Choosing Your Silo Prices: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for silo prices
In today’s global market, sourcing the right silo prices can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in finding competitive pricing but also in ensuring that the selected storage solutions meet specific agricultural and industrial needs. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities of silo pricing by exploring various types, applications, and the factors influencing costs.
Buyers will gain insights into the nuances of silo types—from tower silos designed for optimal feed storage to flat-bottom bins suitable for grain. Furthermore, the guide will delve into critical aspects such as supplier vetting, maintenance considerations, and the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the initial purchase price but also long-term operational expenses.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable information and expert analysis, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any other part of the world, understanding the dynamics of silo prices is essential for optimizing your supply chain and enhancing operational efficiency. With the right knowledge, you can confidently navigate the global market and select the best silo solutions that align with your business goals.
Understanding silo prices Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Bottom Grain Bins | Stiffened structure, large capacity (up to 60,000 Bu), suitable for various grain types | Agriculture, food storage | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install. Cons: Limited lifespan compared to vertical silos. |
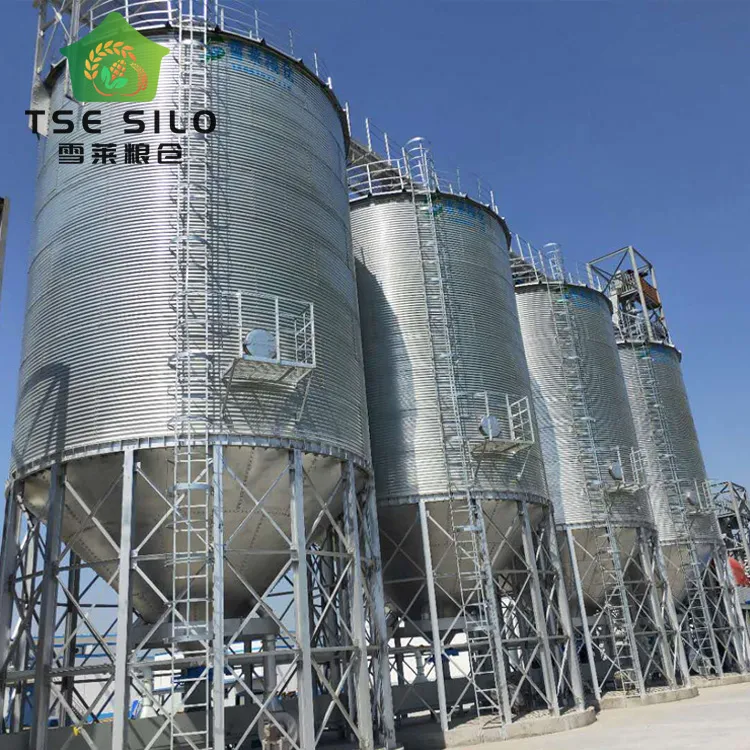
| Tower Silos | Vertical design, lower dry matter loss (6-9%), automated unloading options | Dairy and livestock feed storage | Pros: Efficient space utilization, reduced spoilage. Cons: Higher initial capital cost. |
| Bunker Silos | Horizontal structure, large volumes, requires packing | Bulk feed storage, silage | Pros: Lower construction costs, flexible size. Cons: Higher feed loss (up to 17%). |
| Hopper Silos | Cone-shaped bottom for easy discharge, often used for bulk materials | Waste management, biosolids storage | Pros: Efficient material handling, reduced downtime. Cons: Limited capacity compared to other silo types. |
| Vacuum Storage Systems | Sealed environment, minimizes oxidation, suitable for sensitive materials | Specialty food storage, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Extended shelf life, high-quality preservation. Cons: Higher operational costs. |
What Are Flat Bottom Grain Bins and Their Benefits for B2B Buyers?
