Iso 9000 Vs As9100: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for iso 9000 vs as9100
In today’s competitive global market, understanding the differences between ISO 9000 and AS9100 can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing quality management systems that meet industry-specific standards. While both ISO 9000 and AS9100 emphasize quality assurance, AS9100 is tailored for the aerospace sector, incorporating rigorous requirements that address the unique demands of aerospace manufacturing and maintenance. This guide will delve into the nuances of these standards, exploring their applications, compliance requirements, and the implications for supplier vetting.
With a focus on the diverse needs of international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil—this comprehensive resource is designed to empower organizations in making informed purchasing decisions. We will provide insights into the types of certifications available, the costs associated with obtaining them, and strategies for selecting the right suppliers who adhere to these standards.
By equipping buyers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of ISO 9000 and AS9100, this guide serves as an essential tool for enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring regulatory compliance, and ultimately driving customer satisfaction in an increasingly interconnected marketplace. Whether your organization is new to quality management systems or looking to refine its existing processes, understanding these standards is key to achieving your business objectives.
Understanding iso 9000 vs as9100 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Generic quality management framework applicable across industries | Manufacturing, services, healthcare | Pros: Broad applicability, flexible; Cons: Lacks industry-specific requirements. |
| AS9100 | Aerospace-specific QMS with additional requirements | Aerospace manufacturing and services | Pros: Ensures compliance with strict aerospace regulations; Cons: More complex and resource-intensive. |
| AS9000 | Predecessor to AS9100, less comprehensive | Early aerospace quality management systems | Pros: Simpler than AS9100; Cons: Limited relevance in modern aerospace standards. |
| EN 9100 | European variant of AS9100 | Aerospace sector within Europe | Pros: Aligns with EU regulations; Cons: May not be recognized outside Europe. |
| SJAC 9100 | Japanese version of AS9100 | Aerospace suppliers in Japan | Pros: Tailored to local market needs; Cons: Limited global recognition compared to AS9100. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of ISO 9001 for B2B Buyers?
ISO 9001 serves as a foundational quality management system applicable to various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and services. Its generic nature allows organizations to customize the framework according to their specific operational needs. B2B buyers may find ISO 9001 appealing due to its focus on enhancing customer satisfaction and promoting continuous improvement. However, its lack of industry-specific requirements may be a drawback for businesses seeking rigorous standards tailored to their sector.
How Does AS9100 Stand Out in Aerospace Applications?
AS9100 is a specialized quality management standard developed for the aerospace industry, incorporating additional requirements that address unique challenges such as risk management and product safety. Companies within the aerospace sector, including manufacturers and service providers, are increasingly adopting AS9100 to comply with stringent regulatory standards. While its comprehensive nature ensures high-quality assurance, the complexity and resource demands of implementing AS9100 can be significant considerations for B2B buyers.
What Was the Role of AS9000 in the Evolution of Aerospace Standards?
AS9000, the predecessor to AS9100, was established to address the quality management needs of the aerospace industry. While it laid the groundwork for aerospace-specific quality standards, it is now considered less comprehensive than AS9100. B2B buyers may encounter AS9000 in legacy systems, but its limited scope and relevance in today’s aerospace landscape make it less favorable compared to the more robust AS9100 standard.
What Are the Benefits of EN 9100 for European Aerospace Businesses?
EN 9100 is the European variant of AS9100, designed to meet the specific regulatory requirements of the European aerospace industry. B2B buyers in Europe may prefer EN 9100 for its alignment with EU regulations and its recognition among local stakeholders. However, it may not be as widely recognized outside of Europe, which could pose challenges for companies looking to operate on a global scale.
How Does SJAC 9100 Cater to Japanese Aerospace Suppliers?
SJAC 9100 is tailored specifically for the Japanese aerospace market, reflecting local industry needs and regulatory frameworks. B2B buyers in Japan may find SJAC 9100 beneficial for enhancing their competitive edge within the domestic market. However, its limited recognition outside Japan could restrict opportunities for companies seeking to expand their reach internationally.
Key Industrial Applications of iso 9000 vs as9100
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of iso 9000 vs as9100 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Quality management in manufacturing and servicing of aircraft | Ensures compliance with stringent safety standards and enhances customer trust | Certification process, supplier reliability, regulatory compliance |
| Automotive | Supplier quality assurance in parts manufacturing | Reduces defects and recalls, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction | Traceability of parts, adherence to industry standards, supplier audits |
| Healthcare | Quality systems in medical device manufacturing | Guarantees product safety and efficacy, essential for regulatory approvals | Validation of quality processes, compliance with local regulations, supplier certifications |
| Construction | Quality control in construction materials and processes | Enhances project efficiency and safety, minimizing delays and costs | Material sourcing standards, adherence to safety regulations, supplier reliability |
| Electronics | Quality assurance in electronics manufacturing | Improves product reliability and customer satisfaction, reduces warranty claims | Compliance with international standards, supply chain transparency, quality audits |
How is ISO 9000 vs AS9100 Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, AS9100 is essential for managing quality in the manufacturing and servicing of aircraft. It incorporates stringent safety and regulatory requirements that ensure compliance with both civil and military aviation standards. For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa and South America, understanding these specifications is critical to ensure that their suppliers can meet both local and international compliance standards. This leads to enhanced customer trust and reduced liability risks.
