A Deep Dive into Friesian Cows For Sale Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for friesian cows for sale
In the competitive landscape of livestock trading, sourcing Friesian cows for sale presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. With rising global demand for high-quality dairy products, understanding the intricacies of this market is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing key aspects such as the various types of Friesian cattle available, their specific applications in dairy production, and essential criteria for supplier vetting. Additionally, it delves into pricing structures, including factors influencing costs and how to secure favorable terms for your purchases.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Saudi Arabia, will find valuable insights tailored to their unique market conditions. By equipping yourself with the knowledge contained in this guide, you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business goals. The guide also highlights best practices for ensuring the quality and health of your livestock, as well as compliance with local import regulations, thereby reducing risks associated with cross-border transactions.
Whether you are looking to enhance your dairy operations or invest in high-yield cattle, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market confidently, fostering sustainable growth in your agricultural ventures.
Understanding friesian cows for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holstein Friesian | Black and white markings, large size, high milk yield | Dairy farming, milk production | Pros: High productivity, well-documented breeding history. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Red Pied Friesian | Red and white coloration, good adaptability | Dairy farming, crossbreeding | Pros: Better fat and protein content. Cons: Less common, potentially limited availability. |
| Jersey Friesian Cross | Smaller size, high butterfat content | Specialty dairy markets, premium products | Pros: Higher butterfat, suitable for niche markets. Cons: Lower overall milk yield compared to Holsteins. |
| Friesian Bull | Male variant, used for breeding and beef production | Breeding programs, beef production | Pros: Strong genetics, potential for high-quality offspring. Cons: Requires careful management and breeding plans. |
| Incalf Holstein Heifer | Pregnant heifer, ready for immediate milk production | Dairy operations, herd expansion | Pros: Immediate return on investment, proven genetics. Cons: Higher purchase price, management of pregnancy required. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Holstein Friesians for Sale?
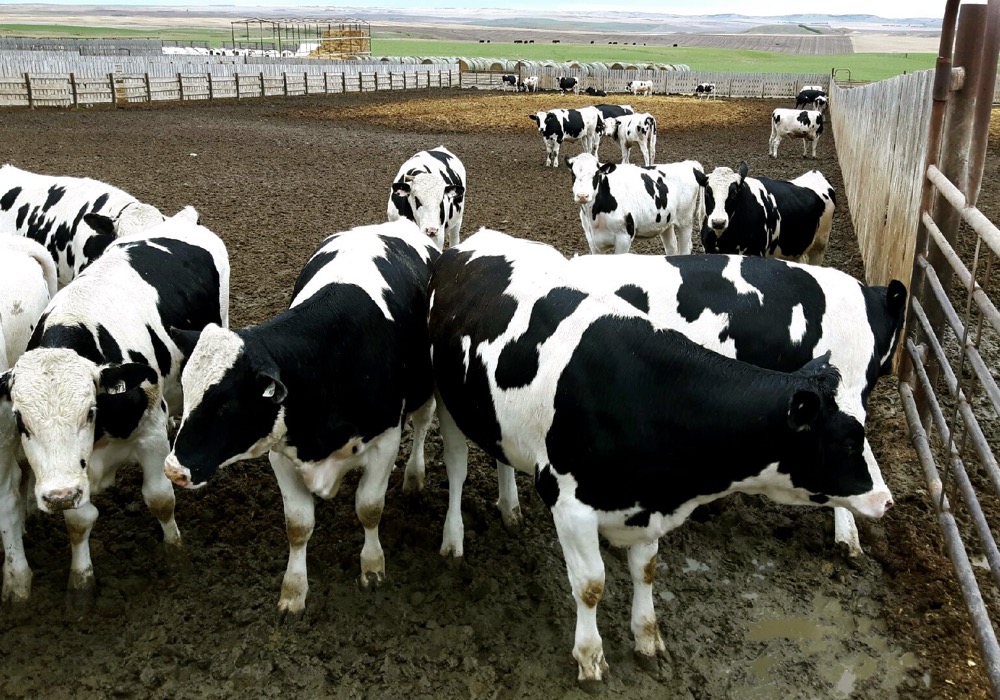
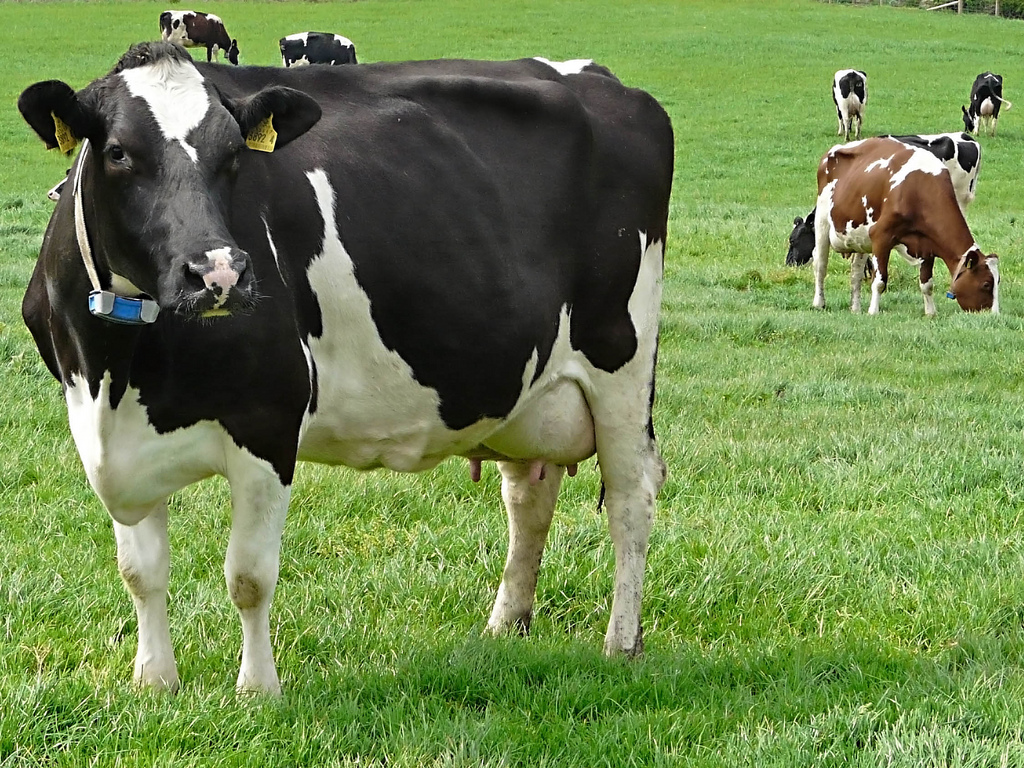
Holstein Friesians are recognized globally for their striking black and white coloration and impressive size, often weighing up to 630 kg. They are renowned for their exceptional milk production capabilities, averaging around 25,000 pounds of milk per lactation, with a lactation cycle lasting approximately 305 days. These cattle are ideal for large-scale dairy operations looking to maximize milk yield and efficiency. Buyers should consider the initial investment against the potential return from high milk sales.
How Do Red Pied Friesians Differ from Holsteins?
Red Pied Friesians, while less common, offer unique advantages such as improved fat and protein content in their milk. Their adaptability to various grazing conditions makes them suitable for diverse farming environments. However, due to their rarity, sourcing these cattle might be challenging, and potential buyers should evaluate local market demand for products derived from this breed. Their ability to thrive in different climates can be a significant asset for international buyers.
Why Consider Jersey Friesian Crosses?
