Incubators For Sale Near Me Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for incubators for sale near me
In the quest for sourcing incubators for sale near me, international B2B buyers often encounter a myriad of challenges, from understanding local regulations to evaluating product quality and supplier reliability. This guide aims to streamline your purchasing journey by providing a comprehensive overview of the global incubator market, tailored specifically for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam.
Navigating through various types of incubators—ranging from simple tabletop models for small-scale hatcheries to advanced commercial systems designed for mass production—can be daunting. Additionally, understanding the applications of each type, including poultry and other livestock, is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide not only delves into the features and specifications that distinguish different incubators but also covers essential aspects like supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and post-purchase support.
By arming yourself with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and business goals. Whether you are expanding your agricultural ventures or establishing a hatchery, this guide serves as a valuable resource to help you navigate the complexities of the incubator market and secure the best options available in your region.
Understanding incubators for sale near me Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forced-Air Incubators | Equipped with fans for even heat distribution; automated egg turning | Poultry farms, commercial hatcheries | Pros: Consistent temperature; higher hatch rates. Cons: Higher upfront cost, requires power. |
| Still-Air Incubators | Relies on natural air circulation; manual temperature management | Small-scale breeders, educational institutions | Pros: Lower cost; simple design. Cons: Less reliable temperature control, requires more monitoring. |
| Cabinet Incubators | Larger capacity; multiple trays for different incubation stages | Large farms, commercial hatcheries | Pros: High efficiency for bulk hatching; customizable settings. Cons: Expensive; requires more space. |
| Tabletop Incubators | Compact size; ideal for beginners; often manual | Hobbyists, small farms | Pros: Affordable; easy to use. Cons: Limited capacity; less automation. |
| Specialty Incubators | Designed for specific egg types (e.g., quail, reptiles) | Niche markets, research institutions | Pros: Tailored features enhance hatching success. Cons: Limited versatility; may be costly. |
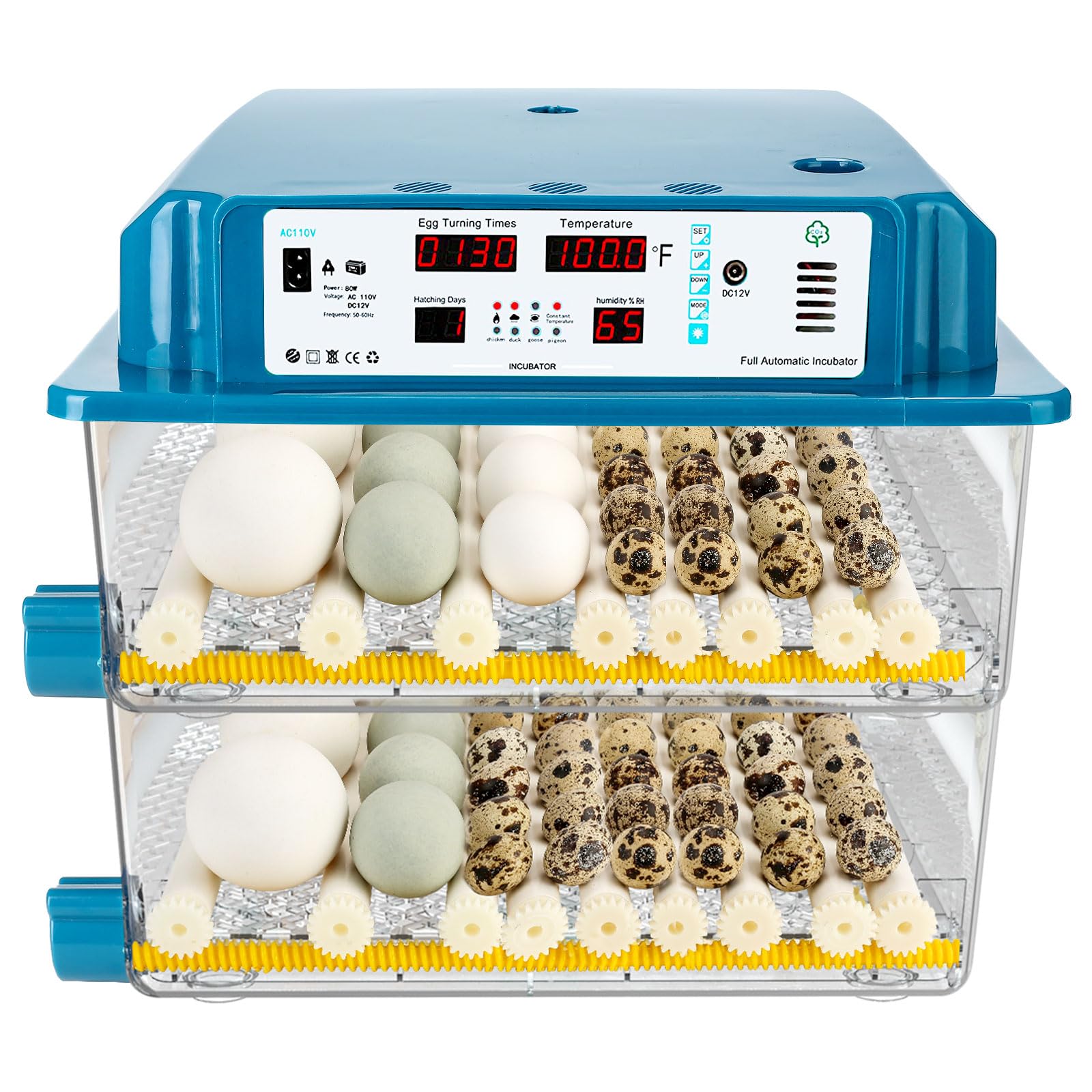
What Are Forced-Air Incubators and Their Applications?