What Role Does ISO 9000 Play in the Automotive Sector?
ISO 9000 serves as a foundational quality management system for automotive suppliers, ensuring that parts and components meet rigorous quality standards. This is particularly important in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where automotive safety regulations are stringent. By implementing ISO 9000, companies can minimize defects and recalls, ultimately leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. Buyers must consider the traceability of parts and the adherence of suppliers to industry standards when sourcing automotive components.
How is Quality Management Ensured in Healthcare?
The healthcare industry relies heavily on ISO 9000 to establish quality systems in medical device manufacturing. Compliance with these standards is crucial for obtaining regulatory approvals, ensuring product safety, and maintaining efficacy. For international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, sourcing from suppliers with ISO 9000 certification can significantly mitigate risks associated with product recalls and regulatory penalties. Buyers should prioritize validation of quality processes and ensure suppliers comply with local and international regulations.
What is the Importance of ISO 9000 in Construction?
In construction, ISO 9000 is used for quality control in materials and processes, which is vital for project efficiency and safety. Adopting this standard helps minimize delays and cost overruns, which are common challenges in construction projects. For buyers in regions like Brazil and the Middle East, understanding the sourcing standards and safety regulations applicable to construction materials is essential. Ensuring supplier reliability and adherence to these standards can lead to successful project outcomes.
How Does ISO 9000 Benefit Electronics Manufacturing?
ISO 9000 plays a critical role in the electronics manufacturing sector by ensuring quality assurance processes are in place. This enhances product reliability and customer satisfaction while reducing warranty claims. For international buyers, particularly in Europe and Africa, compliance with ISO 9000 means suppliers can provide transparency in their supply chain and quality audits. This is crucial in an industry where technology rapidly evolves, and customer expectations for product quality are high.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘iso 9000 vs as9100’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Complexities of Certification
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, the decision to pursue ISO 9000 or AS9100 certification can be overwhelming. Organizations in industries such as aerospace may feel pressured to meet stringent quality standards while also managing limited resources. The challenge lies in understanding which standard best aligns with their operational needs and customer expectations. Buyers often grapple with the additional requirements imposed by AS9100, leading to confusion about the necessary steps for successful certification.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the certification landscape, organizations should start with a comprehensive gap analysis to assess their current quality management systems against the requirements of both ISO 9000 and AS9100. This analysis should involve key stakeholders from various departments, including quality assurance, production, and compliance. Once the gaps are identified, companies can prioritize the specific requirements they need to address, such as enhanced design control or risk management protocols unique to AS9100. Engaging with a certification body that specializes in aerospace standards can also provide tailored guidance and support throughout the certification process, ensuring a smoother transition.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Misalignment in Quality Management Systems
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers face a significant challenge when their quality management systems (QMS) do not align with the expectations of their customers, particularly in the aerospace sector. Companies that are certified to ISO 9000 may struggle to meet the more rigorous demands of AS9100, resulting in potential loss of contracts or damage to their reputation. This misalignment can stem from a lack of understanding of the additional requirements specific to the aerospace industry.
The Solution: To bridge the gap between ISO 9000 and AS9100, organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff focused on the specific nuances of AS9100. This training should cover critical areas such as configuration management and counterfeit parts prevention. Additionally, companies should consider implementing a phased approach to gradually incorporate AS9100 requirements into their existing QMS. This allows for adjustments without overwhelming the team. Establishing a feedback loop from internal audits and customer assessments can help ensure that the QMS evolves to meet both ISO 9000 and AS9100 standards effectively.
Scenario 3: Addressing Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The Problem: In regions like Africa and South America, B2B buyers often encounter regulatory compliance issues when trying to implement ISO 9000 or AS9100 standards. The varying regulatory landscapes can create uncertainty about which standard to adopt, especially for companies looking to penetrate international markets. Failing to comply with industry-specific regulations can lead to costly fines and reputational damage.
The Solution: To address these compliance challenges, organizations should conduct thorough research on the regulatory requirements specific to their target markets, particularly those related to aerospace standards. Building partnerships with local regulatory bodies or industry associations can provide valuable insights into compliance expectations. Furthermore, companies should document their compliance processes and maintain transparency with stakeholders. Utilizing a compliance management software can streamline tracking and reporting processes, ensuring that all regulatory requirements are met consistently. Regularly reviewing and updating compliance strategies in line with changing regulations will also help businesses stay ahead of potential pitfalls.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for iso 9000 vs as9100
When considering materials for quality management systems under ISO 9000 and AS9100, it is essential to analyze specific materials that align with the stringent requirements of these standards. This analysis focuses on three common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials. Each material has unique properties, pros and cons, and impacts on applications relevant to international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum in ISO 9000 and AS9100 Applications?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It typically performs well under moderate temperature and pressure conditions. In aerospace applications governed by AS9100, aluminum is often utilized for structural components due to its strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum:
– Pros: Lightweight, good corrosion resistance, and ease of machining. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other metals.
– Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more susceptible to fatigue over time.
Impact on Application:
In aerospace and automotive industries, aluminum components must comply with specific safety and performance standards. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but buyers must ensure that it meets the regulatory requirements of their respective markets.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for ISO 9000 and AS9100 Standards?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and oxidation. It is suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, making it a preferred choice in industries that require stringent quality control.
Pros and Cons of Using Stainless Steel:
– Pros: High strength and durability, excellent corrosion resistance, and a wide range of grades tailored for specific applications.
– Cons: Higher cost compared to aluminum and can be more challenging to machine. It may also require additional surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application:
In sectors like aerospace, stainless steel is often used for critical components that must withstand extreme conditions. Buyers from different regions should consider local standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) to ensure compliance.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in ISO 9000 and AS9100?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in aerospace applications due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They offer excellent fatigue resistance and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics.
Pros and Cons of Using Composite Materials:
– Pros: Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and tailored properties for specific applications. They also offer excellent resistance to environmental factors.
– Cons: Higher manufacturing complexity and costs. Additionally, they may require specialized recycling processes, which could be a concern for sustainability.
Impact on Application:
In the aerospace industry, composites are crucial for reducing weight and enhancing fuel efficiency. International buyers must be aware of the specific certifications and standards required for composite materials in their markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for ISO 9000 vs AS9100
| Material | Typical Use Case for iso 9000 vs as9100 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components in aerospace | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Critical components in aerospace | High strength and durability | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Composite | Lightweight structures in aerospace | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a clear understanding of the materials relevant to ISO 9000 and AS9100 standards. By considering the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and regional compliance requirements, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for iso 9000 vs as9100
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for ISO 9000 vs AS9100?
In the realm of quality management systems, ISO 9000 and AS9100 cater to different industries with distinct manufacturing processes. Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers evaluate suppliers effectively, ensuring that they meet the specific requirements of their sector.
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Processes for ISO 9000?
The ISO 9000 standard, applicable across various industries, outlines fundamental quality principles. The typical manufacturing process can be broken down into four main stages:
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing raw materials that meet predefined specifications. For ISO 9000 compliance, documentation of material certificates and supplier qualifications is critical. Buyers should verify that suppliers have robust material sourcing protocols, ensuring consistency and quality.
-
Forming: In this stage, raw materials undergo shaping through processes like casting, machining, or molding. ISO 9000 emphasizes process control and monitoring to ensure that forming techniques are consistent and repeatable. Buyers can look for certifications that demonstrate adherence to these controls.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage brings together various components into a final product. For ISO 9000, this involves clear documentation of assembly procedures, including work instructions and training records for personnel involved. B2B buyers should request evidence of a structured assembly process that includes checks for compliance with specifications.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes processes such as painting, coating, or surface treatment to enhance the product’s functionality and aesthetics. ISO 9000 requires quality checks at this stage to ensure that the finishing meets customer expectations. Buyers should inquire about the inspection methods used to validate the finished product quality.
How Does the Manufacturing Process for AS9100 Differ?
AS9100 is a more stringent quality management system tailored specifically for the aerospace industry. Its manufacturing processes involve additional complexity due to the high safety and regulatory standards.
-
Material Preparation: Similar to ISO 9000, AS9100 requires rigorous documentation and qualification of materials. However, it places greater emphasis on traceability, ensuring that materials can be tracked throughout the supply chain. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers maintain comprehensive records of material origins and certifications.
-
Forming: AS9100 mandates advanced techniques for forming processes, including the use of statistical process control (SPC) to monitor variations. This ensures that any deviations are identified and corrected promptly. Buyers can assess suppliers by reviewing their SPC methodologies and data.
-
Assembly: The assembly processes under AS9100 are particularly focused on design control and configuration management. This includes rigorous checks to prevent counterfeit parts from entering the supply chain. B2B buyers should look for suppliers that implement robust verification processes for all components used in assembly.
-
Finishing: AS9100 requires adherence to specific finishing standards that comply with both civil and military aviation regulations. This includes thorough testing and validation of finished products to ensure they meet safety and performance criteria. Buyers should request detailed reports on finishing processes and any certifications related to these standards.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Relevant for ISO 9000 and AS9100?