The Jersey Friesian Cross is a smaller, more compact breed that produces milk with higher butterfat content, making it ideal for specialty dairy products. This breed’s adaptability to smaller farms and niche markets allows buyers to tap into premium dairy segments. However, while they excel in butterfat production, their overall milk yield may be lower than pure Holsteins, necessitating a careful evaluation of market needs before purchase.
What Are the Benefits of Purchasing Friesian Bulls?
Friesian Bulls are primarily sought for breeding purposes, contributing to the genetic diversity and quality of dairy or beef herds. Their robust genetics can lead to high-quality offspring, enhancing herd productivity. Buyers should plan for effective breeding management strategies to maximize the benefits of purchasing bulls, ensuring that they align with their overall herd improvement goals.
How Do Incalf Holstein Heifers Fit into Dairy Operations?
Incalf Holstein Heifers are a strategic choice for dairy operations aiming for immediate returns. These pregnant heifers are poised to enter milk production shortly after purchase, allowing for quicker herd expansion and revenue generation. However, the upfront costs are higher compared to younger stock, and buyers must be prepared to manage the health and care of these animals throughout their pregnancy and subsequent lactation periods.
Key Industrial Applications of friesian cows for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of friesian cows for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Production | High-yield milk production | Friesian cows are known for their exceptional milk yield, averaging 7,000 to 11,000 liters annually. This high production can significantly enhance profitability for dairy farms. | Buyers should ensure the cows are pedigree registered, have full veterinary records, and meet local import regulations. |
| Meat Production | Cross-breeding for beef | Friesian cows can be cross-bred with beef breeds to produce high-quality beef while maintaining milk production. This dual-purpose approach maximizes resource utilization. | Buyers need to evaluate the genetic background and breeding history to ensure optimal growth and yield. |
| Agricultural Research | Genetic studies and breeding programs | Friesian cows serve as a model for genetic research aimed at improving dairy cattle traits, contributing to advancements in livestock breeding. | Research institutions should focus on sourcing from reputable breeders with robust herd management practices. |
| Export and Trade | International livestock trading | The global demand for high-quality dairy cattle provides significant export opportunities, particularly for countries in Africa and the Middle East. | Buyers must consider logistical aspects, such as transport conditions and compliance with international trade regulations. |
| Sustainable Farming | Organic and grass-fed dairy production | Sourcing Friesian cows for organic farming can enhance the marketability of dairy products, appealing to health-conscious consumers. | Buyers should seek certified organic livestock and ensure that suppliers adhere to sustainable farming practices. |
Friesian cows are predominantly utilized in the dairy production industry, known for their remarkable milk yield. With an average lactation output ranging from 7,000 to 11,000 liters annually, these cows are a vital asset for dairy farms looking to enhance profitability. International buyers, particularly from regions with increasing dairy consumption like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing pedigree-registered animals with comprehensive veterinary records to ensure compliance with local import regulations.
In the meat production sector, Friesian cows offer a unique opportunity for cross-breeding with beef cattle. This strategy allows producers to benefit from both high-quality milk and beef, optimizing resource utilization on farms. For buyers, understanding the genetic background and breeding history of the cows is essential to achieve desirable outcomes in meat quality and production efficiency.