Forced-air incubators utilize built-in fans to circulate warm air, ensuring an even temperature throughout the chamber. This technology is vital for poultry farms and commercial hatcheries, where consistent conditions can significantly improve hatch rates. Buyers should consider the operational costs, as these models require electricity and can have a higher initial investment. However, the efficiency and reliability they offer often justify the expense, making them a preferred choice for larger-scale operations.
How Do Still-Air Incubators Work and Who Uses Them?
Still-air incubators operate without fans, relying instead on natural air circulation. This type is often used by small-scale breeders and educational institutions due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. While they are less expensive and easier to maintain, buyers must be prepared for more frequent monitoring of temperature and humidity levels. These incubators are suitable for those just starting in hatching, but their limitations in temperature control can impact hatch rates.
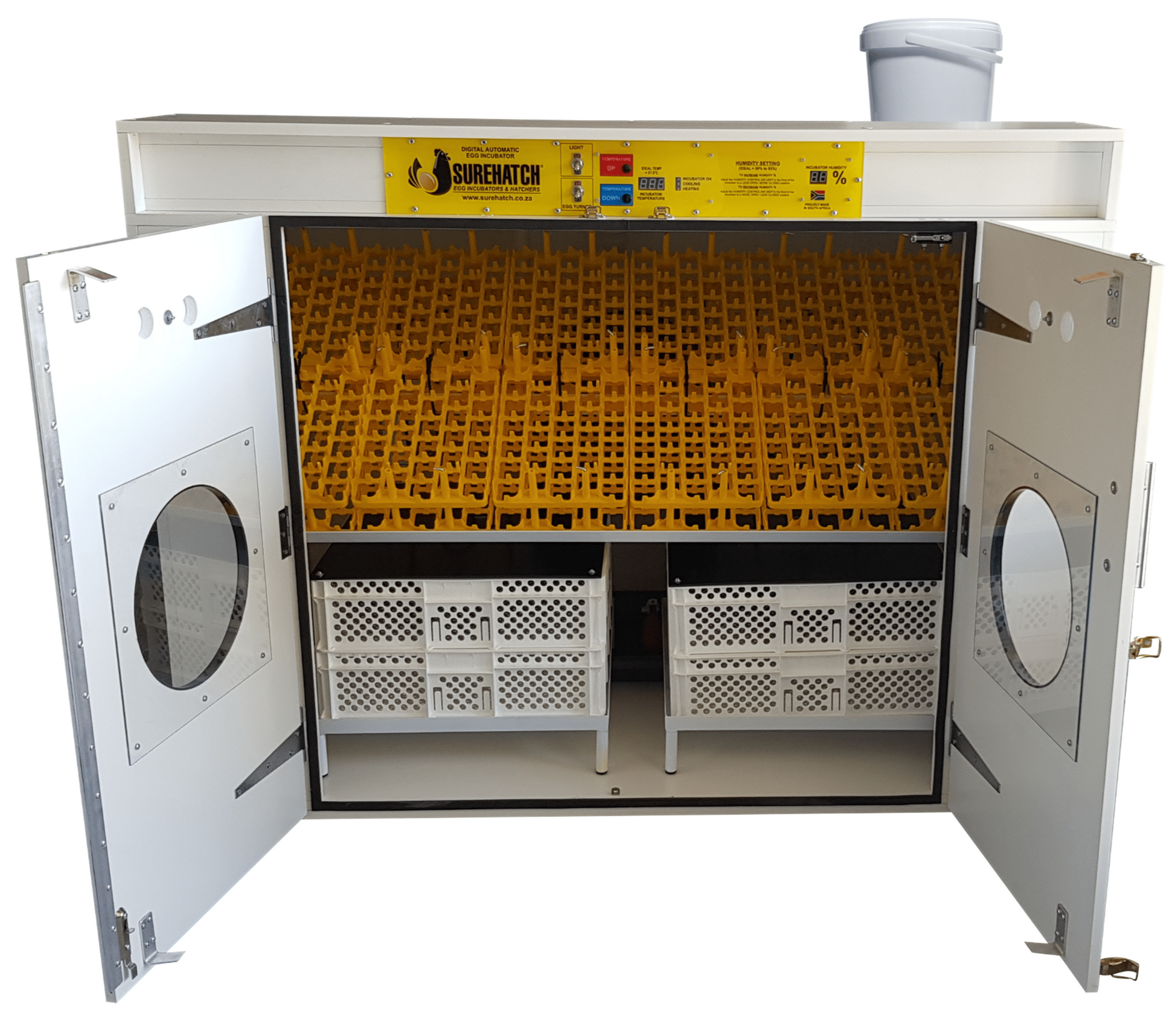
What Are the Benefits of Cabinet Incubators for Commercial Use?