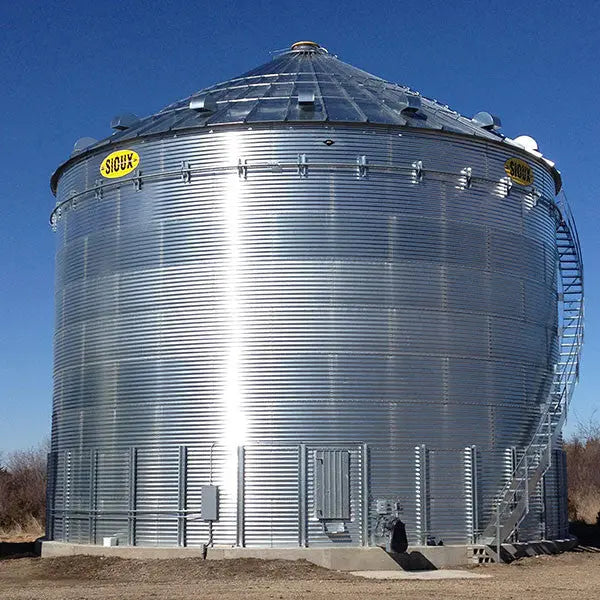
Flat bottom grain bins are characterized by their stiffened structure and significant storage capacity, often accommodating up to 60,000 bushels. They are primarily utilized in agriculture for the storage of grains such as corn, wheat, and soybeans. B2B buyers appreciate these bins for their cost-effectiveness and straightforward installation process. However, they may have a shorter lifespan compared to vertical silo options, which is an important consideration for long-term investment.
How Do Tower Silos Compare in Terms of Efficiency and Cost?
Tower silos are designed for vertical storage and are known for their efficiency, particularly in minimizing dry matter loss during storage (ranging from 6% to 9%). This makes them ideal for dairy and livestock feed storage, where maintaining the quality of the feed is crucial. While the initial capital investment is higher than that of other types, the reduced spoilage and automation options for unloading can lead to lower operational costs over time. Buyers should weigh the upfront costs against the long-term savings.
What Makes Bunker Silos a Popular Choice for Bulk Storage?
Bunker silos are horizontal storage structures that can handle large volumes of feed and silage, making them a popular choice in agricultural settings. Their construction costs are generally lower than those of tower silos, and they offer flexibility in terms of size. However, they come with a downside: a higher rate of feed loss, which can reach up to 17%. For B2B buyers, understanding the trade-offs between initial costs and potential feed loss is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Why Consider Hopper Silos for Waste Management Applications?
Hopper silos feature a cone-shaped bottom that facilitates easy discharge of materials, making them particularly effective in waste management and biosolids storage applications. They are efficient for handling bulk materials and can reduce downtime in operations. However, their capacity is generally limited compared to other silo types, which can be a drawback for businesses needing larger storage solutions. Buyers should evaluate their specific storage needs and operational requirements before selecting hopper silos.
How Do Vacuum Storage Systems Enhance Material Preservation?
Vacuum storage systems create a sealed environment that minimizes oxidation, making them suitable for storing sensitive materials such as specialty foods and pharmaceuticals. These systems significantly extend the shelf life of stored products while maintaining high quality. However, they come with higher operational costs, which can be a concern for budget-conscious B2B buyers. Evaluating the benefits of quality preservation against the costs is crucial for businesses considering this option.
Key Industrial Applications of silo prices
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Silo Prices | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Grain Storage Solutions | Ensures safe storage and reduces spoilage of harvested crops | Capacity needs, local climate conditions, and durability of materials |
| Food Processing | Ingredient Storage | Maintains quality and extends shelf life of raw materials | Compliance with food safety regulations and ease of access for loading |
| Waste Management | Biosolids Storage | Efficient handling and disposal of waste materials | Environmental regulations, material compatibility, and transportation logistics |
| Construction Materials | Bulk Material Storage | Streamlines supply chain and reduces material loss | Size specifications, accessibility for delivery, and pricing stability |
| Renewable Energy | Biomass Storage | Maximizes energy production efficiency from stored biomass | Moisture control, material type, and integration with processing systems |
How Are Silo Prices Applied in Agriculture for Grain Storage Solutions?
In the agriculture sector, silos are primarily utilized for grain storage. B2B buyers in this industry look for solutions that provide safe and efficient storage of harvested crops, minimizing spoilage and waste. The price of silos can vary significantly based on capacity, with larger silos offering better economies of scale. Buyers must consider local climate conditions, as humidity and temperature fluctuations can affect grain quality. Additionally, the durability of materials used in silo construction is crucial for long-term investments.
What Role Do Silo Prices Play in Food Processing for Ingredient Storage?
Food processing companies rely on silos for the storage of bulk ingredients, ensuring the quality and extending the shelf life of raw materials. The prices of these silos are influenced by their ability to comply with stringent food safety regulations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer silos designed for easy access and efficient loading processes. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions with varying regulatory standards, necessitating a thorough understanding of local compliance requirements.