Quality control (QC) is essential for ensuring that products meet established standards. Both ISO 9000 and AS9100 have specific QC checkpoints that B2B buyers should be aware of.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting materials and components upon receipt. For ISO 9000, this includes verifying that incoming materials meet specified criteria. AS9100 takes this further by requiring detailed inspection protocols and documentation for aerospace components.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring ensures that processes remain within specified limits. ISO 9000 emphasizes process adherence, while AS9100 incorporates more rigorous testing and validation at various stages, particularly for safety-critical components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final checkpoint assesses the completed product against specifications. ISO 9000 requires documentation of final inspections, while AS9100 demands comprehensive testing and validation to meet regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide detailed FQC reports.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Understanding the landscape of international and industry-specific standards is crucial for B2B buyers.
-
ISO 9001: As the foundation for both ISO 9000 and AS9100, ISO 9001 provides a framework for quality management applicable across various sectors. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates a basic level of quality assurance.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products marketed in Europe, CE marking signifies compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers in Europe should ensure that suppliers provide CE certification for relevant products.
-
API Standards: For industries related to oil and gas, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards govern quality assurance and product specifications. Buyers should verify that their suppliers comply with applicable API standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must implement robust verification methods to ensure that suppliers adhere to quality control standards. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of supplier facilities can help assess compliance with ISO 9000 or AS9100 standards. Audits should focus on manufacturing processes, documentation, and QC measures.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and QC measures. These reports should include data on inspections, testing results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of supplier quality. This is particularly important for international transactions, where local regulations may differ.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers operating across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and certification nuances is vital.
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific quality control requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations that may affect supplier compliance.
-
Certification Recognition: Not all certifications are recognized globally. Buyers should verify that the certifications held by suppliers are acknowledged in their target markets.
-
Cultural Considerations: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can help bridge cultural gaps that may affect quality perceptions. Buyers should be proactive in addressing any concerns that arise during the manufacturing process.
By comprehensively understanding these manufacturing processes, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive products that meet the highest standards of quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘iso 9000 vs as9100’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in understanding and procuring quality management systems, specifically focusing on ISO 9001 and AS9100 standards. By following this checklist, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs, regulatory requirements, and industry-specific standards.
Step 1: Identify Your Industry Needs
Before choosing between ISO 9001 and AS9100, assess your industry requirements. Understanding the specific quality management needs of your sector—such as aerospace, automotive, or manufacturing—will guide your decision. AS9100 is tailored for the aerospace industry, including stringent safety and regulatory requirements, while ISO 9001 serves a broader range of industries.
Step 2: Define Your Quality Objectives
Establish clear quality objectives that align with your organizational goals. This step is crucial because it will help you determine which standard best supports your mission. Consider whether your focus is on compliance, risk management, or customer satisfaction, as this will influence your choice between the two standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold the appropriate certifications for ISO 9001 or AS9100. Certification demonstrates a commitment to quality management principles and regulatory compliance. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and relevant accreditations from recognized bodies, as this can significantly affect your supply chain reliability.
Step 4: Assess the Scope of Implementation
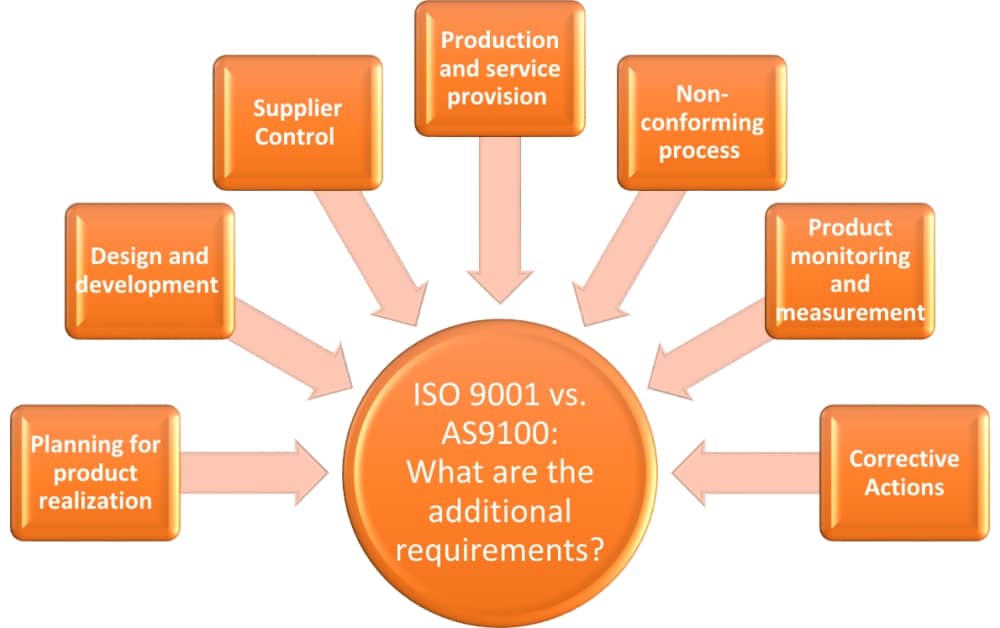
Consider the scope of implementation required for each standard. AS9100 has additional requirements that address aerospace-specific challenges, including risk management and product safety. In contrast, ISO 9001 provides a more generalized framework. Understanding the depth of implementation necessary for your operations can help in resource allocation and planning.