Cabinet incubators are designed for high-capacity hatching, often featuring multiple trays to accommodate various stages of incubation. They are ideal for large farms and commercial hatcheries where efficiency is paramount. These models allow for precise control of temperature and humidity, which can significantly enhance productivity. However, their higher cost and space requirements mean that buyers must assess their operational needs carefully before investing.
Why Choose Tabletop Incubators for Small Operations?
Tabletop incubators are compact and user-friendly, making them perfect for hobbyists and small farms. They are typically manual, requiring hands-on management, which may appeal to those looking for a more involved hatching experience. While they are affordable and easy to store, their limited capacity can be a drawback for those who wish to scale up. Buyers should consider their hatching goals and available space when opting for this type.
What Makes Specialty Incubators Unique?
Specialty incubators cater to specific types of eggs, such as those from quail or reptiles, featuring tailored settings for optimal hatching success. They are commonly used in niche markets and research institutions where precise environmental conditions are crucial. While these incubators can be more expensive and less versatile than general-purpose models, their specialized features can lead to higher hatch rates for specific egg types. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs and budget before making a purchase.
Key Industrial Applications of incubators for sale near me
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of incubators for sale near me | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poultry Farming | Hatching eggs for various poultry species | Increased hatch rates and healthier chicks | Temperature control, humidity management, and automation features. |
| Aquaculture | Incubating fish eggs and larvae | Enhanced survival rates and growth efficiency | Compatibility with aquatic species and water quality monitoring. |
| Biotechnology | Cultivating microbial cultures | Reliable growth conditions for research and production | Sterility, temperature precision, and scalability options. |
| Agriculture | Germinating seeds for crop production | Improved seed viability and faster growth cycles | Size capacity, energy efficiency, and multi-functionality. |
| Educational Institutions | Teaching and research on embryology and incubation | Hands-on learning experience and research opportunities | Safety features, ease of use, and instructional support. |
How Are Incubators Used in Poultry Farming and What Benefits Do They Provide?
In poultry farming, incubators are crucial for hatching eggs from various bird species, including chickens, ducks, and turkeys. These devices create a controlled environment that optimizes temperature and humidity, significantly increasing hatch rates and ensuring the health of chicks. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, selecting incubators with automation features can streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and improve overall productivity. Additionally, sourcing incubators that can accommodate multiple egg types is essential for diversified poultry operations.
What Role Do Incubators Play in Aquaculture?
In aquaculture, incubators are employed to hatch fish eggs and nurture larvae until they are ready for transfer to grow-out facilities. The controlled environment provided by incubators enhances survival rates and growth efficiency, which are critical for profitable fish farming. For buyers from the Middle East or Europe, it’s vital to choose incubators that can maintain optimal water quality and temperature for specific fish species. Features such as water filtration systems and monitoring capabilities can further enhance the effectiveness of these incubators.
How Are Incubators Utilized in Biotechnology?
Biotechnology relies heavily on incubators for cultivating microbial cultures, which are essential for various applications, including pharmaceuticals and food production. These incubators must maintain sterile conditions and precise temperature controls to ensure consistent growth and productivity. B2B buyers in the biotechnology sector should prioritize incubators that offer high levels of sterility and scalability. Additionally, features like dual temperature and humidity monitoring can help maintain optimal conditions for sensitive cultures, making them indispensable in research and production environments.
In What Ways Do Incubators Support Agriculture?
In agriculture, incubators are used for germinating seeds, which significantly improves seed viability and accelerates growth cycles. This is particularly beneficial for farmers looking to optimize their planting schedules and increase yield. International buyers, particularly in developing regions, should consider the size capacity and energy efficiency of incubators, as these factors directly impact operational costs and sustainability. Multi-functional incubators that can accommodate different seed types can also enhance versatility in crop production.
How Are Incubators Beneficial for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions utilize incubators to teach students about embryology and the principles of incubation. These devices provide a hands-on learning experience, allowing students to observe the life cycle of various species. For schools and universities, safety features and ease of use are paramount. Suppliers should offer incubators that are beginner-friendly and come with comprehensive instructional support to facilitate educational programs. This not only enriches the learning environment but also prepares students for careers in agriculture and biology.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘incubators for sale near me’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Incubators for Diverse Needs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of finding incubators that meet specific operational needs, especially when dealing with diverse poultry species or varying batch sizes. The market is flooded with options, but without a clear understanding of which features are essential for their unique requirements, buyers can easily invest in subpar equipment. For instance, a hatchery aiming to produce high volumes of chicken and ducklings may struggle to identify the right incubator type—forced-air versus still-air—that optimizes hatch rates for different eggs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in incubators tailored to their needs. Utilizing online platforms and local resources, such as agricultural cooperatives or trade shows, can yield valuable insights into the best incubator models available. When evaluating options, consider factors like capacity, automation features, and compatibility with the specific types of eggs being incubated. For example, forced-air incubators are generally recommended for chicken and duck eggs due to their superior temperature regulation, while still-air models may be better suited for delicate species like quail. By clearly defining operational goals and requirements before making a purchase, B2B buyers can ensure they select an incubator that maximizes productivity and minimizes losses.