How Are Silo Prices Utilized in Waste Management for Biosolids Storage?
In waste management, silos are essential for the temporary storage of biosolids, facilitating efficient handling and disposal. The investment in silo prices must account for environmental regulations governing waste management practices. B2B buyers should evaluate the compatibility of silo materials with the types of waste being stored, as well as the logistics of transporting the materials to and from the facility. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs, is critical for maximizing return on investment.
How Do Silo Prices Benefit the Construction Materials Sector in Bulk Material Storage?
In the construction materials sector, silos are used for the bulk storage of materials such as cement, sand, and aggregates. This application helps streamline the supply chain and minimizes material loss during storage. Buyers must consider the size specifications of silos to ensure compatibility with delivery vehicles and the construction site layout. Additionally, pricing stability is a key factor, as fluctuations in silo prices can impact overall project budgets.
What Are the Advantages of Silo Prices in Renewable Energy for Biomass Storage?
Silos serve a vital role in the renewable energy sector for storing biomass, which is essential for maximizing energy production efficiency. The price of silos in this context is influenced by their design, which must accommodate specific biomass types while maintaining moisture control. B2B buyers should also consider how the silo integrates with existing processing systems to enhance operational efficiency. As the renewable energy landscape evolves, understanding the implications of silo investments on energy output is crucial for long-term planning.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘silo prices’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Price Fluctuations in Silo Purchases
The Problem: One of the significant challenges B2B buyers face when dealing with silo prices is the unpredictability of market fluctuations. Prices for silos can vary dramatically based on material costs, demand, and even international supply chain disruptions. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, where market access and information may be limited, this volatility can lead to budget overruns or delayed purchasing decisions, ultimately affecting their operations and profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with price fluctuations, B2B buyers should implement a multi-sourcing strategy. This means identifying and establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to receive competitive quotes and understand market trends. Furthermore, buyers should consider locking in prices through long-term contracts or agreements that allow for fixed pricing over a specified period. By conducting thorough market research and leveraging local networks, buyers can better anticipate pricing trends and make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational budgets.
Scenario 2: Understanding Total Cost of Ownership for Silos
The Problem: Many buyers focus solely on the initial purchase price of silos, neglecting to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). This oversight can lead to unforeseen expenses related to maintenance, energy consumption, and operational inefficiencies, particularly in regions with high labor costs or energy prices. For instance, buyers in the Middle East might encounter high electricity rates, which can significantly increase the operational costs of running silos.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers must conduct a comprehensive TCO analysis before making a purchase. This involves evaluating not just the upfront costs but also the projected expenses over the silo’s lifespan, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential depreciation. Buyers should seek suppliers who provide detailed cost breakdowns and operational efficiency metrics. Additionally, investing in energy-efficient silo systems or automation technologies can yield long-term savings and enhance operational effectiveness. Utilizing software tools for financial modeling can also help simulate various scenarios, ensuring buyers are equipped with the necessary data to make informed decisions.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Local Regulations and Standards
The Problem: Compliance with local regulations regarding silo construction and operation is a critical concern for B2B buyers, especially in industries such as agriculture and food processing. Buyers in regions like Europe or the Middle East may face stringent environmental regulations or safety standards that impact the design and functionality of silos. Failure to comply can result in costly fines or operational shutdowns, putting significant financial strain on businesses.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on local regulations and engage with compliance experts early in the purchasing process. This may involve consulting with legal advisors or industry associations to understand the specific requirements related to silo construction, safety standards, and operational practices. Furthermore, when sourcing silos, buyers should prioritize suppliers who have a proven track record of compliance and can provide certification or documentation demonstrating adherence to relevant regulations. By integrating compliance considerations into their procurement strategy, buyers can minimize risks and ensure their operations remain legally sound and sustainable.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for silo prices
What Are the Key Properties of Common Silo Materials?
When selecting materials for silos, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in silo construction: steel, aluminum, reinforced concrete, and fiberglass.
How Does Steel Perform in Silo Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials for silo construction due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high temperature and pressure rating, making it suitable for various agricultural and industrial applications. Steel silos can resist corrosion when treated with protective coatings, although they may require maintenance over time to prevent rust.