Agricultural research institutions leverage Friesian cows for genetic studies and breeding programs aimed at improving dairy cattle traits. These studies can lead to significant advancements in livestock genetics and overall productivity. For such applications, it is crucial for researchers to source animals from reputable breeders known for effective herd management practices.
The export and trade sector sees substantial opportunities with Friesian cows, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where there is a growing demand for quality dairy cattle. Buyers must navigate logistical challenges, including transport conditions and compliance with international trade regulations, to successfully import these livestock.
Lastly, in sustainable farming, sourcing Friesian cows for organic dairy production enhances the appeal of dairy products to health-conscious consumers. Buyers interested in this market segment should seek suppliers that provide certified organic livestock and adhere to sustainable farming practices, ensuring that the cows are raised in environments that support their health and productivity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘friesian cows for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Quality and Health of Friesian Cows
The Problem: B2B buyers often face uncertainty regarding the health and quality of Friesian cows available for purchase. This concern is particularly pronounced when sourcing livestock from international suppliers, as buyers may worry about the authenticity of health certifications, the conditions in which the cows were raised, and whether they meet local health regulations. These apprehensions can lead to hesitation in making a purchase, potentially resulting in lost business opportunities or financial losses if the livestock are not up to standard.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers with a proven track record in livestock export. It is crucial to request comprehensive documentation, including full veterinary records, pedigree certificates, and organic feeding certifications, before finalizing any purchase. Establishing direct communication with suppliers can also help buyers gain insights into the cows’ living conditions and care practices. Additionally, conducting a pre-purchase inspection, possibly through a trusted third-party inspector, can provide peace of mind. This proactive approach ensures that the cows not only meet the buyer’s quality standards but also comply with local health regulations, safeguarding the investment.
Scenario 2: Navigating Import Regulations and Logistics
The Problem: International buyers often grapple with complex import regulations and logistics associated with transporting Friesian cows across borders. Each country has its own set of rules regarding livestock importation, including health certifications, quarantine requirements, and customs documentation. This complexity can lead to delays, increased costs, and potential legal issues, making the procurement process daunting and cumbersome.
The Solution: To streamline the import process, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific regulations that pertain to their country and the country of origin for the Friesian cows. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in livestock transportation can greatly simplify this process. This partner can assist in navigating customs requirements, ensuring that all necessary documents are in place, and coordinating the logistics of transportation to minimize stress on the animals. Furthermore, buyers should maintain open lines of communication with their suppliers to ensure that they are aware of any changes in regulations or requirements that may arise during the import process. This proactive strategy will not only facilitate smoother transactions but also help in avoiding costly delays.
Scenario 3: Assessing Long-term Productivity and Profitability
The Problem: Buyers are often concerned about the long-term productivity and profitability of Friesian cows, particularly in relation to milk yield and overall herd performance. These concerns are heightened in emerging markets where agricultural practices may vary significantly from those in developed countries. Buyers may worry about whether the cows will adapt well to local environmental conditions and whether they will maintain high production levels throughout their lactation cycles.
The Solution: To address these concerns, it is vital for buyers to conduct thorough research on the genetic background and performance records of the Friesian cows they are considering. Engaging with breeders who provide detailed performance data, including historical milk yields and fertility rates, can give buyers a clearer picture of what to expect. Additionally, buyers should consider implementing a robust herd management system that includes regular health assessments, nutrition monitoring, and milking management practices tailored to the local environment. This holistic approach will not only enhance the productivity of the cows but also ensure that buyers can maximize their return on investment over the long term. Establishing a partnership with agricultural extension services or local veterinarians can further support buyers in optimizing herd performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for friesian cows for sale
When selecting materials for the import and sale of Friesian cows, various factors such as durability, cost, and compliance with international standards must be considered. Here, we analyze four common materials relevant to the Friesian cattle trade, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in Livestock Equipment?
Stainless steel is widely used in the construction of equipment and facilities for livestock, including feeding troughs, milking machines, and storage tanks. Its key properties include excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and the ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures. This makes it suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments where hygiene is critical.
Pros: Stainless steel is durable and easy to clean, which is essential for maintaining hygiene standards in dairy operations. Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Cons: The initial cost of stainless steel can be high compared to other materials. Additionally, its manufacturing process can be complex, potentially leading to longer lead times for production.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various cleaning agents and its resistance to rust make it ideal for dairy applications where sanitation is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local health regulations and standards such as ASTM or DIN. Understanding the local market’s preferences for equipment materials can also influence purchasing decisions.
How Does Plastic Compare for Feeding and Watering Systems?
Plastic, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is commonly used in feeding and watering systems for Friesian cows. Its key properties include lightweight construction, resistance to impact, and good chemical resistance.
Pros: Plastic is generally less expensive than metals, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale operations. Its lightweight nature facilitates easy installation and transport.
Cons: While plastic is resistant to many chemicals, it may not be as durable as metals under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy impacts. This could lead to a shorter lifespan for certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic’s resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for feeding and watering systems, but it may not be ideal for areas requiring heavy-duty equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local climate conditions, as extreme temperatures can affect the performance of plastic materials. Compliance with food safety standards is also crucial, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
What Role Does Wood Play in Livestock Housing?
