Bright Wire but still offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Pros: It is more affordable than Bare Bright Copper Wire, making it a popular choice for larger projects. Its mechanical properties are robust, allowing it to withstand significant stress.
Cons: The presence of minor impurities can slightly reduce its conductivity compared to Bare Bright Wire. Additionally, it may require more processing if used in high-purity applications.
Impact on Application: #1 Copper is suitable for various applications, including electrical wiring and plumbing, where high conductivity is essential but budget constraints exist.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the copper grade and ensure compliance with local standards, especially in regions with stringent recycling regulations.
What Are the Key Features of #2 Copper?
2 Copper is often mixed with solder, paint, or other contaminants, making it less desirable for high-purity applications. However, it remains a viable option for various applications, especially in construction and manufacturing.
Pros: Its lower cost makes it accessible for larger projects, and it is readily available in the scrap market.
Cons: The presence of impurities can significantly affect its conductivity and mechanical properties, limiting its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: #2 Copper is commonly used in applications where aesthetics and high conductivity are not critical, such as in construction materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the local market for scrap copper and ensuring proper sorting and grading of materials can help mitigate risks associated with impurities.
How Do Copper Alloys Enhance Scrap Copper Applications?
Copper alloys, such as brass and bronze, combine copper with other metals to enhance specific properties, such as strength and corrosion resistance. These alloys are often used in plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and decorative items.
Pros: The enhanced properties of copper alloys make them suitable for specialized applications where standard copper may not suffice.
Cons: The complexity of processing these alloys can lead to higher manufacturing costs and may require specialized recycling processes.
Impact on Application: Copper alloys are ideal for applications requiring improved strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the alloy composition and relevant standards, such as ASTM and ISO, to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Summary Table of Common Scrap Copper Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for scrap copper for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Bright Copper Wire | Electrical wiring, motors, transformers | High conductivity and purity | Higher cost, prone to physical damage | High |
| #1 Copper | Plumbing, electrical applications | Affordable with robust mechanical properties | Slightly lower conductivity due to impurities | Medium |
| #2 Copper | Construction materials | Cost-effective for large projects | Reduced conductivity and mechanical properties | Low |
| Copper Alloys | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Enhanced strength and corrosion resistance | Higher processing complexity and costs | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in diverse international markets. Understanding these materials’ properties and implications can facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with specific application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for scrap copper for sale
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Scrap Copper?
The manufacturing processes for scrap copper typically involve several stages, each critical for ensuring the quality and usability of the final product. Understanding these processes can aid B2B buyers in assessing the quality of the copper they purchase.
How Is Scrap Copper Prepared for Processing?
The initial stage in the manufacturing process involves material preparation. This includes the collection and sorting of scrap copper based on purity and type. Various grades of copper, such as Bare Bright, #1, and #2, are separated, with pure copper generally being preferred for higher-quality applications. This sorting is crucial as it directly impacts the efficiency of subsequent processes and the quality of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Scrap Copper?
Once sorted, the copper is processed through forming techniques. This stage often involves melting the scrap copper in a furnace. The molten copper is then cast into ingots or billets, which can be further processed into various shapes and forms. Techniques like extrusion and rolling may be used to create wires, sheets, and other products. Each technique has specific temperature and pressure requirements that need to be monitored closely to ensure the integrity of the copper.
How Is Copper Assembled and Finished?
The assembly and finishing processes can vary based on the intended use of the copper. For instance, if the copper is to be used in electrical applications, it may undergo additional treatments such as electroplating or insulation. Finishing processes may also involve surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and overall appearance. These steps ensure that the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Scrap Copper?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the copper manufacturing process, especially for international buyers who require consistency and reliability. The most recognized international standard is ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with such standards indicates that the manufacturer has processes in place to enhance customer satisfaction and ensure product quality.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO 9001, buyers should consider industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications. These certifications demonstrate that the copper products meet stringent safety and performance requirements relevant to their specific industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Scrap Copper Processing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to monitor and ensure the quality of copper throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify that they meet specified standards before processing.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that production parameters remain within acceptable limits.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the manufacturing process, finished products are subjected to rigorous testing to confirm they meet required specifications and standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods can be employed to assess the quality of scrap copper. Common methods include:
- Chemical Analysis: To determine the composition and purity of the copper, ensuring it meets the required standards.
- Mechanical Testing: To evaluate the strength and ductility of the copper, which is essential for applications where performance is critical.