Pros: Steel silos are robust and can handle significant loads, making them ideal for storing heavy materials. They are also relatively easy to manufacture and can be customized to meet specific size requirements.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion if not properly maintained, especially in humid environments. Additionally, the initial capital cost can be high, depending on the thickness and treatment of the steel used.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of materials, including grains, seeds, and some chemicals. However, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive substances without additional protective measures.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Silo Construction?
Aluminum is another material gaining traction in silo construction, especially in environments where weight reduction is crucial. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for storing various materials, including chemicals and food products.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier installation and transportation. Its corrosion resistance reduces maintenance costs over time, making it a cost-effective option in the long run.
Cons: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, which can be a significant factor for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, it has a lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum silos are particularly well-suited for food storage and chemicals due to their non-reactive nature. However, they may not be the best choice for heavy agricultural products.
Why Choose Reinforced Concrete for Silos?
Reinforced concrete is often used for large-scale silos due to its exceptional strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and is less prone to corrosion compared to metal options.
Pros: The longevity of reinforced concrete makes it a solid investment for long-term storage solutions. It also provides excellent thermal insulation, which can be beneficial for certain stored products.
Cons: The initial cost of reinforced concrete silos can be high, and they require specialized construction techniques. Additionally, they are not as easily transportable as metal silos.
Impact on Application: Reinforced concrete is suitable for a wide range of materials, including grains and liquids. However, it may not be ideal for applications requiring frequent relocation or modification.
What Role Does Fiberglass Play in Silo Design?
Fiberglass is a composite material that offers unique advantages for silo construction, particularly in specialized applications. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into various shapes.
Pros: Fiberglass silos are highly resistant to chemical attacks, making them suitable for storing aggressive substances. Their lightweight nature facilitates easier installation and maintenance.
Cons: The primary limitation of fiberglass is its relatively high cost compared to traditional materials. Additionally, it may not be as structurally robust as steel or concrete, limiting its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Fiberglass is ideal for storing chemicals and food products due to its non-reactive properties. However, it may not be suitable for bulk agricultural materials that require heavier-duty storage solutions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Silos
| Material | Typical Use Case for silo prices | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Grain and heavy material storage | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Food and chemical storage | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | Medium |
| Reinforced Concrete | Large-scale agricultural storage | Long-lasting and thermally insulating | High initial construction cost | High |
| Fiberglass | Chemical and specialized product storage | Lightweight and highly corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and lower structural strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for silo prices
What Are the Main Stages of Silo Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing of silos involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary specifications for strength, durability, and safety.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Silos are typically constructed from high-strength steel or reinforced concrete, depending on the application and storage needs. For steel silos, raw materials are sourced in coil form, which is cut and prepped for forming. Quality control starts here, with checks for material composition and mechanical properties to ensure they meet industry standards.
2. Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the steel or concrete into the desired silo configuration. Common forming techniques include:
- Roll Forming: For steel silos, coils are fed into a roll-forming machine that shapes them into a cylindrical structure.
- Welding: The formed sections are welded together using techniques such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding to ensure robust seams.
- Casting: For concrete silos, the material is poured into molds and allowed to cure, forming a solid structure.
These techniques are chosen based on the design specifications and the intended use of the silo.
3. Assembly
After forming, the silo components are assembled. This stage may involve erecting the silo on-site or assembling pre-fabricated parts in the factory. Key processes include:
- Joining: Components are joined using bolts or welds, depending on the design.
- Installation of Accessories: Features such as hoppers, roofs, and ventilation systems are integrated during assembly to optimize functionality.
The assembly process is critical, as it affects the overall structural integrity and performance of the silo.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that protect the silo from environmental factors. This may include:
- Surface Treatment: Steel silos are often coated with protective paint or galvanized to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Quality Checks: Before shipping, each silo undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure all components meet design specifications and safety standards.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Silos?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the silo manufacturing process. Adhering to international standards not only guarantees product reliability but also builds trust with B2B buyers.
Relevant International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to any organization. It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards particularly relevant for silos used in oil and gas sectors.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated at multiple stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected for quality and conformity to specifications before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures adherence to set quality parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection is conducted before the product is shipped, ensuring it meets all specifications and standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Silo Manufacturing?
To ensure the structural integrity and performance of silos, several testing methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or radiographic testing are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the silo.