Scenario 2: Managing Temperature and Humidity for Optimal Hatch Rates
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is maintaining the precise environmental conditions necessary for successful hatching. Incubators must provide consistent temperature and humidity levels, but many buyers underestimate the importance of monitoring and adjusting these factors throughout the incubation process. Fluctuations can lead to poor hatch rates, which directly impacts profitability and operational efficiency, especially in high-stakes markets.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in incubators equipped with advanced monitoring systems that allow for real-time tracking of temperature and humidity. Additionally, incorporating external monitoring devices, such as digital thermometers and hygrometers, can provide an extra layer of assurance. Regular training for staff on how to set up and calibrate the incubator before use is essential. This includes pre-conditioning the incubator to stabilize temperature and humidity before placing eggs inside. Buyers should also establish a routine for checking conditions multiple times a day, particularly during critical periods of development. By proactively managing these environmental factors, businesses can significantly enhance their hatch rates and overall productivity.
Scenario 3: Navigating After-Sales Support and Warranty Concerns
The Problem: After purchasing an incubator, buyers may encounter issues related to equipment malfunctions or performance inconsistencies. Without reliable after-sales support, resolving these problems can be time-consuming and costly. B2B buyers, especially in regions with limited access to technical assistance, often feel stranded when faced with equipment failures that threaten their operations.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive after-sales support and robust warranty options. Before finalizing a purchase, inquire about the warranty coverage specifics, including duration and what issues are covered. It’s also beneficial to choose suppliers who provide readily accessible customer service, such as phone support or online chat options. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer training programs or resources for troubleshooting common incubator issues. Establishing a relationship with the supplier can facilitate quicker resolutions and ongoing support. For instance, regular maintenance checks can be scheduled to ensure that the equipment operates efficiently, thus preventing unexpected downtime. By investing in reliable after-sales support, B2B buyers can safeguard their operations and ensure a sustainable hatching process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for incubators for sale near me
What Are the Key Materials Used in Incubator Manufacturing?
When selecting incubators for sale, understanding the materials used in their construction is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and durability. The choice of material can significantly impact temperature regulation, longevity, and overall functionality. Below, we analyze four common materials used in incubators, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polycarbonate Influence Incubator Performance?
Polycarbonate is a popular choice for incubator construction due to its excellent thermal insulation properties. This material can withstand high temperatures and has a high impact resistance, making it suitable for environments where durability is essential. Polycarbonate incubators can maintain stable internal conditions, which is critical for successful hatching.
Pros: The lightweight nature of polycarbonate reduces shipping costs, and its transparency allows for easy monitoring of the incubation process. Additionally, it is resistant to UV radiation, which can prolong the life of the incubator.
Cons: While polycarbonate is durable, it can be more expensive than other materials like plastic. It may also scratch easily, which can affect visibility over time.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is compatible with various incubation media, making it versatile. However, it is essential to ensure that the material used is food-grade to avoid contamination.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and the Middle East should verify compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and material standards. ASTM and ISO certifications can provide assurance of quality.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Incubator Design?
Stainless steel is another common material used in incubators, particularly in commercial settings. Known for its strength and corrosion resistance, stainless steel can endure harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for long-term use.
Pros: Its durability ensures a longer lifespan for the incubator, and it is easy to clean, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene standards in poultry farming. Stainless steel also offers excellent temperature retention.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, as stainless steel is generally more expensive than other materials. Additionally, it can be heavy, which may increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for incubators that require frequent cleaning and maintenance, especially in commercial hatcheries where biosecurity is a priority.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should look for compliance with JIS and DIN standards, which may dictate specific requirements for stainless steel grades used in food-related applications.
How Does High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Benefit Incubators?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is increasingly used in incubator manufacturing due to its excellent chemical resistance and lightweight properties. This material is particularly beneficial in environments where exposure to various chemicals is a concern.
Pros: HDPE is cost-effective and offers good insulation properties. It is also resistant to moisture, which helps maintain the necessary humidity levels within the incubator.
Cons: While HDPE is durable, it is less impact-resistant than polycarbonate or stainless steel. Over time, it may degrade when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: HDPE is suitable for smaller, portable incubators, making it a favorite among hobbyists and small-scale farmers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local environmental regulations is essential, especially in countries with strict plastic usage laws. Buyers should also consider the availability of HDPE in their region.
Why Is Glass Used in Incubator Design?
Glass, particularly tempered glass, is sometimes used in incubators for its aesthetic appeal and clarity. It allows for easy observation of the incubation process without opening the incubator.
Pros: Glass provides excellent insulation and is easy to clean. It is also chemically inert, making it safe for various incubation media.
Cons: The fragility of glass makes it less suitable for high-impact environments. It can also be heavier, increasing shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for small incubators or display models where visibility is crucial but may not be suitable for larger, commercial operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the glass used meets safety standards to prevent breakage during transport and use. Compliance with local building codes is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Incubators
| Material | Typical Use Case for incubators for sale near me | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | Small to medium-sized incubators for poultry | Excellent thermal insulation | Scratches easily, higher cost | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Commercial incubators for large-scale hatcheries | High durability and corrosion resistance | Expensive, heavier | High |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Portable incubators for hobbyists | Cost-effective and moisture resistant | Less impact resistance | Low |
| Glass | Display or small incubators | Aesthetic appeal and easy monitoring | Fragile and heavier | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis of materials provides B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when selecting incubators that meet their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for incubators for sale near me
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Incubators?