Step 5: Review Supplier Experience and References
Conduct thorough research on suppliers’ experience and their performance history in implementing ISO 9001 or AS9100. Request case studies, testimonials, and references from clients in similar industries. This step is vital as it provides insights into the supplier’s capability to meet your quality management needs effectively.
Step 6: Analyze Cost Implications
Evaluate the total cost of compliance and implementation for each standard. While AS9100 may involve higher costs due to its specific requirements and training needs, it can also lead to long-term savings through improved operational efficiency and risk mitigation. Consider both upfront costs and potential returns on investment to make a balanced decision.
Step 7: Plan for Continuous Improvement
Implement a strategy for continuous improvement regardless of the standard chosen. Both ISO 9001 and AS9100 emphasize the importance of ongoing assessment and enhancement of processes. Establish metrics and regular review processes to ensure that your quality management system evolves in line with changing industry standards and customer expectations.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of selecting between ISO 9001 and AS9100, ensuring that their choice aligns with their strategic goals and industry requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for iso 9000 vs as9100 Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in ISO 9000 vs AS9100 Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure for sourcing ISO 9000 and AS9100 certifications is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of materials can vary significantly between ISO 9000 and AS9100. AS9100, being aerospace-specific, often necessitates higher-grade materials that comply with stringent safety and quality standards. This can lead to increased material costs, particularly for buyers in industries with lower regulatory demands.
-
Labor: Labor costs can also differ based on the complexity of the certification process. AS9100 typically requires a higher level of expertise and specialized training for quality management, which may increase labor costs compared to ISO 9000. Companies must factor in these costs when considering the overall budget for certification.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead expenses can be more pronounced in AS9100 certifications due to the additional compliance requirements. These may include investments in specialized equipment and software for tracking and maintaining compliance with aerospace standards.
-
Tooling and Quality Control: The need for advanced tooling and rigorous QC processes in AS9100 can add to the overall cost. This is particularly relevant for manufacturers aiming to minimize defects and ensure safety in aerospace applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and logistics costs can vary depending on the certification’s requirements. AS9100 may necessitate specific handling and shipping protocols, leading to higher logistics costs.
-
Margin: Finally, profit margins may differ based on the perceived value and demand for each certification. AS9100 certifications often command higher premiums due to their specialized nature and the critical safety implications involved in aerospace manufacturing.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect ISO 9000 vs AS9100 Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of ISO 9000 and AS9100 certifications, including volume or minimum order quantities (MOQ), specifications and customization, quality certifications, and supplier dynamics.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes can lead to reduced per-unit costs, particularly for AS9100, where the upfront costs for compliance and certification can be spread across a larger production run. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions may drive up costs, especially in AS9100, where specific requirements must be met. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality Certifications: The presence of additional quality certifications or compliance with international standards can impact pricing. Suppliers with recognized certifications may charge more, but this often translates to lower risk and higher quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence costs. Established suppliers with a track record of successful AS9100 compliance may charge a premium but offer greater assurance of quality and timely delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms on shipping and delivery can help manage logistics costs. Buyers must clarify who bears the responsibility for shipping costs and risks, which can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for ISO 9000 and AS9100?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing ISO 9000 and AS9100 certifications, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation with suppliers can yield better pricing and terms. Buyers should leverage their understanding of the cost structure and market dynamics to negotiate favorable deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO, which includes all costs associated with procurement, including maintenance and compliance costs over time. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying pricing structures. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, taxes, and tariffs that could affect the final price.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough research on industry standards and benchmark pricing against competitors. This information can empower buyers to make competitive offers and ensure they are not overpaying.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for ISO 9000 and AS9100 certifications can fluctuate based on numerous factors, including market demand, geographic location, and specific supplier capabilities. Therefore, it is recommended that buyers conduct extensive market research and seek multiple quotes to establish a clear understanding of the pricing landscape.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing iso 9000 vs as9100 With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to ISO 9000 and AS9100
In the competitive landscape of quality management systems (QMS), businesses often seek alternatives to ISO 9000 and AS9100. These alternatives can provide varying levels of performance, cost efficiency, and ease of implementation, tailored to specific industry needs. This analysis compares ISO 9000 and AS9100 against two viable alternatives: Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM).