- Hydrostatic Testing: For silos intended for liquid storage, hydrostatic testing checks for leaks and verifies structural integrity under pressure.
- Load Testing: This simulates the silo’s operational conditions to ensure it can withstand the intended load.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial to ensure product reliability.
Supplier Audits
Conducting supplier audits can help buyers assess the manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes of potential suppliers. This can include site visits, reviews of quality management systems, and assessments of compliance with international standards.
Requesting Reports and Certifications
Buyers should request documentation regarding quality certifications, testing results, and compliance with relevant standards. This transparency is essential for building trust and ensuring that the supplier adheres to high-quality standards.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the silos meet the required specifications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, especially in diverse markets such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, buyers should be aware of specific nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context can facilitate better communication and negotiation regarding quality expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulations regarding construction and manufacturing standards. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in addition to international standards.
- Logistics and Shipping Considerations: Quality control extends to the shipping process. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have measures in place to protect the product during transport, minimizing the risk of damage.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the silo industry, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that will lead to successful procurement outcomes. Emphasizing quality and reliability not only protects investments but also enhances operational efficiency in the long run.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘silo prices’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring silos, this guide provides a practical checklist. Understanding silo prices and making informed decisions are crucial for optimizing storage solutions and managing costs effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before exploring pricing, establish clear technical specifications for the silo you need. Consider factors such as capacity, material (e.g., steel or concrete), and intended use (e.g., grain storage, waste management). This step ensures you receive accurate quotes tailored to your specific requirements.
Step 2: Research Market Prices
Investigate the current market prices for different types of silos. Look at various suppliers and platforms to gather a range of prices. Understanding the price spectrum will help you identify competitive offers and avoid overpaying.
- Tip: Pay attention to any discounts or promotions that may be available, as prices can fluctuate significantly.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Vetting suppliers is essential to ensure reliability and quality. Review their company profiles, including years in business, certifications, and customer testimonials. This will help you gauge their reputation in the industry.
- Tip: Request references from clients in similar sectors to gain insights into the supplier’s performance and customer service.
Step 4: Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While initial costs are important, consider the Total Cost of Ownership, which includes maintenance, operation, and potential feed loss. For example, tower silos may have higher upfront costs but lower operational expenses over time due to reduced spoilage.
- Tip: Calculate potential savings from reduced feed loss and easier unloading processes to make a more informed decision.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes that break down costs. Ensure that the quotes include all relevant factors, such as delivery, installation, and any additional services like maintenance plans.
- Tip: Compare not just the prices but also the services included in each quote to assess overall value.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with industry regulations. This is particularly important for silos used in food storage or agricultural applications.
- Tip: Ask for copies of certifications and check their validity to avoid potential legal or safety issues down the line.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction.
- Tip: Don’t hesitate to negotiate; suppliers may have flexibility in pricing or terms, especially for bulk orders.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for silos more effectively, ensuring they secure the best prices and solutions tailored to their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for silo prices Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Silo Prices?
Understanding the cost structure of silo prices is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Steel and stainless steel are common materials used in silo construction, with stainless steel offering durability and corrosion resistance, albeit at a higher price point. The type of silo—whether it’s a flat-bottom, hopper-bottom, or tower silo—also influences material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the installation. Skilled labor may command higher wages, which can increase the total cost of ownership.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These costs are typically distributed across all units produced, making them a significant factor in pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be necessary for custom designs or specialized silos. This is often a one-time cost but can add to the unit price if customization is required.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that silos meet industry standards incurs additional costs. Buyers should inquire about the QC processes employed by manufacturers, as this can affect both price and quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are a vital consideration, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and local tariffs can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the supplier’s business model and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Silo Costs?
Several factors can influence silo pricing, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Ordering in bulk can lead to reduced unit prices. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, which is advantageous for businesses looking to scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom silos that meet specific requirements or configurations may incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to receive accurate quotes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO) can lead to increased costs but may offer long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can impact the total landed cost of the silo.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Silo Prices?
B2B buyers should leverage various strategies to ensure cost-efficiency in their silo purchases:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage in discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially if you are placing a large order. Don’t hesitate to request discounts or additional services, such as installation.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with the silo, not just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential feed loss, which can significantly impact profitability over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: When sourcing silos from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, be aware of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and import duties that can affect pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from different suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best overall deal.
-
Verify Supplier Credentials: Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and a good reputation in the market. This can save costs related to quality issues in the long run.