The manufacturing process of incubators typically involves several crucial stages, each integral to ensuring the final product meets the high standards required for effective poultry incubation.
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. High-quality plastics and metals are often utilized for durability and thermal insulation, while electronic components such as sensors and displays are sourced from reputable suppliers. Manufacturers may perform tests on materials to ensure they meet specific performance criteria, such as heat resistance and electrical conductivity.
Forming Techniques Used in Incubator Production
After material preparation, the forming stage involves various techniques depending on the components being produced. For instance, plastic components may undergo injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mold to create precise shapes. Metal parts often use stamping or CNC machining to achieve the required dimensions. This stage is critical, as the accuracy of these components directly impacts the incubator’s performance.
Assembly of Incubator Components
Once the parts are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process can be highly automated or manual, depending on the scale of production. Automated assembly lines can enhance efficiency and consistency, while manual assembly may allow for more intricate work on complex models. Each component, from heating elements to ventilation systems, is carefully integrated, ensuring that all systems function cohesively.
Finishing Processes That Enhance Product Quality
The final stage involves finishing processes, which may include painting, labeling, and quality checks. Finishing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the incubators but also provides protective coatings that increase longevity. Additionally, final inspections are performed to ensure that all components are correctly installed and that the incubator meets safety and operational standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Incubator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for incubators, ensuring that the products are reliable and meet international standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Incubator Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. Additionally, certifications like CE mark for Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for specific components may be relevant, depending on the incubator’s design and intended use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the initial inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random inspections are conducted to monitor the production line. This includes checks on assembly accuracy, component functionality, and adherence to safety protocols.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are packaged and shipped, they undergo a final inspection where functionality tests are performed. This includes testing temperature regulation, humidity control, and overall performance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Incubators?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to verify the functionality and reliability of incubators. Common testing procedures include:
-
Thermal Testing: Ensures that the incubator maintains the required temperature range consistently. This is critical for successful egg hatching.
-
Humidity Testing: Similar to thermal testing, this verifies that humidity levels remain stable and within specified parameters.
-
Electrical Safety Testing: Ensures that all electrical components function safely under operational conditions. This often involves stress testing to simulate prolonged use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control. Buyers should request documentation of quality management systems, including certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and the overall quality culture of the supplier.
How Can Reports and Third-Party Inspections Enhance Trust?
Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can also help buyers understand the consistency of product quality. Third-party inspections by reputable organizations add another layer of trust. These inspections can verify that the supplier’s processes align with international standards and that products meet specified quality benchmarks.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of regional compliance requirements and nuances in quality assurance. For example, specific markets may have additional certifications or testing requirements that must be met before products can be imported. Understanding these regulations can aid buyers in making informed decisions and avoiding potential compliance issues.
How Can Buyers Navigate Different Regulatory Landscapes?
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscapes of their target markets. This may involve consulting local regulatory bodies or industry associations to ensure compliance with regional standards. Engaging with local experts can also provide valuable insights into market-specific requirements, enhancing the buyer’s ability to navigate complexities effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of incubators is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions. Verifying supplier quality control through audits, reports, and third-party inspections further ensures that the incubators meet international standards, ultimately leading to successful operations in poultry incubation.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘incubators for sale near me’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing incubators effectively, this guide provides a structured checklist. By following these steps, international buyers can streamline their procurement process, ensuring they select the right incubators for their needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before starting your search for incubators. Consider factors such as the type of eggs you plan to incubate (e.g., poultry, quail, or exotic birds), the expected volume, and the desired level of automation. This clarity will help you narrow down your options and ensure compatibility with your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Local Suppliers
Identifying suppliers within your geographical proximity can significantly reduce shipping times and costs. Start by searching online marketplaces and local directories for businesses specializing in incubators. Pay attention to customer reviews and ratings to gauge the reliability of these suppliers.
- Tip: Use search terms such as “incubators for sale near me” or “local poultry equipment suppliers” to enhance your results.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Offerings
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, take the time to review their product range. Look for incubators that fit your specifications and compare different models based on features such as temperature control, humidity settings, and egg-turning mechanisms.
- Consider: Whether you need forced-air models for larger volumes or still-air incubators for specific egg types.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to verify the credentials of your chosen suppliers. Check for certifications that ensure compliance with industry standards, as this can be indicative of product quality and reliability.
- Key Certifications to Look For:
- ISO certifications
- Local agricultural or health department approvals
Step 5: Request Samples or Demonstrations
If possible, request samples or demonstrations of the incubators you are considering. This hands-on experience can provide valuable insights into the functionality and ease of use of the equipment.
- Ask for: Detailed user manuals and support documentation to assess the learning curve associated with the incubators.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have a shortlist of incubators, compare pricing across different suppliers. Keep in mind the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping fees, installation costs, and potential maintenance expenses.
- Payment Options: Look for flexible payment terms that can accommodate your budget and cash flow needs.
Step 7: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
After securing your purchase, ensure that the supplier offers robust after-sales support. This includes warranty coverage, availability of spare parts, and customer service responsiveness.