Wood is often used in the construction of barns and shelters for Friesian cows. Its properties include natural insulation, ease of sourcing, and aesthetic appeal.
Pros: Wood provides excellent insulation, helping to maintain a comfortable environment for livestock. It is also relatively easy to work with, allowing for customizable designs.
Cons: Wood is susceptible to rot and insect damage, which can compromise its structural integrity over time. Additionally, it may require regular maintenance and treatment to prolong its lifespan.
Impact on Application: In regions with milder climates, wood can be an effective material for livestock housing. However, in harsher environments, its durability may be a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the wood sourced complies with local regulations regarding sustainability and pest control. Understanding local building codes is essential for successful construction.
Why Is Concrete Important for Livestock Facilities?
Concrete is a foundational material used in the construction of livestock facilities, including floors and feedlots. Its properties include high compressive strength and durability.
Pros: Concrete is extremely durable and can withstand heavy loads, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. It is also resistant to moisture and pests.
Cons: The initial cost of concrete can be high, and its installation requires skilled labor. Additionally, concrete can be cold, which may not be ideal for animal comfort.
Impact on Application: Concrete’s durability makes it suitable for long-term installations, but its thermal properties should be considered in regions with extreme temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local construction practices and standards, including those related to environmental impact and animal welfare.
| Material | Typical Use Case for friesian cows for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Milking machines, feeding troughs | Excellent corrosion resistance | High initial cost | High |
| Plastic | Feeding and watering systems | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Wood | Livestock housing | Natural insulation and aesthetic appeal | Susceptible to rot and pests | Medium |
| Concrete | Floors and feedlots | Extremely durable | High installation cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in the Friesian cattle trade, emphasizing the importance of durability, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with international standards. Understanding these factors can significantly influence purchasing decisions and operational success in various global markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for friesian cows for sale
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Friesian Cows?
The manufacturing process for Friesian cows involves several crucial stages that ensure the delivery of high-quality livestock to international markets. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Goes into Breeding Quality Friesian Cows?
Material preparation begins with the selection of superior breeding stock. This includes evaluating genetic lineage, health status, and productivity potential. Reputable breeders often use advanced genetic testing and pedigree analysis to ensure that the cows meet the desired standards for milk production and health. Additionally, feed quality is critical during this stage. Cows are typically raised on a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals, which contributes to their overall health and productivity.
How Are Friesian Cows Formed and Assembled?
The formation stage focuses on the breeding process itself. Using artificial insemination techniques, breeders can select specific traits, such as milk yield and fat content. This method enhances the genetic quality of the offspring, ensuring that they inherit desirable characteristics from both parents.
Once calves are born, they enter an assembly phase where they are nurtured and monitored closely. This includes regular health check-ups, vaccination, and weaning protocols. The calves are typically bottle-fed or given milk replacers until they are ready to transition to solid food. During this phase, attention to detail is paramount, as early nutrition directly impacts future productivity.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in the Breeding Process?
The finishing stage involves preparing the cows for sale. This includes ensuring that they are in optimal health and condition. Buyers often look for specific weight benchmarks and physical attributes, such as coat condition and muscle tone. Breeders may employ finishing techniques such as controlled feeding programs, specialized diets, and stress-reduction practices to improve the overall quality of the cows.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Friesian Cows?
Quality assurance is an essential aspect of the livestock industry, particularly for B2B buyers who demand high-quality products. Various international standards apply, including ISO 9001, which sets out criteria for a quality management system. This standard is crucial for ensuring that suppliers maintain consistent quality and continuous improvement.
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also be relevant, depending on the region and specific market requirements. These certifications indicate compliance with safety and quality standards, enhancing buyer confidence in the livestock’s quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Supply Chain?
Quality control checkpoints are vital in maintaining the integrity of the livestock supply chain. Typically, these checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting incoming materials, such as feed and breeding stock, to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the breeding and raising process, regular health assessments and growth monitoring are conducted to identify any issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a thorough inspection of the cows is performed to ensure they meet the health, size, and weight specifications required by buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Conducting audits is one of the most effective methods. Buyers should request to see documentation regarding the supplier’s quality management systems and any relevant certifications.
In addition, buyers can seek third-party inspections, which provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations and compliance with international standards. Regular reporting from suppliers about their quality control metrics can also provide insight into their commitment to quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in the Quality Assurance of Friesian Cows?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of Friesian cows. Common practices include:
- Health Testing: Regular veterinary checks for diseases and health conditions are essential. Blood tests, fecal examinations, and vaccination records are typically reviewed.
- Genetic Testing: To confirm the pedigree and genetic viability of breeding stock, DNA testing is often utilized.
- Nutritional Analysis: Feed quality is analyzed to ensure it meets the nutritional requirements for optimal growth and milk production.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different countries may have varying regulations regarding animal health and importation. For example, some regions may require specific health certifications or quarantine periods before livestock can enter the country.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of the documentation required for international shipments, which may include pedigree certificates, veterinary records, and organic feed certifications. Ensuring that all paperwork is in order can prevent delays and complications during the import process.