Conclusion and Disclaimer
Silo pricing is influenced by a myriad of factors, including materials, labor, and logistics. Understanding these components and how they interact can empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. While indicative prices can provide a baseline, actual costs may vary based on specific requirements and supplier negotiations. Always engage with multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence to achieve the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing silo prices With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Silo Prices in Grain Storage Solutions
In the realm of grain storage, traditional silos have long been a staple due to their durability and efficiency. However, as the agricultural landscape evolves, so too do the options available for storage solutions. This analysis explores how silo prices compare to alternative storage methods, focusing on the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases for each option.
Comparison of Silo Prices with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Silo Prices | Bunker Storage | Grain Bags |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity, minimal spoilage | Moderate capacity, risk of spoilage | Good for short-term, variable spoilage |
| Cost | High initial investment; variable TCO | Lower initial cost, but higher long-term costs | Low initial cost, but frequent replacement needed |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant site preparation | Easier to set up, less site prep | Very easy to implement, requires minimal infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance once installed | Moderate maintenance required | High maintenance; bags can tear or degrade |
| Best Use Case | Long-term storage for large quantities | Medium to large-scale operations | Small-scale or temporary storage needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Bunker Storage
Bunker storage is a method where grains are stored in open-air piles, covered with tarps. This method is often more affordable than silos, making it appealing for farmers looking to minimize upfront costs. However, while the initial investment is lower, the long-term cost of ownership can be significant due to potential spoilage, feed loss, and the need for maintenance. Bunker storage is best suited for medium to large-scale operations where the cost of spoilage can be mitigated by efficient management practices.
Grain Bags
Grain bags are a flexible storage solution that allows for easy transport and quick setup. They are particularly advantageous for small-scale operations or temporary storage needs, as they require minimal infrastructure and can be set up in various locations. The initial cost of grain bags is relatively low compared to silos or bunker storage. However, they have a shorter lifespan and can be prone to damage from environmental factors, necessitating frequent replacements. This makes them less ideal for long-term storage but a viable option for short-term needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Storage Solution
When selecting a storage solution, B2B buyers must carefully consider their specific needs, including storage duration, capacity requirements, and budget constraints. Silos offer a high-capacity and long-term solution with minimal spoilage, ideal for large-scale operations. In contrast, bunker storage and grain bags provide flexibility and lower initial costs, suitable for medium and small operations, respectively. Ultimately, the choice between these options will depend on the buyer’s operational scale, financial strategy, and long-term storage goals. By assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for silo prices
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Silos that Affect Prices?
When evaluating silo prices, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key properties that directly impact the cost and functionality of silos:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a silo primarily refers to the type of steel or other materials used in its construction. High-strength steel is often preferred for its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can influence the lifespan of the silo and the total cost of ownership, as higher-quality materials may reduce maintenance and replacement costs. -
Capacity
Silo capacity is typically measured in bushels (Bu) or cubic meters, indicating the volume of grain or other materials the silo can hold. Understanding the capacity required for your operations helps ensure you don’t overspend on larger silos than necessary, or conversely, underspend and risk running out of storage space. Accurately assessing your needs can lead to significant cost savings. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variations in the dimensions and specifications of the silo. High tolerance levels can ensure that the silo fits perfectly into existing infrastructure and meets regulatory standards. For international buyers, especially in regions with strict building codes, understanding tolerance levels is essential to avoid costly modifications or compliance issues. -
Insulation and Temperature Control
Insulation properties are vital for maintaining the quality of stored materials, especially in extreme climates. Silos equipped with effective insulation systems can help regulate temperatures, preventing spoilage and loss of quality. B2B buyers should consider the additional costs associated with insulation and temperature control features, as they can greatly enhance product integrity. -
Unloading Systems
The type of unloading system integrated into the silo can significantly affect operational efficiency. Options include gravity unloaders, augers, and pneumatic systems. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each system is essential for optimizing workflow and minimizing labor costs. Buyers should evaluate how the unloading method impacts the overall cost of ownership.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Silo Prices?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can streamline the procurement process and facilitate better negotiations. Here are several essential terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of silos, OEMs often provide tailored solutions that meet specific operational needs. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality, reliable products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts inventory costs and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and managing storage space effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. By issuing an RFQ, buyers can compare offers and negotiate better deals. Understanding how to craft an effective RFQ can lead to more favorable pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For international B2B buyers, familiarity with Incoterms can help mitigate risks associated with shipping and ensure clarity in agreements. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with acquiring, operating, and maintaining an asset over its lifespan. For silos, this includes initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. Understanding TCO is crucial for making informed investment decisions and evaluating long-term value. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This is a critical factor for buyers needing to align silo purchases with operational timelines. Clear communication about lead times can prevent delays in production and ensure timely project completion.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding silo purchases, ultimately leading to better investment outcomes and operational efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the silo prices Sector
What are the Key Trends Influencing Silo Prices Globally?