- Important: A good warranty can protect your investment, especially for high-value equipment like incubators.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement process for incubators, ensuring they find the right equipment to meet their operational requirements effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for incubators for sale near me Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Incubators?
When sourcing incubators, understanding the various cost components is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing incubators, such as plastics, metals, and electronic components, significantly influence the overall cost. Higher-quality materials often lead to better performance and durability, which can justify a higher price point.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve wages paid to workers involved in the production process. This can vary based on the location of manufacturing and the skill level required. For example, labor costs in countries with a higher standard of living may be significantly higher than in developing regions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, impacting the final pricing of the incubators.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tools and machinery for production can be substantial. This cost is often amortized over the production run, which means larger orders can benefit from lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the incubators meet specific standards and certifications incurs additional costs. Implementing robust QC processes helps in maintaining product reliability, which is essential for B2B buyers who rely on performance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and tariffs can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and desired profit. Understanding the typical margins within the industry can assist buyers in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Incubator Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of incubators, especially for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can affect pricing. Bulk orders typically enjoy discounts, which can lead to significant savings for buyers looking to source large quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized incubators designed for specific applications or unique features (like advanced temperature controls) often come at a premium. Buyers should assess whether these features align with their needs to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Incubators constructed from high-quality, certified materials may cost more upfront but can lead to lower total ownership costs due to durability and efficiency.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge higher prices but often provide better support and warranties.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial. Different terms can shift costs related to shipping, insurance, and customs duties, impacting the overall price.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Incubator Prices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies are essential:
-
Research Market Prices: Before entering negotiations, research prevailing market prices for similar incubators. This provides a baseline for discussions and helps identify fair pricing.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. Highlighting long-term savings can justify higher initial costs.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow concerns. Propose staggered payments or longer payment periods to facilitate budget management.
-
Assess Shipping Costs: Discuss logistics and shipping options with suppliers. Sometimes, negotiating on shipping terms can yield significant savings.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, favorable terms, and improved support. Long-term partnerships often result in loyalty discounts.
Conclusion
While the cost structure for incubators encompasses various components, understanding these elements empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By considering price influencers and employing strategic negotiation tactics, buyers can optimize their sourcing process, ensuring they acquire high-quality incubators at competitive prices. Always remember that prices can vary widely based on specific requirements and market conditions, so it’s advisable to approach sourcing with flexibility and an open mind.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing incubators for sale near me With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Incubators for Sale Near Me
When considering the best solutions for hatching eggs, it’s essential to evaluate various options available in the market. While incubators for sale near you offer a reliable method for egg incubation, other alternatives can also achieve similar results. Understanding the differences between these options can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Incubators For Sale Near Me | DIY Incubation Methods | Brooders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High success rates with proper use and monitoring | Varies widely; success dependent on environment control | Effective for post-hatching care but not for initial incubation |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on features | Low initial cost (mainly materials) | Moderate cost for setup and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly with clear instructions; some models automatic | Requires knowledge of temperature/humidity management | Simple setup, but requires ongoing monitoring |
| Maintenance | Regular checks and cleaning; some models require more upkeep | Minimal if using passive methods; higher with active monitoring | Ongoing care needed for temperature, bedding, and feeding |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for commercial hatcheries and serious hobbyists | Suitable for low-budget projects or educational purposes | Perfect for raising chicks post-hatch until they are ready for the outdoors |
What Are the Pros and Cons of DIY Incubation Methods?
DIY incubation methods involve using materials available at home, such as cardboard boxes and light bulbs, to create a makeshift incubator. This approach is cost-effective and can be an educational project, especially in regions with limited access to commercial incubators. However, the success rate can be highly variable due to inconsistent temperature and humidity control, which may lead to lower hatch rates. Additionally, this method often requires a good understanding of incubation principles to be effective.
How Do Brooders Serve as an Alternative?
Brooders are primarily used for raising chicks after they hatch rather than for the incubation process itself. They provide a warm environment that mimics a mother hen’s care, ensuring that chicks stay healthy during their early development. While brooders are essential for the post-hatching phase, they do not serve the purpose of incubating eggs. Therefore, they are best used in conjunction with incubators or other hatching methods, making them less of a direct alternative but rather a complementary solution.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, selecting the right egg incubation solution depends on various factors, including budget, scale of operation, and desired success rates. Incubators for sale near you are a robust choice for those looking for reliability and efficiency, particularly in commercial settings. Conversely, DIY methods may appeal to educational institutions or small-scale operations with budget constraints, while brooders are essential for post-hatching care. By thoroughly evaluating these options, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and resources.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for incubators for sale near me
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Incubators for B2B Buyers?
When considering incubators for sale, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Temperature Control Range
The temperature control range is vital for ensuring optimal hatching conditions. Most poultry incubators operate best at around 99.5°F (37.5°C) for chicken eggs. A precise temperature range allows for flexibility in hatching different species, which can be a competitive advantage in diverse markets. Buyers should look for incubators with reliable temperature regulation features, such as digital thermostats and alarms for deviations.
2. Humidity Control
Humidity levels, typically maintained between 60% and 80%, are critical for successful hatching. Incubators equipped with hygrometers and automated humidification systems can significantly improve hatch rates. For B2B buyers, understanding the humidity control capabilities can affect their production efficiency and ultimately, profitability.