Conclusion: How to Ensure Quality in Your Friesian Cow Purchases?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring quality in the procurement of Friesian cows involves a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. By focusing on supplier credibility, auditing practices, and adherence to international quality standards, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their livestock operations and contribute to their business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘friesian cows for sale’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers looking to procure Friesian cows for sale. Given the rising demand for high-quality dairy products globally, it is imperative to ensure that your sourcing process is thorough and informed. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of purchasing Friesian cattle, ensuring you make well-informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating any sourcing activities, clearly outline your requirements. Consider factors such as the age, breed, health status, and lactation performance of the Friesian cows you wish to acquire. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your procurement strategy and helps you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers.
- Age and Type: Are you looking for heifers, pregnant cows, or calves?
- Health Standards: Specify any health certifications required, such as veterinary records.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify reputable suppliers specializing in Friesian cattle. Evaluate their market presence, customer reviews, and the range of livestock they offer. Researching suppliers helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing and ensures you find a reliable partner.
- Online Directories: Use platforms like livestock marketplaces and trade directories.
- Industry Recommendations: Seek recommendations from industry peers or agricultural associations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s critical to verify that suppliers hold the necessary certifications and adhere to international livestock trade regulations. This ensures the animals are healthy and meet quality standards, which is essential for your business’s reputation and compliance.
- Documentation: Request certificates such as pedigree, veterinary health records, and organic feeding certifications.
- Compliance: Ensure they are compliant with export regulations specific to your country.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have a shortlist of potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines. This step is vital for comparing offers and understanding the total cost of ownership associated with each supplier.
- Pricing Structure: Look for transparent pricing that includes all costs, such as FOB prices and potential tariffs.
- Delivery Options: Assess logistics capabilities and timelines to ensure timely delivery.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
Whenever possible, arrange site visits to the suppliers’ farms or request virtual tours. This allows you to inspect the living conditions of the cattle and assess the overall quality of the operation. Observing the supplier’s practices firsthand can provide valuable insights into their reliability and animal welfare standards.
- Animal Welfare: Check for cleanliness, space, and overall health of the cattle.
- Operational Standards: Observe feeding practices and herd management techniques.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you select a supplier, enter negotiations to finalize terms and conditions. This should include payment schedules, delivery dates, and any warranties or guarantees. A well-structured contract protects both parties and ensures clarity in the transaction.
- Legal Review: Consider having legal counsel review the contract to safeguard your interests.
- Flexibility: Discuss clauses for unforeseen circumstances, such as delays or health issues with the cattle.
Step 7: Plan for Post-Purchase Support
Finally, ensure that you have a strategy for post-purchase support, including veterinary care, feeding, and management practices. Establishing a relationship with your supplier for ongoing support can help you maximize the productivity and health of your new cattle.
- Supplier Communication: Maintain open lines of communication for advice and support.
- Training: Consider training programs for your staff on proper cattle management practices.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing Friesian cows effectively, ensuring a successful procurement process that meets their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for friesian cows for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Friesian Cows?
Understanding the cost structure involved in sourcing Friesian cows is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This includes the cost of the cows themselves, which can vary significantly based on age, breed purity, and health status. For example, bottle-fed calves may range from $350 to $550, while pregnant heifers can go up to $1,100.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with breeding, feeding, and caring for the livestock. Skilled labor is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of the cows, particularly in breeding operations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment, and utilities necessary for the upkeep of the livestock. High-quality facilities ensure better health outcomes and higher milk production rates.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Investments in specialized farming equipment, such as milking machines and feeding systems, can impact the overall cost structure. Efficient equipment can lead to better productivity and lower long-term operational costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the health and quality of the livestock through regular veterinary checks and certifications adds to the overall cost. Documentation such as pedigree certificates and veterinary records is crucial for international trade.
-
Logistics: Transporting livestock across borders can be complex and costly. Expenses include shipping, insurance, and compliance with international veterinary regulations, which can vary significantly by region.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their prices to cover operational costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the supplier’s margin can provide insights into the pricing landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Friesian Cows?
Several factors influence the pricing of Friesian cows, impacting the total cost for buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and consider larger orders to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: The specific requirements for the cows, such as breed purity or age, can affect the price. Customized orders often incur additional costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Cows with superior genetics, higher milk production rates, and certifications (e.g., organic or free-range) will typically command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality livestock.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, location, and the supplier’s experience can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer more reliable quality and service, justifying higher prices.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon shipping terms (like FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the total cost. Understanding these terms helps buyers anticipate additional expenses related to shipping and insurance.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Friesian Cows?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips:
-
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices. Suppliers often expect some level of bargaining, especially for larger orders.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the purchase price but also long-term care and operational costs. Cheaper cows may lead to higher veterinary expenses down the line.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and import duties that may affect the overall price. Ensure to factor these into your budget.