The silo prices sector is currently experiencing significant transformation driven by a combination of global economic factors, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Key drivers include increased demand for efficient grain storage solutions due to fluctuating agricultural outputs and climate change, which necessitates robust storage capabilities. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focusing on silo systems that not only provide storage but also enhance preservation and reduce spoilage.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends within the silo market. Innovations such as IoT-enabled silos allow real-time monitoring of grain conditions, leading to improved management of inventory and reduced losses. Additionally, automation in the filling and unloading processes is gaining traction, significantly cutting down labor costs and operational inefficiencies.
Market dynamics are also influenced by fluctuating raw material costs and geopolitical factors. For instance, disruptions in supply chains can lead to sudden price hikes, compelling buyers to explore alternative suppliers or materials. As a result, international buyers are urged to engage in thorough market analysis and consider long-term contracts to hedge against volatility.
How are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Silo Prices?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the silo prices sector. The environmental impact of grain storage systems, particularly their carbon footprint, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking solutions that minimize energy consumption and waste. This shift is driving demand for silos constructed from recycled or sustainably sourced materials, which can also enhance a company’s corporate social responsibility profile.
Ethical supply chains are paramount in today’s market, with buyers showing preference for suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building design are becoming important benchmarks for evaluating suppliers. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through transparent sourcing practices and eco-friendly production methods.
Incorporating sustainability into purchasing decisions not only aligns with global trends but also offers potential cost savings in the long run. Efficient silos that reduce spoilage and energy use can contribute to lower operational costs, making ethical sourcing a viable business strategy.
What is the Historical Context of Silo Prices in B2B Markets?
The evolution of silo prices reflects the broader changes in agricultural practices and technological advancements over the decades. Historically, the use of silos dates back to ancient civilizations, but their modern incarnation began to take shape in the early 20th century. Initially, silos were primarily built from wood and brick, but the introduction of steel and reinforced concrete revolutionized their durability and efficiency.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the rise of industrial agriculture led to increased demand for larger and more sophisticated storage solutions, resulting in significant price fluctuations based on material availability and technological innovations. Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of silo types, including tower and bunker silos, each with varying costs associated with construction, maintenance, and operational efficiency.
As agricultural practices continue to evolve in response to climate change and global demand for food security, the silo prices sector will likely see ongoing changes influenced by technological advancements and sustainability initiatives. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers to navigate current market dynamics effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of silo prices
-
How do I determine the appropriate silo type for my storage needs?
Choosing the right silo type depends on several factors, including the type of grain or material being stored, the volume required, and your budget. Tower silos are ideal for long-term storage with minimal waste, while flat-bottom silos are better for bulk materials and easier loading/unloading. Evaluate your storage requirements, local climate, and any specific operational needs, such as automation or accessibility, to make an informed decision. -
What are the average costs associated with purchasing a silo?
The cost of silos varies significantly based on size, type, and materials used. For instance, a basic flat-bottom silo can range from $14,000 to $100,000, while larger, specialized silos may exceed $200,000. Beyond the purchase price, consider ongoing operational costs, maintenance, and any necessary equipment for loading and unloading, as these can substantially affect your total investment. -
What factors should I consider when vetting silo suppliers?
When vetting silo suppliers, assess their industry experience, customer reviews, and product quality. Check for certifications and compliance with international standards, especially if you’re sourcing from abroad. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support, warranty terms, and delivery timelines. Establishing a strong relationship with a reputable supplier is crucial for long-term success. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for silo purchases?
Many suppliers do impose minimum order quantities, particularly for custom-built silos. MOQs can vary by manufacturer and may be influenced by production capabilities and material availability. If your needs do not meet a supplier’s MOQ, consider negotiating terms or exploring alternative suppliers who can accommodate smaller orders without compromising quality. -
What payment terms are typically offered by silo suppliers?