| Comparison Aspect | Iso 9000 Vs As9100 | Six Sigma | Total Quality Management (TQM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Ensures compliance with quality standards in aerospace; more stringent in AS9100 | Focuses on process improvement and defect reduction; data-driven approach | Emphasizes continuous improvement across all organizational processes |
| Cost | Initial certification can be costly; ongoing maintenance required | Potentially high upfront training costs; long-term cost savings through efficiency | Generally lower cost; focuses on internal resources and training |
| Ease of Implementation | ISO 9000 is easier to implement; AS9100 requires more specialized knowledge | Requires training and cultural shift; can be complex | Requires commitment from all employees; gradual implementation can be challenging |
| Maintenance | Regular audits and updates needed for compliance | Continuous monitoring and improvement of processes | Requires ongoing commitment and employee involvement |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace and related industries needing rigorous compliance | Manufacturing and service industries focused on efficiency | Organizations looking for a holistic approach to quality across all functions |
What Are the Key Benefits and Drawbacks of Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at reducing defects and improving process quality. Its structured approach is beneficial for organizations that prioritize measurable improvements and operational excellence. However, the implementation of Six Sigma can be resource-intensive, requiring significant training and cultural changes within the organization. Companies might find that while the initial investment is high, the long-term cost savings from increased efficiency can be substantial.
How Does Total Quality Management (TQM) Differ from ISO 9000 and AS9100?
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive management approach that seeks to improve quality and performance across all organizational processes. Unlike ISO 9000 and AS9100, which are standards focused on compliance, TQM emphasizes a cultural shift towards quality at every level of the organization. The key advantage of TQM is its potential for fostering employee engagement and collaboration. However, TQM requires a long-term commitment from all staff, and its gradual implementation may pose challenges for organizations seeking quick results.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting a quality management system, B2B buyers should consider their industry requirements, organizational culture, and the specific challenges they face. ISO 9000 and AS9100 are excellent choices for organizations in the aerospace sector or those needing rigorous compliance. In contrast, Six Sigma may be more suitable for manufacturing firms focused on efficiency, while TQM can benefit organizations seeking a comprehensive quality approach across all departments. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on aligning the selected methodology with the organization’s strategic goals and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for iso 9000 vs as9100
What Are the Key Technical Properties of ISO 9000 and AS9100?
1. Quality Management System (QMS) Framework
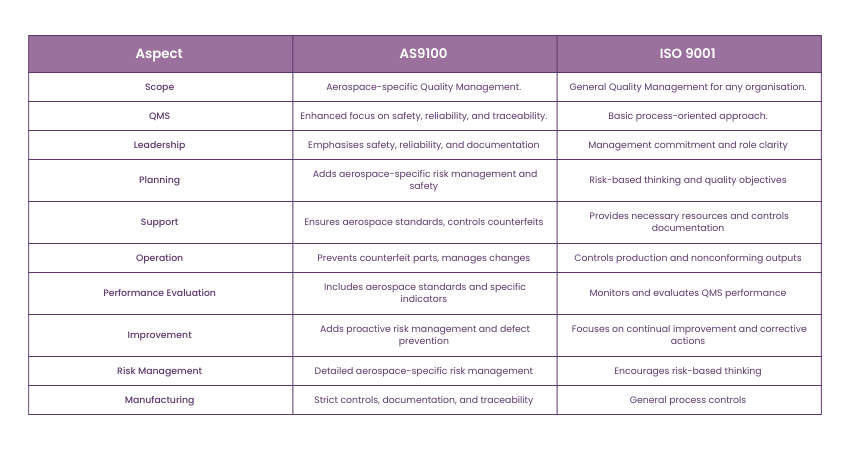
Both ISO 9000 and AS9100 provide a structured framework for organizations to establish and maintain an effective Quality Management System (QMS). ISO 9000 serves as a foundational standard applicable across various industries, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. In contrast, AS9100 is specifically tailored for the aerospace sector, incorporating additional requirements that address the unique challenges of aerospace manufacturing and maintenance. For B2B buyers, understanding these frameworks is crucial for selecting suppliers that can meet industry-specific quality standards.
2. Regulatory Compliance Requirements
AS9100 emphasizes stringent regulatory compliance relevant to the aerospace industry, ensuring organizations adhere to safety, security, and product reliability regulations. This focus is critical for businesses that operate in or supply to the aerospace sector, as it minimizes risks associated with non-compliance. ISO 9000, while also promoting compliance, does so in a more generalized manner, applicable to various industries. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate compliance with AS9100 if they operate in aerospace, as it indicates a commitment to rigorous quality standards.
3. Risk Management Practices
The AS9100 standard includes comprehensive risk management practices that are vital for identifying and mitigating potential risks throughout the product lifecycle. This includes aspects such as configuration management and counterfeit parts prevention, which are especially pertinent in the aerospace field. In contrast, ISO 9000 offers a broader approach to risk but may lack the specific requirements necessary for high-stakes industries. B2B buyers in sectors that require high reliability should seek suppliers certified to AS9100 to ensure robust risk management is in place.
4. Continuous Improvement Processes
Both standards advocate for continuous improvement, but AS9100 incorporates specific tools and methodologies tailored to the aerospace industry, such as design control and product safety measures. These additional processes enhance the quality and reliability of products, which is paramount in aerospace applications. B2B buyers should evaluate a supplier’s commitment to continuous improvement practices, as this can lead to better product quality and customer satisfaction over time.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in ISO 9000 and AS9100 Contexts?
1. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of ISO 9000 and AS9100, understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers looking for quality assurance in their supply chains. OEMs often hold certifications that align with these standards, ensuring that products meet specific quality benchmarks.
2. Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, especially in the aerospace sector, understanding MOQs is vital for inventory management and cost control. Suppliers adhering to AS9100 may have different MOQs based on their production capabilities and quality assurance processes.
3. Request for Quotation (RFQ)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When engaging suppliers, particularly those certified under AS9100, buyers should include quality requirements in their RFQs to ensure that potential suppliers can meet the necessary standards.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. They are crucial for B2B transactions, particularly in global supply chains. Understanding the relevant Incoterms can help buyers navigate logistics and risk management, especially when sourcing from suppliers adhering to ISO 9000 or AS9100 standards.
5. Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA)
CAPA refers to processes used to investigate and rectify non-conformities in products or processes. In both ISO 9000 and AS9100 contexts, CAPA is essential for maintaining quality standards and ensuring continuous improvement. B2B buyers should inquire about a supplier’s CAPA processes to assess their commitment to quality management.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers that align with their quality management needs, particularly in sectors governed by stringent standards like aerospace.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the iso 9000 vs as9100 Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ISO 9000 vs AS9100 Sector?
Market Overview & Key Trends
The landscape of quality management systems is evolving rapidly, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and heightened regulatory scrutiny. For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances between ISO 9000 and AS9100 is crucial. The aerospace sector, which heavily relies on AS9100, is experiencing an upswing due to increased air travel demand and the push for innovations in sustainable aviation. Concurrently, ISO 9000 remains relevant across various industries, providing a foundational framework for quality assurance.
Emerging trends such as digital transformation, including the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), are reshaping how organizations implement these standards. Companies are increasingly utilizing advanced data analytics to enhance compliance monitoring and streamline processes. Additionally, the growing emphasis on risk management, particularly in supply chains disrupted by global events, is prompting organizations to adopt more robust quality management systems that align with AS9100’s stringent requirements.
Furthermore, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate compliance with these standards. The increasing demand for certifications is a direct response to regulatory pressures and the need for transparency in supply chains. As such, international buyers are encouraged to consider these certifications not just as compliance checkboxes but as strategic assets that enhance their market position.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B Practices in the ISO 9000 vs AS9100 Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the B2B landscape, particularly for organizations adhering to ISO 9000 and AS9100 standards. The environmental impact of manufacturing and supply chain operations is under scrutiny, compelling companies to adopt sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint, utilizing eco-friendly materials, and implementing waste reduction strategies.
For organizations certified under ISO 9000 and AS9100, integrating sustainability into their quality management systems not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances their brand reputation. Buyers are more likely to engage with suppliers who have sustainable certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, which aligns with the principles of continuous improvement inherent in both ISO 9000 and AS9100.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are demanding transparency and accountability in sourcing, especially in regions where labor practices may be questionable. Certifications that focus on ethical sourcing practices help build trust and long-term relationships between buyers and suppliers. As sustainability becomes a core component of business strategy, organizations that prioritize these values will likely gain a competitive edge in the global market.
What Is the Evolution and History of ISO 9000 and AS9100 Relevant for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of ISO 9000 and AS9100 reflects the growing need for standardized quality management across industries. ISO 9000 was introduced in the late 1980s as a generic framework for quality assurance applicable to all sectors. Its focus on customer satisfaction and process improvement laid the groundwork for organizations worldwide.
In contrast, AS9100 emerged in the late 1990s specifically to address the unique challenges of the aerospace industry. Developed by key aerospace stakeholders, including major manufacturers and regulatory bodies, AS9100 incorporates additional requirements tailored to ensure safety and compliance in aerospace manufacturing and maintenance. Its adoption has been pivotal for organizations aiming to compete in the highly regulated aerospace market.
This historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it underscores the importance of choosing the right certification based on industry requirements. Buyers looking to partner with suppliers in aerospace should prioritize AS9100, while those in other sectors can benefit from the foundational principles of ISO 9000. Understanding this evolution helps buyers make informed decisions about supplier qualifications and the strategic value of quality certifications in their procurement processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of iso 9000 vs as9100
-
How do I choose between ISO 9001 and AS9100 for my business?
Choosing between ISO 9001 and AS9100 depends on your industry and specific quality requirements. ISO 9001 is suitable for a wide range of sectors, providing a framework for establishing effective quality management systems. In contrast, AS9100 is tailored for the aerospace industry, incorporating additional criteria essential for compliance with aerospace regulations. Evaluate your business goals, the needs of your clients, and the regulatory environment before making a decision. -
What are the key differences between ISO 9001 and AS9100?