-
Understand Regional Differences: Prices can vary significantly based on the region. Research local market conditions and competitor pricing to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Documentation: Ensure all necessary documentation is in place to avoid delays or additional costs during shipping. Proper paperwork is essential for smooth cross-border transactions.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional factors. Always consult multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing friesian cows for sale With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Friesian Cows for Sale
In the context of sourcing dairy cattle, particularly Friesian cows, buyers may encounter various alternatives that can fulfill similar operational goals. These alternatives might cater to specific agricultural needs, production efficiencies, or economic considerations. Below, we explore the comparative aspects of Friesian cows against two viable alternatives: Jersey cows and dairy technology solutions such as automated milking systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Friesian Cows For Sale | Jersey Cows | Automated Milking Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High milk yield (up to 18,000 liters/lactation) | Moderate yield (around 6,000-10,000 liters/lactation) | Consistent output with high efficiency |
| Cost | $350 – $1,100 per animal | $1,200 – $1,500 per animal | $20,000 – $150,000 depending on setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires pasture and care | Similar to Friesians, but specific care for Jerseys | Requires initial setup and training |
| Maintenance | Regular health checks and feeding | Similar to Friesians, but may require more protein-rich diets | Regular maintenance and software updates |
| Best Use Case | High-volume dairy production | Specialty cheese production, smaller farms | Large-scale dairy operations focusing on efficiency |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Jersey Cows
Jersey cows are known for their rich milk with high butterfat content, making them ideal for cheese and butter production. While they yield less milk than Friesians, their milk is often more valuable due to its quality. The initial investment in Jerseys can be higher, but their feed efficiency and lower maintenance needs can lead to cost savings in the long run. However, they may not be the best choice for operations focused solely on high-volume milk production, as they typically produce less milk per lactation compared to Friesians.
Automated Milking Systems
Automated milking systems represent a technological alternative to traditional dairy farming methods. These systems can significantly enhance efficiency by allowing cows to be milked on-demand, thereby increasing overall milk production. The upfront costs can be substantial, ranging from $20,000 to $150,000, depending on the system’s complexity and the scale of operation. While they reduce labor costs and allow for better herd management, the systems require ongoing maintenance and can be complex to operate. For large-scale operations, however, they can lead to substantial increases in productivity and profitability.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When determining the best solution for dairy production, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational goals, budget constraints, and production capacities. Friesian cows are an excellent choice for high-volume milk production, while Jersey cows can offer quality advantages for niche markets. Alternatively, investing in automated milking systems may be the right fit for larger operations looking to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Ultimately, the decision should align with the buyer’s strategic objectives and the specific demands of their local market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for friesian cows for sale
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Friesian Cows?
When considering the purchase of Friesian cows, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are some essential properties:
-
Milk Yield
Friesian cows are renowned for their high milk production, averaging between 6,000 to 11,000 liters annually. This significant yield is a primary reason for their popularity among dairy farmers. For B2B buyers, knowing the expected milk output helps in forecasting profitability and ensuring that the investment aligns with production goals. -
Fat and Protein Content
The milk produced by Friesian cows typically contains around 3.5% fat and 3.2% protein. These nutritional components are critical for dairy product manufacturing, affecting the quality of cheese, butter, and yogurt. Buyers should assess these levels to ensure they meet market demands and regulatory standards. -
Lactation Cycle
Friesian cows have a standard lactation period of about 305 days, followed by a dry period before calving again. Understanding this cycle is vital for managing herd productivity and planning breeding schedules. Buyers must consider this when determining operational efficiency and resource allocation. -
Age and Breeding Status
The age and breeding status of Friesian cows can significantly impact their productivity. Pregnant heifers are typically sold at 24-32 months of age, while open heifers range from 6-12 months. Buyers should verify the breeding status to ensure they are acquiring cows that will meet their production timelines and goals. -
Conformation and Weight
Friesian cows generally weigh between 580 kg to 630 kg and exhibit a large, lean frame. Their physical attributes influence their health, fertility, and overall productivity. Buyers should consider these factors when evaluating potential purchases, as they can affect longevity and milk production. -
Health Certifications
Accompanying health certifications, such as veterinary records and pedigree information, are essential for verifying the quality and health status of the cattle. Buyers should prioritize obtaining these documents to ensure compliance with import regulations and to mitigate risks associated with disease transmission.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Friesian Cattle Market?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several important terms:
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers gauge their purchasing power and plan inventory levels accordingly. For Friesian cattle, it may dictate the scale of a buyer’s operations and investment strategies. -
FOB (Free on Board)
FOB indicates that the seller is responsible for the goods until they are loaded onto the transport vessel. Buyers should consider this term when calculating total costs, as it affects pricing and liability during shipping. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formalized request from buyers for price quotes from suppliers. This process is vital for comparing offers and negotiating favorable terms. For Friesian cattle, it allows buyers to assess multiple suppliers and make informed decisions based on pricing and quality. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, particularly for buyers importing Friesian cattle across borders. -
Pedigree
Pedigree refers to the documented ancestry of the cattle. This is crucial for understanding genetic traits and potential milk production capabilities. Buyers should look for pedigree information to ensure they are investing in high-quality breeding stock. -
Calving Interval
This term describes the time between successive calvings. A shorter calving interval is preferable for maximizing productivity. Buyers should inquire about the calving history of Friesian cows to evaluate their potential for sustained milk production.
Understanding these technical properties and industry terms enables B2B buyers to make well-informed decisions when investing in Friesian cows, ensuring they select the right cattle that meet their operational requirements and market needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the friesian cows for sale Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing the Friesian Cows for Sale Sector?
The global demand for dairy products continues to rise, driven by population growth and increasing urbanization, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This growth is leading to a heightened interest in high-yield dairy breeds, with Friesian cows—particularly Holstein Friesians—at the forefront due to their exceptional milk production capabilities. With an average lactation yield of up to 18,000 liters per cow, these breeds are considered a strategic investment for dairy producers looking to enhance their output and profitability.