- Electrical Conductivity Testing: To ensure that the copper will perform adequately in electrical applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are some strategies to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and QC practices. Buyers can assess compliance with international standards and identify areas for improvement.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their QC processes and results from recent tests. This transparency is key to building trust.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can perform various tests and provide certification that the products meet specified requirements.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
Navigating the quality assurance landscape can be complex for international buyers, especially when dealing with suppliers from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key nuances to consider include:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. For instance, European buyers may require CE certification, while buyers from the Middle East may look for compliance with local regulations.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Understanding how quality is perceived in different cultures can help buyers communicate their expectations more effectively. This can lead to better partnerships and improved product quality.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping and customs regulations can affect the quality of copper during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures to minimize damage.
In conclusion, an in-depth understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for scrap copper is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with rigorous QC practices, buyers can ensure they acquire high-quality copper that meets their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘scrap copper for sale’
The following guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure scrap copper effectively. By following these actionable steps, you can ensure a successful sourcing experience that meets your specific business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for scrap copper. This includes specifying the types of copper you need, such as bare bright wire, #1 tubing, or #2 copper. Understanding the quality and purity levels required for your applications is crucial, as different grades can affect the performance of your end products.
- Considerations: Assess whether you need clean or insulated copper, and define the acceptable contamination levels based on your production processes.
Step 2: Research Market Prices
Stay informed about current market prices for various grades of copper. Prices can fluctuate due to market demand, geopolitical events, and economic conditions. By monitoring these trends, you can make informed purchasing decisions and negotiate effectively with suppliers.
- Resource Utilization: Use online platforms that provide real-time pricing data and historical trends to benchmark prices when approaching suppliers.
Step 3: Identify Potential Suppliers
Compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in scrap copper. Look for companies with a solid reputation and extensive experience in the industry. Utilize online marketplaces, trade shows, and industry associations to find qualified suppliers.
- Networking: Engage with industry peers or forums for recommendations on trustworthy suppliers, especially those with operations in your target regions like Africa, South America, and Europe.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your shortlisted suppliers have the necessary certifications and licenses for handling scrap copper. This not only guarantees compliance with local regulations but also signifies a commitment to quality and ethical practices.
- Documentation: Request copies of certifications such as ISO 9001 or environmental compliance documents to validate their credibility.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the operational capabilities of each supplier, including their sorting, processing, and shipping facilities. A supplier’s ability to handle large volumes of scrap copper efficiently can impact your supply chain reliability.
- Facility Visits: If possible, visit suppliers’ facilities to evaluate their processes and ensure they align with your quality expectations.
Step 6: Request Samples and Quality Assurance
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples of the scrap copper to evaluate its quality. This step is essential to confirm that the material meets your specifications and to mitigate the risk of receiving subpar products.
- Quality Checks: Implement a quality assurance process that includes chemical analysis to verify purity levels, especially if the copper will be used in critical applications.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Secure Contracts
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms, including pricing, delivery schedules, and payment options. A well-defined contract should outline all aspects of the transaction, protecting both parties involved.
- Legal Review: Consider having legal counsel review contracts to ensure all terms are fair and transparent, minimizing potential disputes in the future.
By diligently following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for scrap copper, ensuring they acquire high-quality materials while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for scrap copper for sale Sourcing
When sourcing scrap copper for sale, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Scrap Copper Pricing?
The cost structure for scrap copper encompasses several critical components:
-
Materials: The base cost of scrap copper fluctuates based on market demand and supply conditions. Prices can vary significantly depending on the type of copper (e.g., Bare Bright, #1 and #2 copper), with higher purity generally commanding a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs are incurred during collection, sorting, and processing of scrap copper. Skilled labor may be necessary for quality assurance and to ensure that the material meets specific industry standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, equipment depreciation, and utilities. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead, impacting the overall pricing of scrap copper.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Specialized tools and machinery are required for the processing and refining of copper. The initial investment in these tools affects the overall cost structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the purity and quality of scrap copper incurs additional costs. Suppliers often invest in testing and certification processes to meet buyer specifications, which can influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are significant, especially for international transactions. The geographical location of suppliers and buyers can affect shipping costs, lead times, and ultimately, pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, market conditions, and the specific relationship with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Scrap Copper Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of scrap copper, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders may attract bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should negotiate terms that align with their purchasing capabilities to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Specific requirements regarding purity levels and forms (e.g., wire, tubing) can lead to variations in pricing. Customization often incurs additional costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certifications for their copper. Certified materials can ensure compliance with industry standards, though they may come at a higher price.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability, reputation, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Long-term partnerships may yield better pricing structures and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international commercial terms is essential for international buyers. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact overall costs.