The primary difference lies in their focus: ISO 9001 is a generic standard applicable across various industries, while AS9100 is specifically designed for aerospace. AS9100 includes additional requirements related to risk management, product safety, and counterfeit parts prevention, which are not present in ISO 9001. If your business operates in the aerospace sector, AS9100 may offer the specialized framework needed to meet industry-specific challenges. -
What are the benefits of obtaining AS9100 certification for my aerospace business?
AS9100 certification enhances your company’s credibility in the aerospace market by demonstrating compliance with stringent quality and safety standards. It facilitates access to international aerospace supply chains, boosts customer confidence, and can lead to improved operational efficiencies. Additionally, it helps organizations address regulatory requirements effectively, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties. -
How can I ensure my suppliers are compliant with ISO 9001 or AS9100?
To verify supplier compliance, request copies of their certifications and conduct audits to assess their quality management systems. Engaging in regular communication about quality processes and performance metrics is essential. Additionally, consider utilizing third-party certification bodies that specialize in ISO and AS9100 certifications to ensure impartiality and thoroughness in the evaluation process. -
What is the typical timeline and cost for obtaining ISO 9001 or AS9100 certification?
The timeline for certification can vary significantly based on the organization’s size and readiness, typically ranging from three to six months. Costs also vary, depending on factors like consultancy fees, training, and audit expenses, often ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. It is advisable to budget for ongoing maintenance and potential re-certification every three years. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) I should expect from suppliers certified in ISO 9001 or AS9100?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely based on the supplier and the product type. Generally, suppliers with ISO 9001 or AS9100 certification may have more flexible MOQs due to established quality systems, but this is not guaranteed. Discussing your specific needs with potential suppliers can help negotiate terms that suit both parties while maintaining quality standards. -
How do I handle logistics and supply chain management when sourcing from international suppliers?
When sourcing internationally, establish clear communication channels and logistics plans to manage timelines, costs, and quality expectations. Utilize logistics partners experienced in international trade to navigate customs and regulatory requirements. Implementing a robust quality assurance process will help maintain product standards throughout the supply chain, ensuring compliance with ISO 9001 or AS9100. -
What payment terms should I consider when working with international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). Consider using escrow services or letters of credit for high-value transactions to protect both parties. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring your suppliers feel secure in the transaction.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Iso 9000 Vs As9100 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Smithers – AS9100 Quality Management Solutions
Domain: smithers.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: AS9100 is a quality management standard specifically for the aerospace industry, built on the foundation of ISO 9001:2015. ISO 9001:2015 is the fundamental quality standard recognized internationally, focusing on customer satisfaction and continual improvement. AS9100 includes additional requirements tailored to aerospace needs, such as risk management, project management, configuration management…
2. BPRHub – Aerospace Quality Standards Comparison
Domain: bprhub.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: AS9000 vs AS9100: Aerospace Quality Standards Compared – BPRHub Products Compliance Module, Operations Module, Solutions By Standard, Solutions By Industry, Management Differences, Purpose and Scope of AS9000 vs. AS9100, Key differences between AS9000 and AS9100, Development of AS9000, Introduction of AS9100, Revisions and Updates to AS9100.
3. Practical Machinist – ISO Certification Insights
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: ISO9000 and AS9100 certification processes, need for consultants, relevance of certification for customers, experiences with ISO implementation, challenges faced by small shops, importance of documentation and consistency in processes, recommendations for consulting services.
4. CyberNines – CMMC Certification Solutions
Domain: blog.cybernines.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification) is specifically designed for Department of Defense (DoD) contractors handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or Federal Contract Information (FCI). It requires a rigorous certification process and periodic renewal. ISO 9000, AS9100, and ISO 27001 are international quality management standards that focus on quality assurance, safety, and …
5. Reddit – AS9100 Certification Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: AS9100 certification is aimed at organizations in the aerospace industry. It emphasizes common sense practices that should be implemented at any level of a manufacturing operation. The discussion suggests that while the costs of certification and audits may not be justifiable without an aerospace contract, having the infrastructure in place early on is beneficial. It is recommended to document pro…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for iso 9000 vs as9100
As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of quality management systems, understanding the distinctions between ISO 9000 and AS9100 is paramount. ISO 9000 serves as a versatile framework applicable across various industries, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. In contrast, AS9100 is tailored specifically for the aerospace sector, incorporating stringent requirements essential for compliance with safety regulations and industry-specific challenges.
Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in leveraging these standards effectively. By aligning supplier selection and management processes with either ISO 9000 or AS9100, organizations can enhance their operational efficiencies, mitigate risks, and improve product quality. This alignment not only strengthens supply chain resilience but also fosters trust with stakeholders, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance and quality assurance are increasingly scrutinized.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to assess their specific needs against these standards and consider certifications that will provide a competitive edge. By embracing the right quality management system, businesses can position themselves for growth and success in the global marketplace. Invest in your quality journey today to ensure a sustainable future.