Emerging technologies in livestock management, such as precision farming and genetic selection, are reshaping sourcing practices. International buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to access global suppliers, facilitating smoother transactions and fostering competitive pricing. Moreover, the shift towards integrated supply chains is becoming prevalent, enabling buyers to engage directly with producers, thus minimizing costs and ensuring better quality control. As economies in Brazil and Saudi Arabia continue to diversify, the demand for Friesian cows is expected to grow, further stimulating market dynamics.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Friesian Cattle Trade?
Sustainability has become a critical concern in the livestock sector, with buyers increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of dairy farming, including greenhouse gas emissions and land use, is prompting stakeholders to seek more sustainable farming methods. B2B buyers must consider suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly practices, such as rotational grazing and organic feeding, which contribute to lower carbon footprints.
Furthermore, the certification of sustainable practices is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to request documentation like organic grass-feed certificates and animal welfare certifications to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical standards. This focus on sustainability not only aligns with global trends but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust. As the market evolves, suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing will likely gain a competitive edge, appealing to conscientious buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Is the Historical Context of Friesian Cattle and Its Importance for Today’s Market?
The Friesian breed has a rich history that dates back to the 18th century in the Netherlands, where selective breeding began to enhance its dairy capabilities. The establishment of herdbooks in the late 19th century marked a pivotal moment, allowing for systematic breeding practices that improved milk yield and quality. Notably, the introduction of Holstein genetics in the 1970s further boosted the production capabilities of Friesian cattle, making them a preferred choice for dairy farmers worldwide.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the breed’s evolution and adaptability to various farming conditions. The historical significance of Friesian cattle, particularly in relation to their high productivity, positions them as a cornerstone in the global dairy market. As buyers navigate their sourcing decisions, this knowledge can inform discussions with suppliers and help establish expectations regarding performance and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of friesian cows for sale
-
How do I ensure the quality of Friesian cows when sourcing them internationally?
To ensure the quality of Friesian cows, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request full veterinary records, pedigree certificates, and evidence of compliance with international animal health standards. Engage with suppliers who have established reputations and positive reviews in the industry. It’s also beneficial to conduct a site visit or use third-party inspection services to verify the health and living conditions of the livestock before finalizing any purchase. -
What are the key characteristics of Friesian cows that I should consider?
Friesian cows are renowned for their high milk production, with lactation yields reaching up to 18,000 liters per cycle. They typically weigh around 580-630 kg and are characterized by their distinctive black and white markings. Additionally, they have excellent reproductive rates and can calve frequently throughout their lifespan. Understanding these characteristics will help you assess their suitability for your dairy farming needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when buying Friesian cows?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, you may encounter options such as full upfront payment, partial deposits with balance upon delivery, or payment on credit terms. It’s essential to discuss these terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow capabilities. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, especially in international transactions. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for Friesian cows?
Minimum order quantities can differ based on the supplier and the specific livestock type. Some suppliers may require a minimum of five to ten animals, while others may allow smaller orders. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to find flexible options that fit your needs. Additionally, consider the logistics and transportation costs associated with smaller orders, as they may disproportionately affect your overall expenses. -
How can I customize my order for Friesian cows?
Customization of your order may include selecting specific age groups, health status, or breeding characteristics. Communicate your specific requirements clearly to the supplier, including preferences for pregnant heifers, calves, or yearlings. Many suppliers are willing to accommodate special requests, especially if they have a diverse inventory. Be sure to confirm the availability of the desired livestock and any additional costs that may arise from special orders. -
What documentation is required for importing Friesian cows?
When importing Friesian cows, you will need several key documents, including veterinary health certificates, pedigree papers, and a certificate of origin. Additionally, some countries require import permits and compliance with local agricultural regulations. Ensure that your supplier can provide all necessary documentation to facilitate a smooth import process and avoid delays at customs. -
What logistics should I consider when transporting Friesian cows internationally?
International transportation of Friesian cows requires careful planning. Consider factors such as the mode of transport (air or sea), duration of transit, and the health and comfort of the livestock during shipping. Work with logistics providers experienced in livestock transport to ensure compliance with animal welfare standards. Additionally, factor in customs clearance and potential quarantine requirements upon arrival in your destination country. -
How do I vet suppliers of Friesian cows effectively?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their reputation through industry references, online reviews, and trade associations. Request detailed information about their breeding practices, herd health management, and export experience. Consider visiting their facilities, if possible, or utilizing third-party auditing services to assess their operations. Strong communication and transparency from the supplier are also indicators of reliability and professionalism in the livestock trade.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Friesian Cows For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Briscoe Farm – Holstein Friesian Cattle
Domain: briscoefarm.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Product: Holstein Friesian Cows, Heifers, Bulls, Calves
Price:
– Bottle-feeding calves (6-8 weeks): $350 each
– Older calves (weaned): $550 each
– Yearling cows: $750 each
– Pregnant heifers: $1100 each
– Adult bulls: $800 each
Description: Holstein Friesian Dairy Cattle are considered the best dairy cattle in the world, known for high milk yields (up to 18,000 litres per lactation) with 3.82% fat…
2. Cows.ie – Friesian Cattle Insights
Domain: cows.ie
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Friesian cattle are believed to have origins tracing back to the 18th century, with a history of cross-breeding with native cattle in Friesland and the north of Holland. The Netherlands herdbook was established in 1873 and the Friesland herdbook in 1879. Friesian cattle are known for their ability to graze on low lying and upland grassland, with selective breeding resulting in a resilient animal c…
3. Cattle Exchange – Gelbvieh, Jerseys, Holsteins
Domain: cattle-exchange.drovers.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: 1. Gelbvieh – Bred Heifers, open heifers, bulls and steers. Listing # 32147890, Location: Irving, TX, Breed: Gelbvieh.