3. Egg Capacity
Egg capacity refers to how many eggs an incubator can hold, impacting the scale of operations. Small tabletop models may be suitable for hobbyists or small farms, while commercial incubators designed for larger operations can accommodate hundreds of eggs. Buyers need to assess their production goals and select an incubator that meets their capacity needs without compromising on quality.
4. Airflow System
The type of airflow system can greatly affect the health of embryos. Forced-air incubators, which use fans to circulate warm air, provide even heating and are generally preferred for larger operations. In contrast, still-air incubators rely on natural airflow and are more suited for smaller batches. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
5. Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a significant factor in operational costs. Incubators designed with energy-efficient components can reduce electricity bills, making them more sustainable for long-term use. B2B buyers should prioritize models with energy-saving features, especially in regions where electricity costs are high.
6. Build Material and Durability
The materials used in an incubator’s construction can impact its longevity and performance. High-quality plastic or metal casing can provide better insulation and durability. Buyers should consider the climate of their operation area; for instance, extreme temperatures may require more robust materials to maintain consistent internal conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Incubators?
Understanding industry terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the purchasing process more effectively. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the incubator industry, knowing whether a product is OEM can indicate quality and compatibility with other equipment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who may need to balance inventory levels with production needs. Understanding MOQ can help in negotiating better pricing and terms.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For incubators, an RFQ can help buyers compare options from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping and delivery of incubators.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving it. This is crucial for buyers who may require incubators for specific timelines, such as seasonal hatching cycles. Knowing the lead time can help in planning and inventory management.
6. Warranty and Service Agreements
Warranties and service agreements provide assurances regarding the longevity and support for the incubators. Buyers should be aware of the terms and duration of warranties, which can vary significantly between manufacturers. Understanding these aspects can help mitigate risks associated with equipment failure.
By being informed about these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make smarter, more strategic decisions when purchasing incubators.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the incubators for sale near me Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Incubators for Sale Near Me Sector?
The global incubator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for poultry production and advancements in incubation technology. The rise in poultry consumption, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is a key driver. These markets are transitioning towards more sustainable agricultural practices, prompting a shift from traditional to automated incubation solutions. Notably, the trend towards automated incubators that offer precise control over temperature and humidity is gaining traction, allowing for higher hatch rates and improved animal welfare.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled incubators, are also reshaping sourcing strategies. These smart devices provide real-time monitoring and analytics, enabling farmers and hatchery operators to optimize their processes efficiently. For international B2B buyers, understanding local market needs and technological compatibility is crucial. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam are particularly focused on sourcing incubators that can cater to local species and climatic conditions, making it imperative to align product offerings with regional requirements.
Additionally, the impact of e-commerce on sourcing trends cannot be overlooked. Online platforms are facilitating easier access to a variety of incubators, allowing buyers to compare features, prices, and customer reviews more effectively. This shift is democratizing access to high-quality incubation technology, benefiting smaller farmers and businesses that may not have had the resources to invest in such solutions previously.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing for Incubators for Sale Near Me?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the sourcing of incubators, with environmental impact being a central concern for B2B buyers. As the poultry industry faces scrutiny over its carbon footprint, the demand for eco-friendly incubators is rising. Buyers are now seeking products made from sustainable materials and those that consume less energy. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where stringent environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices.
Ethical sourcing is another critical factor influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are more inclined to work with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to responsible manufacturing processes and fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as important indicators for B2B buyers looking to ensure that their supply chains align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
In addition, the use of biodegradable or recyclable materials in the manufacturing of incubators is gaining prominence. Suppliers that prioritize these materials not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also appeal to buyers who are increasingly conscious of their purchasing choices. This shift towards sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping the incubator market and influencing buyer behavior across various regions.
What Is the Historical Context of the Incubator Market and Its Evolution?
The history of incubators dates back to ancient times when rudimentary designs were developed to mimic the natural brooding of birds. Over the years, technological advancements have transformed the incubator landscape, leading to the development of sophisticated automated systems. In the 19th century, the introduction of forced-air incubators marked a significant milestone, allowing for more consistent temperature and humidity control.
As poultry farming practices evolved, so did the demand for more efficient incubation methods. The 20th century saw the rise of electric incubators, which streamlined the hatching process and improved hatch rates. Today, the market continues to evolve with the integration of digital technologies, such as IoT and AI, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing innovation in the sector and the potential for future advancements that can enhance productivity and sustainability in poultry farming.
In summary, international B2B buyers in the incubator market must navigate a landscape shaped by technological innovation, sustainability concerns, and evolving market dynamics to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of incubators for sale near me
-
How do I choose the right incubator for my business needs?
Selecting the right incubator depends on several factors, including the type of eggs you plan to hatch, the scale of your operation, and your budget. For smaller operations, tabletop models may suffice, while larger hatcheries may require cabinet-style incubators with separate trays for incubation and hatching. Consider automation features, such as automatic egg turning and digital monitoring, which can streamline operations and improve hatch rates. Additionally, ensure the incubator is suitable for the specific species of poultry you are incubating, as different birds have varying temperature and humidity requirements. -
What are the key features to look for in a commercial incubator?