What Are Some Tips for Buyers in Negotiating Scrap Copper Prices?
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Frequent communication and trust can foster favorable negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider all costs associated with sourcing scrap copper, including logistics, processing, and potential quality issues, rather than just the upfront price.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, regional market trends, and local regulations that may impact pricing. Understanding these factors can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Stay Updated on Market Trends: Keeping an eye on global copper prices, which can fluctuate due to geopolitical events, trade policies, and economic changes, will enable buyers to time their purchases effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, sourcing scrap copper requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, awareness of these factors can lead to more informed decisions and cost-effective sourcing strategies. Always remember that prices are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing scrap copper for sale With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Scrap Copper for Sale
In the realm of metal recycling, particularly for copper, businesses often explore various solutions to maximize their returns and operational efficiency. While scrap copper for sale remains a popular choice due to its intrinsic value and widespread demand, it is essential to consider alternative methods that may offer similar or enhanced benefits. This analysis compares scrap copper for sale against two viable alternatives: copper recycling through industrial processes and investing in copper futures.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Scrap Copper For Sale | Copper Recycling (Industrial Processes) | Copper Futures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High demand; quick liquidity | Moderate performance; dependent on processing efficiency | Speculative; dependent on market trends |
| Cost | Variable; influenced by market prices | Initial investment in machinery; ongoing operational costs | High risk; potential for significant gains/losses |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple; requires sourcing and selling | Complex; requires infrastructure and expertise | Requires market knowledge and trading platform |
| Maintenance | Minimal; mainly involves logistics | High; ongoing maintenance of machinery and processes | Low; only requires monitoring of market conditions |
| Best Use Case | Quick cash flow; small to medium operations | Large-scale recycling facilities | Investors looking for profit in commodity markets |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Copper Recycling?
Copper recycling through industrial processes involves collecting scrap copper and processing it into reusable forms. The primary advantage is that it contributes to sustainability and reduces the need for virgin copper extraction, which is environmentally damaging. Additionally, recycling can yield high-quality copper products. However, this method requires significant investment in machinery and facilities, along with expertise to operate effectively. The operational costs can be high, and processing efficiency can vary, impacting overall performance.
How Do Copper Futures Work as an Alternative?
Investing in copper futures offers a different approach, focusing on trading contracts for future delivery of copper at predetermined prices. This method can be lucrative for savvy investors who can predict market trends. The primary benefit is the potential for substantial profits without the need for physical handling of copper. However, this alternative carries high risks, as market fluctuations can lead to significant losses. Moreover, it requires a deep understanding of commodity markets and access to trading platforms, making it less accessible for businesses focused on physical materials.
Conclusion: Which Solution is Right for Your Business?
When deciding between scrap copper for sale, copper recycling, and copper futures, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs and capabilities. If immediate cash flow is a priority, selling scrap copper may be the best option. Conversely, businesses with the capacity for large-scale operations and a commitment to sustainability may find copper recycling to be a more rewarding long-term investment. For those looking to engage with the financial markets and willing to take on risks, investing in copper futures could be a viable alternative. Ultimately, the choice will depend on factors such as operational capacity, market knowledge, and financial goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for scrap copper for sale
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Scrap Copper?
Understanding the technical properties of scrap copper is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are key specifications that play a significant role in the quality and value of scrap copper:
-
Material Grade
Copper is categorized into several grades based on its purity and condition. Common grades include Bare Bright Wire (highest quality, typically stripped and shiny), No. 1 Copper (clean, unalloyed copper tubing), and No. 2 Copper (contains some impurities, such as oxidation or insulation). Material grade affects pricing and usability, with higher grades commanding premium rates in the market. -
Conductivity
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, typically rated at 100% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). The conductivity can decrease when copper is alloyed with other metals, impacting its application in electrical components. Buyers should consider conductivity specifications to ensure the scrap copper meets their manufacturing requirements. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the resistance of copper to being pulled apart. While pure copper has a tensile strength of about 210 MPa, alloys may vary. Understanding tensile strength is essential for industries that require durability and reliability in their products, particularly in construction and electrical applications. -
Oxidation Levels
The presence of oxidation can indicate the quality of scrap copper. Oxidized copper may have reduced conductivity and aesthetic value. Buyers need to assess oxidation levels, as higher oxidation can lead to lower pricing and additional processing costs. -
Thickness and Tolerance
Thickness refers to the gauge of copper materials, which can vary widely, affecting their applications. Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. Accurate measurements are critical for industries that require precise specifications, such as electronics manufacturing.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Scrap Copper Transactions?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the scrap copper market. Here are several key terms commonly used:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In scrap copper, OEMs may require specific grades and specifications for their manufacturing processes, influencing pricing and supply agreements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest quantity of scrap copper that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when planning inventory levels and ensuring cost-effective procurement. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to request pricing and terms from suppliers. It helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate and favorable quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping and delivery, impacting overall pricing and logistics. -
Scrap Value
Scrap value refers to the market price of scrap copper based on its grade and current demand. This value can fluctuate due to market conditions, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about pricing trends to make profitable purchasing decisions. -
Bale Weight
This term refers to the weight of bundled scrap copper, often measured in tons. Knowing bale weight is critical for logistics planning, shipping costs, and compliance with local regulations regarding weight limits.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies, ensuring they acquire high-quality scrap copper that meets their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the scrap copper for sale Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Scrap Copper Sector?