Payment terms for silo purchases can vary widely. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some may offer financing options or extended payment plans, especially for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreements to ensure transparency and avoid unexpected costs. -
How can I ensure the quality of the silo I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications and materials used in the silo’s construction. Ask for certifications from recognized industry standards and consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible. Additionally, seek references from previous clients to understand their experiences. A comprehensive quality assurance process should be in place, including inspections during and after production. -
What are the logistics involved in importing silos internationally?
Importing silos involves several logistics considerations, including customs regulations, shipping methods, and costs. Ensure compliance with local import laws and tariffs, which can vary by country. Work closely with your supplier and a reliable freight forwarder to manage shipping schedules and documentation. Understanding the total landed cost, including shipping and duties, is essential for budgeting. -
How long can I expect my silo to last with proper maintenance?
With proper maintenance, silos can last 20 years or more. Regular inspections and maintenance, such as checking for structural integrity and ensuring seals are intact, are vital for longevity. Implementing preventive measures, like moisture control and pest management, can further enhance durability. Consult with your supplier for specific maintenance guidelines tailored to the type of silo you purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Silo Prices Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Grain Handling Direct – Flat Bottom Grain Bins
Domain: grainhandlingdirect.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Maximize your grain storage capacity with cost-effective flat bottom grain bins from Grain Handling Direct. Ideal for long-term storage of large quantities of a single grain type, flat bottom bins offer the lowest cost per bushel for bulk storage solutions. High-quality stiffened and unstiffened flat bottom bins from manufacturers like GSI, Brock Grain Systems, and AGI Westeel. Available in variou…
2. Silo – Silo Container Set
Domain: heysilo.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Silo Container Set”,”regular_price”:”$99.00 USD”,”sale_price”:”$45.00 USD”},{“name”:”Silo Vacuum Storage System”,”regular_price”:”$599.00 USD”,”sale_price”:”$499.00 USD”}],”availability”:”In stock (2 products)”,”highest_price”:”$649.00 USD”}
3. JMS Equipment – Biosolids Storage Solutions
Domain: jmsequipment.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Biosolids Storage Hoppers and Silos are essential for wastewater treatment applications, providing temporary storage and complete Bio-Handling Systems. Key details include: 1. **Types of Storage**: Live Bottom Hoppers and Silos for wet dewatered sludge, truck delivery, and downstream processes. 2. **Capital Costs**: Initial expenses range from $50,000 to over $1,000,000 depending on size, material…
4. Grain Silos – Used Options Available
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Used Grain Silos available on eBay. Total results: 203 items. Price range: Under $1,500.00 to over $2,980.00. Condition options: New (11 items), Used (477 items), Not Specified (4 items). Buying formats include Auction (12 items), Buy It Now (481 items), Accepts Offers (249 items). Shipping options include local pickup and free shipping within 25 miles. Notable listings include:
– Food Grain Bin/S…
5. Silo 1604 – Contemporary American Cuisine
Domain: siloelevatedcuisine.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Silo 1604 offers creative, world-class cuisine with a focus on contemporary American classics, prime steaks, and seafood. The restaurant features a casual yet elegant dining environment and has four private dining rooms available for groups ranging in size from 8 to 90, with audio-visual equipment provided. Operating hours are as follows: Lunch (Monday – Friday 11:00 AM – 2:30 PM), Daily Brunch (S…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for silo prices
In the evolving landscape of silo prices, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international B2B buyers. With substantial price variations observed across different silo types—ranging from flat bottom to tower silos—buyers must evaluate not only initial acquisition costs but also the total cost of ownership (TCO). Factors such as feed loss, unloading expenses, and maintenance requirements significantly influence long-term profitability.
By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can negotiate better pricing, optimize supply chains, and enhance operational efficiency, all of which are crucial for maintaining competitive advantages in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As the demand for efficient grain storage solutions grows, it’s essential for buyers to remain proactive in market research and supplier engagement. By understanding market trends and engaging with reputable suppliers, businesses can secure favorable pricing and terms that align with their operational needs.
Looking ahead, we encourage buyers to take action—analyze your storage requirements, explore diverse silo options, and engage with suppliers to make informed purchasing decisions that support your business’s growth and sustainability.