2. Milking jersey cows for sale. Listing # 32147615, Location: Dallas, TX, Breed: Holstein, Jersey.
3. Holstein Friesian, fresh cows, bred, replacement heifers and calves. Listing # 32148122, Location: Longview, TX, Breed: Holstein.
4. Charolais open/Bred Heifers, Bulls & calves f…
4. Firmaschaap – Holstein Friesian Heifers
Domain: firmaschaap.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Holstein Friesian heifers specifications: Black & white and/or red & white; Age pregnant heifers: 24-32 months at time of calving; Age open heifers: 6-12 months; Pedigree registered; Lactations: 20-35 liters per day; Annual lactation: 7,000-11,000 liters/year; Fat: 4.0%; Protein: 3.2%; Known for being the highest milk producing cows in the world; Average lifetime milk production: 30,000 kg; Averag…
5. AG Online – Livestock Listings
Domain: agonline.co.nz
Introduction: Listings for sale include various classes of livestock such as Dairy (Autumn Calving Cows, Heifers, Calves, Herd In Milk, InCalf Cows, Service Bulls), Beef (Bulls, Steers, Store Bulls, Weaner Bulls, Heifers), and Sheep (Ewes, Hoggets, Lambs). Upcoming sales are conducted by PGG Wrightson, featuring On Farm and Saleyard options. The site also lists Wanted to Buy opportunities for Dairy, Beef, Sheep…
6. Australia’s Livestock Exporters – Holstein Friesians Dairy Cattle
Domain: australiaslivestockexporters.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Holstein Friesians Dairy Cattle are considered the best dairy cattle in the world, with approximately 83% of Australian dairy cows being Holstein. Key production details include:
– Average annual production: Up to 18,000 litres of milk per lactation
– Milk composition: 3.82% fat, 3.21% protein
– Average lactation period: 305 days.
The company exports various types of heifers, including young u…
7. Livestock Animal Exchange – Holstein Cows For Sale
Domain: livestockanimalexchange.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Product: Holstein Cows For Sale
Price Range: $350.00 – $1,370.00
Delivery Duration: Within the United States: 1 to 3 days; Out of the United States: 4 to 6 days.
Available Options: Bulls, Cows, Heifers, Calves, Cow/Calf Pairs.
Contact Information: Call/Text +1 (940) 463-5084 / Whatsapp +1 (415) 244-2410 / Email: [email protected]
8. The Livestock Traders – Holstein-Friesian Cattle
Domain: thelivestocktraders.nl
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: {“breed”:”Holstein-Friesian”,”color_variants”:[“black/white”,”red/white”],”origin”:”Netherlands”,”milk_yield”:{“1st_lactation”:”no less than 7,000 kg”,”2nd_lactation”:”no less than 8,000 kg”,”3rd_or_subsequent_lactation”:”no less than 9,000 kg”},”fat_content”:”4.2%”,”protein_content”:”3.2%”,”age_at_delivery”:”18-30 months”,”weight”:”450-550 kg”,”pregnancy_duration”:”3-6 months”,”stud_book”:”All an…
9. GrassTec Group – Premium Dairy Cattle for Sale
Domain: grasstecgroup.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: [{“stock_type”:”1st & 2nd Calvers”,”breed”:”JEX”,”liters_per_cow”:5900,”fat”:”4.88%”,”protein”:”3.9%”,”kg_ms”:534,”status”:”For Sale”},{“stock_type”:”A-Grade Milking Cows”,”breed”:”Hol/Fr”,”liters_per_cow”:6300,”fat”:”4.55%”,”protein”:”3.83%”,”kg_ms”:544,”status”:”For Sale”},{“stock_type”:”Herd Sale Grazing Friesian Type”,”breed”:”Hol/Fr”,”liters_per_cow”:5500,”fat”:”4.25%”,”protein”:”3.50%”,”kg_m…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for friesian cows for sale
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Friesian Cows?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of Friesian cows presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. With their exceptional milk production capabilities—averaging up to 18,000 liters per lactation—Friesian cows are a valuable asset for expanding dairy operations. Understanding the pricing structure, which ranges from $350 for bottle-fed calves to $1,100 for pregnant heifers, allows buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their market needs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Dairy Business?
Investing in high-quality Friesian breeding stock not only boosts productivity but also meets the growing global demand for dairy products. Leveraging established supply chains, particularly those with direct farm-to-export models, can enhance reliability and reduce costs. Furthermore, ensuring that cattle come with comprehensive documentation, including pedigree and veterinary records, is crucial for maintaining quality assurance.
What’s Next for International Buyers of Friesian Cattle?
As you consider your next steps, remember that the future of dairy farming lies in sustainable and efficient sourcing strategies. Engage with reputable suppliers who can facilitate smooth import processes and provide ongoing support. By investing in Friesian cows today, you position your business to thrive in the competitive dairy market of tomorrow. Don’t hesitate to reach out and explore how these remarkable animals can enhance your operations.