The global scrap copper market is experiencing notable transformations driven by several key factors. One major driver is the rising demand for copper due to its essential role in renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles, and telecommunications infrastructure. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly turning to scrap copper as a sustainable alternative to mining. Furthermore, technological advancements in recycling processes are enhancing efficiency, enabling better recovery rates and higher-quality materials.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as blockchain and IoT, are revolutionizing the sourcing landscape by providing transparency and traceability in transactions. These technologies facilitate real-time tracking of copper from collection to processing, assuring buyers of the material’s origin and quality. Additionally, online marketplaces are gaining traction, allowing international buyers to connect with suppliers more efficiently, thereby expanding their sourcing options.
Market dynamics are also influenced by price fluctuations, often dictated by global supply and demand trends. Buyers must stay informed about market prices, which can vary significantly based on location and material grade. As the international market becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding regional trends and price movements is crucial for buyers looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing scrap copper.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Scrap Copper Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the scrap copper industry. The environmental impact of mining is significant, leading to increased scrutiny of traditional sourcing methods. Consequently, businesses are prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainable practices, recognizing that their supply chains can significantly affect their environmental footprint.
Ethical supply chains ensure that copper is sourced responsibly, minimizing harm to the environment and promoting fair labor practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers with certifications indicating adherence to environmental standards, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, the focus on ‘green’ materials is prompting suppliers to innovate in recycling methods. Companies are investing in technologies that improve the efficiency of the copper recycling process, reducing waste and energy consumption. As a result, scrap copper is not only an economically viable option but also a responsible choice for businesses looking to align with sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of the Scrap Copper Market?
The scrap copper market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, scrap copper was seen primarily as waste, often discarded or underutilized. However, as the demand for copper surged, particularly in the electronics and construction sectors, the value of scrap copper began to be recognized.
The recycling of copper has a long history, with practices dating back to ancient civilizations. Today, the industry is shaped by advances in technology and increased awareness of environmental issues. In recent years, the emphasis on recycling has intensified, driven by regulatory pressures and a global push towards sustainability. This evolution has transformed scrap copper into a valuable commodity, appealing to international B2B buyers seeking both economic and ethical sourcing solutions.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of the scrap copper market, including sustainability considerations and historical context, equips international buyers with the insights needed to make informed sourcing decisions. This comprehensive approach not only enhances procurement strategies but also aligns with broader corporate responsibility goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of scrap copper for sale
-
How do I assess the quality of scrap copper before purchasing?
To assess the quality of scrap copper, buyers should conduct a visual inspection to identify the type of copper and any impurities. Look for clean, bright copper wire, which indicates a higher grade. Additionally, buyers can request a sample or utilize testing equipment to measure the copper’s purity. Checking certifications or documentation from the supplier can also provide assurance regarding the quality and sourcing of the copper. -
What are the best practices for sourcing scrap copper internationally?
Sourcing scrap copper internationally requires thorough research and vetting of suppliers. Start by identifying reputable suppliers in your target regions, focusing on those with positive reviews and established business histories. It’s essential to verify their compliance with international trade regulations and environmental standards. Establish clear communication regarding pricing, quality specifications, and logistics to ensure a smooth purchasing process. -
What are common payment terms for scrap copper transactions?
Payment terms for scrap copper can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, terms may include upfront payment, payment upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after receipt of goods. It’s crucial to clarify these terms during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Some suppliers may also offer discounts for larger orders or prompt payments, which can enhance cost-effectiveness for buyers. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for scrap copper purchases?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for scrap copper can differ based on the supplier and the specific type of copper being purchased. Some suppliers may set an MOQ to ensure efficient shipping and handling costs. Buyers should inquire about MOQs during the initial discussions and consider consolidating orders with other businesses to meet these requirements if necessary. -
How can I ensure compliance with international shipping regulations for scrap copper?