When sourcing a commercial incubator, prioritize features that enhance functionality and user experience. Look for forced-air circulation for even temperature distribution, digital thermostats for precise control, and humidity monitoring capabilities. Automatic egg turning mechanisms can also significantly improve hatch rates by simulating natural conditions. Additionally, consider the incubator’s capacity, energy efficiency, and warranty options, as these factors will impact your operational costs and overall investment in the equipment. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for incubators when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production and shipping. For international buyers, it’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to understand their policies. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or allow flexibility based on your specific needs. Always clarify the MOQ and any associated pricing before finalizing your order to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing incubators?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers and can include upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon delivery. Many international suppliers may require a deposit (often 30%) to secure your order, with the remaining balance due before shipping or upon receipt of the goods. It is advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and to use secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, to protect your investment. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly documented in your purchase agreement. -
How can I ensure the quality of the incubators I purchase?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, looking for those with certifications, positive reviews, and a history of reliability. Request samples or visit the factory if possible to inspect the manufacturing process and quality control measures. Additionally, inquire about warranties and after-sales support, as reputable suppliers will often provide warranties and responsive customer service. Consider working with suppliers who offer quality assurance documentation, such as ISO certifications or product testing results, to further validate their claims. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing incubators?
Logistics is critical when importing incubators, especially regarding shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping and the specific regulations of your destination country. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, is accurate to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, factor in shipping costs, insurance, and potential tariffs or taxes to calculate the total landed cost of your incubators. -
Are there customization options available for incubators?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific business needs, such as modifying size, color, or additional features like enhanced monitoring systems or specialized heating elements. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements and ask for a detailed proposal that includes costs and lead times. Keep in mind that customized orders may have longer production times and higher MOQs, so plan accordingly. It’s beneficial to establish a good relationship with your supplier to facilitate effective communication and collaboration on customized solutions. -
What are the best practices for maintaining incubators for optimal performance?
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your incubators. Clean the incubator thoroughly before each use to prevent contamination and disease. Monitor temperature and humidity levels consistently, making adjustments as necessary to maintain optimal conditions for hatching. It’s also advisable to perform routine checks on the incubator’s mechanical components, such as fans and heating elements, to ensure they are functioning correctly. Keeping a maintenance log can help track any issues and ensure that your equipment remains in peak condition.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Incubators For Sale Near Me Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Incu-Bright™ – Key Product
Domain: incubatorwarehouse.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details:
1. **Incu-Bright™ Ultra Bright LED Light Egg Candler**
– Price: $20.99
– Brightness: 250 Lumen CREE LED Bulb
– Power Source: Cordless (batteries included)
– Material: Durable aluminium casing
– Features: Universal silicone ring, recessed bulb design, cool LED lights, easy click on/off button, unmatched performance, two-year IncuCare warranty.
– Des…
2. Target – Top-Rated Egg Incubators
Domain: target.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Target – Top-Rated Egg Incubators, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Dickey’s Incubators – 2 by 2 Incubator/Hatcher
Domain: dickeyincubators.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Dickey’s Incubators offers a 2 by 2 incubator/hatcher featuring 2 automatic turning trays and 2 hatching trays. Their incubators have 3 turning trays and 1 hatching tray, while the hatcher includes 5 trays with covers. Each incubator tray can hold 400 quail eggs, 125 Chuckar Pheasant eggs, or up to 96 chicken eggs. Additionally, trays can accommodate 47 goose, turkey, duck, or peafowl eggs. This a…
4. HHD – Automated Egg Incubators
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, HHD – Automated Egg Incubators, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Surehatch – Incubators & Poultry Solutions
Domain: surehatch.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Surehatch USA offers a range of proven incubators and poultry solutions, including: 1. Incubators & Hatchers – Premium models trusted worldwide for performance and durability. 2. Brooders & Heaters – SureGrow™ poultry brooders for heating needs. 3. Drinkers & Feeders – SureGrow™ durable, farmer-friendly drinkers and feeders. 4. Nest Boxes – SureNest™ made of rust-resistant materials. 5. Egg Grader…
6. Chick Cozy Incubator – Top Choice for Egg Hatching
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Chick Cozy Incubator – Good reviews, automatic egg turning, visible embryo development. 2. Brinsea Incubator – Recommended for quality. 3. Nurture Right 360 – Used for 4 years, excellent hatch rates (90-100%), holds a good number of eggs, automatic turner, good price. 4. Availability – Can be purchased on Amazon or at Tractor Supply.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for incubators for sale near me
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of incubators is essential for businesses looking to enhance their poultry operations. As highlighted, selecting the right incubator—whether it be a manual or automatic model—can significantly impact hatch rates and overall productivity. Buyers should consider factors such as capacity, technology (forced-air vs. still-air), and additional features that can aid in monitoring conditions throughout the incubation process.
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market demands and leveraging strong supplier relationships can lead to advantageous sourcing decisions. This approach not only ensures access to quality products but also fosters collaboration and innovation within the poultry sector.
As the global demand for poultry products continues to rise, investing in high-quality incubators will be paramount. We encourage you to explore local and international suppliers, compare offerings, and engage in strategic partnerships that align with your business objectives. By taking these proactive steps, you position your enterprise for success in a competitive landscape, paving the way for sustainable growth and improved operational efficiency.