To ensure compliance with international shipping regulations, buyers should familiarize themselves with the import/export laws of their country and the supplier’s country. This includes understanding customs documentation, tariffs, and any restrictions on scrap metal trade. Engaging a freight forwarder or logistics expert can provide additional guidance and streamline the process, ensuring that all necessary paperwork is correctly completed. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing scrap copper?
Logistics for importing scrap copper involve several factors, including transportation modes, shipping costs, and delivery timelines. Buyers should consider whether to use air freight for speed or sea freight for cost efficiency. Additionally, it’s important to discuss packaging and handling methods with suppliers to minimize damage during transit. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can facilitate a smoother import process. -
How can I verify the credibility of a scrap copper supplier?
To verify the credibility of a scrap copper supplier, buyers should conduct due diligence by checking business licenses, certifications, and industry affiliations. Requesting references from previous clients can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability. Additionally, utilizing platforms that provide reviews and ratings can help assess the supplier’s reputation in the market. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from scrap copper suppliers?
Quality assurance measures from scrap copper suppliers typically include certifications of purity and adherence to industry standards. Suppliers should provide documentation detailing the copper’s grade and source. Buyers should also expect clear return policies in case the delivered copper does not meet agreed-upon specifications. Regular quality audits and sample testing can further ensure the reliability of the supplied material.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Scrap Copper For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eBay – Scrap Copper Products
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: scrap copper products for sale, including various types of copper wire such as Multi Strand #2 Stranded – Bare Bright Copper Wire, and copper bullion bars. Prices range from $12.50 for 2 pounds of copper wire to $117.00 for 18 pounds of Bare Bright Scrap Copper Wire. Shipping options vary, with some items offering free shipping.
2. ScrapAd – Copper (Cu)
Domain: scrapad.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Copper (Cu) is the 29th chemical element in the periodic table. It is a reddish-coloured metal with a metallic transition lustre, softer than iron but harder than zinc. Copper is part of the copper family along with gold and silver. It can be found in various alloys, primarily bronze and brass, which have different characteristics based on their composition. The copper recycling process involves c…
3. SGT Scrap – Copper Pricing
Domain: sgt-scrap.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: #1 Copper: $3.95 / Lb
#2 Copper: $3.75 / Lb
Bare Bright Copper Wire: $4.05 / Lb
#2 – Insulated Wire 55%: $1.44 / Lb
Fire Wire 18 awg solid only: $2.12 / Lb
Romix Wire: $2.30 / Lb
THHN 82% (#12 AWG – #2AWG): $3.00 / Lb
Aluminum Rads Clean: $0.43 / Lb
Aluminum Copper Rads: $2.00 / Lb
Aluminum Copper Rads Steel Ends: $1.75 / Lb
Yellow Brass / EDM Wire: $2.53 / Lb
Red Brass Clean: $3.05 / Lb
Lead: $0….
4. Niagara Metals – Copper Products
Domain: niagarametals.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“Copper Products”: [{“Type”: “#1 Copper”, “Price”: “$2.90”, “Description”: “High-purity copper with a minimum 99% copper content, free from significant impurities. Typically sourced from clean copper pipes, wires, or solid pieces.”}, {“Type”: “#2 Copper”, “Price”: “$2.73”, “Description”: “Lower purity copper with a minimum 94% copper content, often containing impurities such as solder, paint, or …
5. Arrowscrap – Copper Scrap Pricing
Domain: arrowscrap.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, Arrowscrap – Copper Scrap Pricing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for scrap copper for sale
In the evolving landscape of scrap copper trading, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal component for international B2B buyers. The fluctuating prices and varying quality of copper scrap demand a keen understanding of market dynamics and supplier capabilities. By prioritizing relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can secure high-quality materials at competitive prices, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and profitability.
Understanding the nuances of copper grades—such as Bare Bright Wire versus #2 Tubing—allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific processing needs. Moreover, leveraging technology and platforms dedicated to scrap metal trading can streamline procurement processes, making it easier to connect with reputable suppliers across regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, the demand for recycled copper is projected to rise due to global sustainability initiatives and increasing industrial applications. This presents a significant opportunity for businesses to capitalize on the growing market. International buyers are encouraged to engage proactively in sourcing strategies, fostering partnerships that not only meet immediate needs but also align with long-term sustainability goals. Embrace the future of scrap copper trading—your next strategic partnership awaits.